Research Progress in Methods to Estimate High-resolution Direction of Arrival
-
摘要: 随着阵列信号处理的广泛应用, 波达方位(DOA)估计作为阵列信号处理的核心问题得到较大发展。文中首先对基于均匀线性阵列的窄带目标方位估计中的基于波束形成的传统算法和近10年的新兴算法进行了总结。分析了传统波束形成方法分辨力受限的原因, 讨论了自适应波束形成方位谱、子空间方法以及压缩感知等更高分辨力的方法; 进一步, 基于实际应用的需要, 总结了宽带目标方位估计方法、基于稀疏阵列的DOA估计方法以及二维DOA估计方法的进展。最后介绍了基于人工智能的方法在DOA方位估计中的新进展。文中的研究可应用于现代雷达声呐探测、无线电通信以及导航中, 具有较高的应用价值。Abstract: With the widespread application of array signal processing, the estimation of direction of arrival(DOA) as the core problem of array signal processing has made significant progress. This paper first summarizes the traditional algorithms based on beamforming for narrowband target direction estimation relying on uniform linear arrays and emerging algorithms in the past decade. Then, it analyzes the reasons for the limited resolution of traditional beamforming-based methods and discusses higher-resolution methods such as adaptive beamforming direction spectrum, subspace methods, and compressed sensing. Furthermore, for the needs of practical applications, the paper summarizes the progress of broadband target DOA estimation methods, sparse array-based DOA estimation methods, and two-dimensional DOA estimation methods. Finally, the new advances of artificial intelligence-based methods in DOA estimation are introduced. The research in this paper can be applied to modern radar/sonar detection, radio communication, and navigation, showing high application value.
-
Key words:
- signal processing /
- direction of arrival /
- high resolution /
- broadband /
- sparse array
-
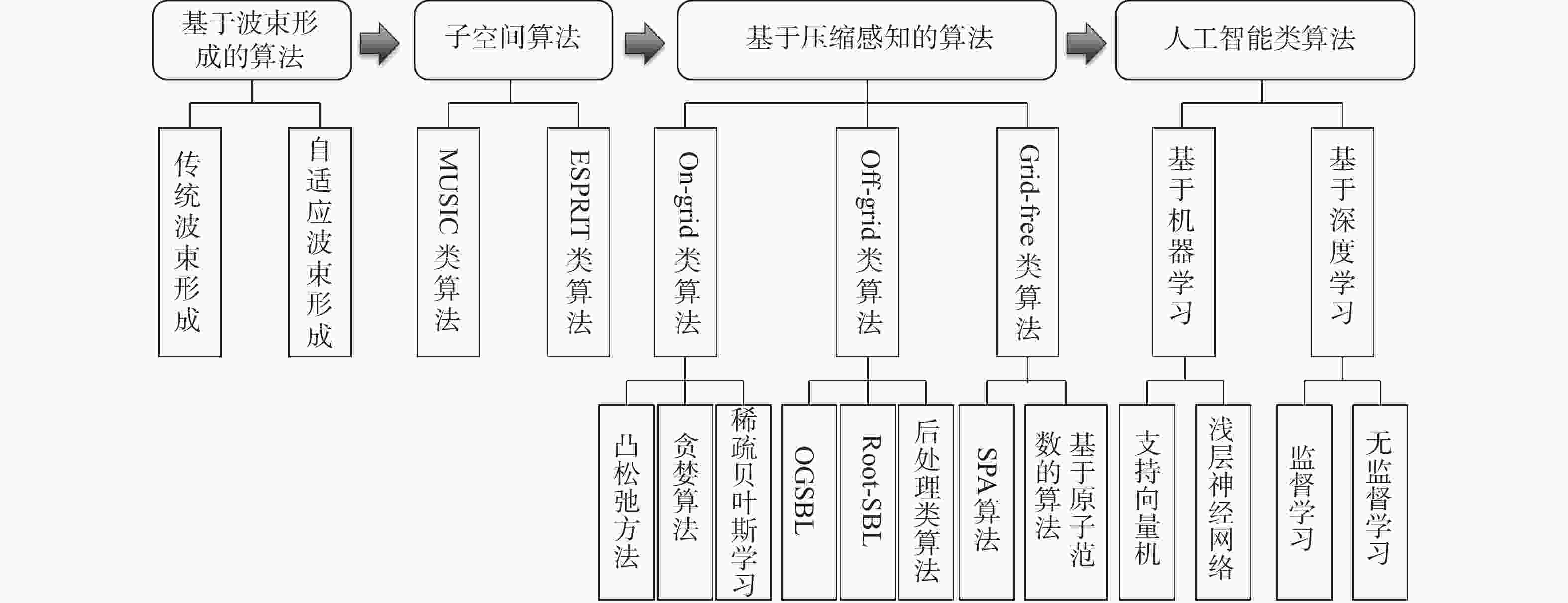
图 1 窄带目标方位估计方法发展过程
注: MUSIC为多重信号分类(multiple signal classification); ESPRIT为旋转矢量不变技术(estimating signal parameter via rotational invariance techniques); OGSBL为基于离网模型的稀疏贝叶斯学习(off-grid sparse Bayesian learning); SPA为稀疏参数估计算法(sparse paramaters algorithm)
Figure 1. Development process of narrowband target DOA estimation methods
表 1 窄带目标DOA估计方法优缺点对比
Table 1. Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of narrowband target DOA estimation methods
方法 算法 优点 缺点 基于波束形成的算法 常规波束形成 稳健性强; 计算复杂度低 分辨率低 自适应波束形成 旁瓣低; 分辨率高 计算复杂度高 子空间算法 MUSIC类算法 高信噪比、多块拍下分辨率高 低信噪比、小块拍下分辨率低; 难以处理相干信号 ESPRIT类算法 高信噪比、多块拍下分辨率高 低信噪比、小块拍下分辨率低; 难以处理相干信号;
要求阵列平移不变基于压缩感知的算法 凸松弛优化算法 稳健性强; 分辨率高; 可处理相干信号 计算复杂度高; 需要参数选择 贪婪算法 计算复杂度低; 可处理相干信号 分辨率低 SBL算法 稳健性强; 无需稀疏度先验信息;
可处理相干信号计算复杂度高 -
[1] BARTLETT M S. Smoothing periodograms from time-series with continuous spectra[J]. Nature, 1948, 161(4096): 686-687. doi: 10.1038/161686a0 [2] LI J, STOICA P, WANG Z. Doubly constrained robust Capon beamformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(9): 2407-2423. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.831998 [3] MESTRE X, LAGUNAS M A. Finite sample size effect on minimum variance beamformers: Optimum diagonal loading factor for large arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 54(1): 69-82. [4] GERSHMAN A B, LUO Z Q, SHAHBAZPANAHI S, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming based on worst-case performance optimization[M]. Hoboken, New Jersey, United States: Copyright © 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , 2006: 49-89. [5] SANTOSH S, SHARMA K. A review on multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. International Journal of Engineering Research, 2013, 2(3): 239-244. [6] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas & Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276-280. [7] BARABELL A. Improving the resolution performance of eigenstructure-based direction-finding algorithms[C]// Processing International Conf. on Acoustics Speech & Signal. Boston, Ma. , USA: IEEE, 1983: 336-339. [8] RAO B D, HARI K V S. Performance analysis of root-MUSIC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(12): 1939-1949. doi: 10.1109/29.45540 [9] ERMOLAEV V T, GERSHMAN A B. Fast algorithm for minimum-norm direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(9): 2389-2394. doi: 10.1109/78.317860 [10] ERMOLAEV V T, GERSHMAN A B. Eigenvalue analysis of spatial covariance matrices for correlated signals[J]. Electronics Letters, 1992, 12(28): 1114-1115. [11] 韩芳明, 张守宏, 潘复平. 阵列误差对MUSIC算法性能的影响与校正[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 30(5): 585-589.HAN F M, ZHANG S H, PAN F P. Effect of array uncertainty on the performance of MUSIC and its calibration[J]. Journal of Xidian University(Natural Science), 2003, 30(5): 585-589. [12] ROY R, PAULRAJ A, KAILATH T. ESPRIT——A subspace rotation approach to estimation of parameters of cisoids in noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1986, 34(5): 1340-1342. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1986.1164935 [13] OTTERSTEN B, VIBERG M, KAILATH T. Performance analysis of the total least squares ESPRIT algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1991, 39(5): 1122-1135. doi: 10.1109/78.80967 [14] ZOLTOWSKI M D, HAARDT M, MATHEWS C P. Closed-form 2D angle estimation with rectangular arrays in element space or beamspace via unitary ESPRIT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(2): 316-328. doi: 10.1109/78.485927 [15] HAARDT M, NOSSEK J A. Unitary ESPRIT: How to obtain increased estimation accuracy with a reduced computational burden[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1995, 43(5): 1232-1242. doi: 10.1109/78.382406 [16] GOLDSTEIN J S, REED I S, SCHARF L L. A multistage representation of the Wiener filter based on orthogonal projections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1998, 44(7): 2943-2959. doi: 10.1109/18.737524 [17] HIEMSTRA J D. Robust implementations of the multistage Wiener filter[D]. Blacksburg, VA, USA: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 2003. [18] SONG A, LI Y, LIU J, et al. DOA estimation of noncircular signals with multistage Wiener filter and polynomial rooting[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013, 42(1): 53-57. [19] SHI Y, WANG S, HUANG Z. An algorithm for 2D DOA source parameters estimate based on multistage wiener filters[C]//2006 International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems. Guilin China: IEEE, 2006: 398-401. [20] XIN J, ZHENG N, SANO A. Simple and efficient nonparametric method for estimating the number of signals without eigendecomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(4): 1405-1420. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.889982 [21] VIBERG M, OTTERSTEN B. Sensor array processing based on subspace fitting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1991, 39(5): 1110-1121. doi: 10.1109/78.80966 [22] VIBERG M, OTTERSTEN B, KAILATH T. Detection and estimation in sensor arrays using weighted subspace fitting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1991, 39(11): 2436-2449. doi: 10.1109/78.97999 [23] MARCOS S, BENIDIR M. Source-bearing estimation and sensor positioning with the propagator method[C]//Advanced Signal Processing Algorithms, Architectures, and Implementations. [S.l.]: SPIE, 1990, 1348: 312-323. [24] MARCOS S, MARSAL A, BENIDIR M. The propagator method for source bearing estimation[J]. Signal Processing, 1995, 42(2): 121-138. doi: 10.1016/0165-1684(94)00122-G [25] EVANS J E, JOHNSON J R, SUN D F. Application of advanced signal processing techniques to angle of arrival estimation in ATC navigation and surveillance systems[R]. Massachusetts Avenue Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Lincoln Laboratory, 1982. [26] SHAN T J, WAX M, KAILATH T. On spatial smoothing for direction-of-arrival estimation of coherent signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1985, 33(4): 806-811. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1985.1164649 [27] PILLAI S U, KWON B H. Forward/backward spatial smoothing techniques for coherent signal identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(1): 8-15. doi: 10.1109/29.17496 [28] 王布宏, 王永良, 陈辉. 相干信源波达方向估计的加权空间平滑算法[J]. 通信学报, 2003, 24(4): 31-40.WANG B H, WANG Y L, CHEN H. Weighted spatial smoothing algorithm for direction of arrival estimation of coherent sources[J]. Journal on Communications, 2003, 24(4): 31-40. [29] KUNG S, LO C, FOKA R. A Toeplitz approximation approach to coherent source direction finding[C]//IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing(ICASSP). Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 1986. [30] 王布宏, 王永良, 陈辉. 一种新的相干信源DOA估计算法: 加权空间平滑协方差矩阵的Toeplitz矩阵拟合[J]. 电子学报, 2003, 31(9): 1394-1397.WANG B H, WANG Y L, CHEN H. A novel genetic approach to DOA estimation of coherent sources based on weighted spatial smoothing and Toeplitz matrix fitting[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2003, 31(9): 1394-1397. [31] GORODNITSKY I F, RAO B D. Sparse signal reconstruction from limited data using FOCUSS: A re-weighted minimum norm algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(3): 600-616. doi: 10.1109/78.558475 [32] COTTER S F, RAO B D, ENGAN K, et al. Sparse solutions to linear inverse problems with multiple measurement vectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(7): 2477-2488. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.849172 [33] KARABULUT G Z, YONGACOGLU A. Sparse channel estimation using orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm[C]//IEEE 60th Vehicular Technology Conference. Los Angeles, CA, USA: IEEE, 2004. [34] NEEDELL D, VERSHYNIN R. Uniform uncertainty principle and signal recovery via regularized orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 2009, 9(3): 317-334. doi: 10.1007/s10208-008-9031-3 [35] NEEDELL D, TROPP J A. CoSaMP: Iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2009, 26(3): 301-321. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2008.07.002 [36] MALIOUTOV D, CETIN M, WILLSKY A S. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(8): 3010-3022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.850882 [37] 牛俊儒. 基于稀疏重构的窄带信号DOA估计研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2017. [38] TIPPING M E. Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1(3): 211-244. [39] WIPF D P, RAO B D. Sparse Bayesian learning for basis selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8): 2153-2164. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.831016 [40] JI S, XUE Y, CARIN L. Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(6): 2346-2356. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.914345 [41] BABACAN S D, MOLINA R, KATSAGGELOS A K. Bayesian compressive sensing using laplace priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(1): 53-63. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2032894 [42] WILLIAMS P M. Bayesian regularization and pruning using a Laplace prior[J]. Neural Computation, 1995, 7(1): 117-143. doi: 10.1162/neco.1995.7.1.117 [43] LI K, YIN X Y, ZONG Z Y. Bayesian seismic multi-scale inversion in complex Laplace mixed domains[J]. Petroleum Science, 2017, 14(4): 694-710. doi: 10.1007/s12182-017-0191-0 [44] GERVEN M, CSEKE B, OOSTENVELD R, et al. Bayesian source localization with the multivariate laplace prior[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2009, 2(1): 1901-1909. [45] MECKLENBRÄUKER C F, GERSTOFT P, ZÖCHMANN E. C-LASSO and its dual for sparse signal estimation from array data[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 130: 204-216. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.06.029 [46] JIANG T, ZHANG X, LI Y. Bayesian compressive sensing using reweighted Laplace priors[J]. Aeu-international Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2018, 97: 178-184. [47] YANG Z, XIE L, ZHANG C. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 61(1): 38-43. [48] DAI J, BAO X, XU W, et al. Root sparse Bayesian learning for off-grid DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 24(1): 46-50. [49] WANG Q, ZHAO Z, CHEN Z, et al. Grid evolution method for DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(9): 2374-2383. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2814998 [50] WANG Q, YU H, LI J, et al. Adaptive grid refinement method for doa estimation via sparse bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2023, 48(3): 806-819. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2023.3235055 [51] YANG Z, XIE L, ZHANG C. A discretization-free sparse and parametric approach for linear array signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(19): 4959-4973 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2339792 [52] BHASKAR B N, TANG G, RECHT B. Atomic norm denoising with applications to line spectral estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(23): 5987-5999. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2273443 [53] TANG G, BHASKAR B N, SHAH P, et al. Compressed sensing off the grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(11): 7465-7490. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2277451 [54] YANG Z, XIE L. Enhancing sparsity and resolution via reweighted atomic norm minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 64(4): 995-1006. [55] WANG Y, TIAN Z. IVDST: A fast algorithm for atomic norm minimization in line spectral estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(11): 1715-1719. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2870539 [56] JYOTHI R, BABU P, WANG Y, et al. DYANOM—Dykstra’s projection based atomic norm solver[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 182: 107958. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107958 [57] WAX M, SHAN T J, KAILATH T. Spatio-temporal spectral analysis by eigenstructure methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1984, 32(4): 817-827. [58] LIU Z, WANG X, ZHAO G, et al. Wideband DOA estimation based on sparse representation—an extension of l1-SVD in wideband cases[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication and Computing(ICSPCC 2013). Kunming, China: IEEE, 2013: 1-4. [59] LUO J A, ZHANG X P, WANG Z. A novel aliasing-free subband information fusion approach for wideband sparse spectral estimation[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2017, 2017(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1186/s13634-016-0440-1 [60] LUO J A, ZHANG X P, WANG Z. A new subband information fusion method for wideband DOA estimation using sparse signal representation[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP). Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2013: 4016-4020. [61] TANG Z, BLACQUIERE G, LEUS G. Aliasing-free wideband beamforming using sparse signal representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(7): 3464-3469. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2140108 [62] XU X, ZHANG M, YE Z. Wideband DOA estimation based on sparse signal representation[C]//2012 Fifth International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design(ISCID). Hangzhou, China: IEEE, 2012, 2: 10-13. [63] GERSTOFT P, MECKLENBRÄUKER C F, XENAKI A, et al. Multisnapshot sparse Bayesian learning for DOA[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(10): 1469-1473. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2598550 [64] GERSTOFT P, MECKLENBRÄUKER C F. Wideband sparse Bayesian learning for DOA estimation from multiple snapshots[C]//2016 IEEE Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2016. [65] NANNURU S, GEMBA K L, GERSTOFT P, et al. Sparse Bayesian learning with multiple dictionaries[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 159: 159-170. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.02.003 [66] VALAEE S. Array processing for detection and localization of narrowband, wideband and distributed sources[D]. Montreal, Quebec, Canada: McGill University, 1994. [67] HUNG H, KAVEH M. Focussing matrices for coherent signal-subspace processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1988, 36(8): 1272-1281. doi: 10.1109/29.1655 [68] DORON M. On focusing matrices for wide-band array processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1992, 40(6): 1295-1302. doi: 10.1109/78.139236 [69] SELLONE F. Robust wideband DOA estimation[C]//2005 IEEE/SP 13th Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing(SSP). Bordeaux, France: IEEE, 2005. [70] MA F, ZHANG X. Wideband DOA estimation based on focusing signal subspace[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2019, 13: 675-682. doi: 10.1007/s11760-018-1396-4 [71] WANG L, ZHAO L, BI G, et al. Novel wideband DOA estimation based on sparse Bayesian learning with Dirichlet process priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 64(2): 275-289. [72] ZHANG J, BAO M, ZHANG X P, et al. DOA estimation for heterogeneous wideband sources based on adaptive space-frequency joint processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 1657-1672. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3160802 [73] 王朋, 迟骋, 纪永强, 等. 二维解卷积波束形成水下高分辨三维声成像[J]. 声学学报, 2019, 44(4): 613-625.WANG P, CHI C, JI Y Q, et al. Two-dimensional deconvolved beamforming for high-resolution underwater three-dimensional acoustical imaging[J]. Acta Acustica, 2019, 44(4): 613-625. [74] 汪敬东, 王乾威, 蔡献祥, 等. 基于 STK 的台湾铺路爪雷达系统性能分析[J]. 电子技术与软件工程, 2022, 12: 78-81. [75] PAL P, VAIDYANATHAN P P. Nested arrays: A novel approach to array processing with enhanced degrees of freedom[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(8): 4167-4181. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2049264 [76] YANG M, SUN L, YUAN X, et al. Improved nested array with hole-free DCA and more degrees of freedom[J]. Electronics Letters, 2016, 52(25): 2068-2070. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.3197 [77] LIU C L, VAIDYANATHAN P P. Super nested arrays: Linear sparse arrays with reduced mutual coupling—Part II: High-order extensions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(16): 4203-4217. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2558167 [78] SHI Z, XU L, ZHENG W. Low complexity DFT based DOA estimation for synthetic nested array using single moving sensor[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2018, 101: 857-874. doi: 10.1007/s11277-018-5720-7 [79] XIONG J, WANG W Q, CHEN H, et al. Compressive sensing-based range and angle estimation for nested FDA radar[C]//2015 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2015: 608-611. [80] SUN F, GAO B, CHEN L, et al. A low-complexity ESPRIT-based DOA estimation method for co-prime linear arrays[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(9): 1367. doi: 10.3390/s16091367 [81] ZHANG D, ZHANG Y, ZHENG G, et al. Improved DOA estimation algorithm for co-prime linear arrays using root-MUSIC algorithm[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(18): 1277-1279. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.2292 [82] ZHENG W, ZHANG X, ZHAI H. Generalized coprime planar array geometry for 2D DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(5): 1075-1078. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2664809 [83] ZHENG W, ZHANG X, GONG P, et al. DOA estimation for coprime linear arrays: An ambiguity-free method involving full DOFs[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 22(3): 562-565. [84] PAL P, VAIDYANATHAN P P. Coprime sampling and the MUSIC algorithm[C]//2011 Digital Signal Processing and Signal Processing Education Meeting. Sedona, AZ, USA: IEEE, 2011: 289-294. [85] ZHOU C, ZHOU J. Direction-of-arrival estimation with coarray ESPRIT for coprime array[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(8): 1779. doi: 10.3390/s17081779 [86] ZHANG Y D, AMIN M G, HIMED B. Sparsity-based DOA estimation using co-prime arrays[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2013: 3967-3971. [87] SHEN Q, CUI W, LIU W, et al. Underdetermined wideband DOA estimation of off-grid sources employing the difference co-array concept[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 130: 299-304. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.07.022 [88] QIN Y, LIU Y, LIU J, et al. Underdetermined wideband DOA estimation for off-grid sources with coprime array using sparse Bayesian learning[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(1): 253-263. doi: 10.3390/s18010253 [89] SHI Z, ZHOU C, GU Y, et al. Source estimation using coprime array: A sparse reconstruction perspective[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 17(3): 755-765. [90] ZHOU C, GU Y, FAN X, et al. Direction-of-arrival estimation for coprime array via virtual array interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(22): 5956-5971. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2872012 [91] WAX M, SHAN T S, KAILATH T. Spatio-temporal spectral analysis by eigenstructure methods[J]. IEEE Transcantion on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 1984, 32(4): 817-827. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1984.1164400 [92] YE C B, ZHU B Z, LI B B, et al. Computationally efficient 2D-DOA estimation for uniform planar arrays: RD-ROOT-MUSIC algorithm[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 38(4): 685-694. [93] JHANG W, CHEN S W, CHANG A C. Efficient hybrid DOA estimation for massive uniform rectangular array[J]. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences, 2020, 103(6): 836-840. [94] SHEN F F, LIU Y M, ZHAO G H, et al. Sparsity-based off-grid DOA estimation with uniform rectangular arrays[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(8): 3384-3390. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2800906 [95] ZHANG Z, WANG Y, TIAN Z. Efficient two-dimensional line spectrum estimation based on decoupled atomic norm minimization[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 163: 95-106. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.04.024 [96] TIAN X, LEI J, DU L. A generalized 2D DOA estimation method based on low-rank matrix reconstruction[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 17407-17414. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2820165 [97] 刘学承, 朱敏, 武岩波. 适用任意平面阵列的二维宽带DOA快速估计算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2022, 43(7): 102-111.LIU X C, ZHU M, WU Y B. A fast 2D wideband direction-of-arrival estimation method with arbitrary planar arrays[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2022, 43(7): 102-111. [98] PARK Y, SEONG W, GERS T P. Block-sparse two-dimensional off-grid beamforming with arbitrary planar array geometry[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2020, 147(4): 2184-2191. doi: 10.1121/10.0000983 [99] 陈涛, 史林, 黄桂根, 等. 适用于任意几何结构平面阵列的无网格DOA估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 1052-1058.CHEN T, SHI L, HUANG G G, et al. Gridless DOA estimation algorithm for planar arrays with arbitrary geometry[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 1052-1058. [100] LI J, LI Y, ZHANG X. Two-dimensional off-grid DOA estimation using unfolded parallel coprime array[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(12): 2495-2498. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2872955 [101] QIN S, ZHANG Y D, AMIN M G. Improved two-dimensional DOA estimation using parallel coprime arrays[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 172: 107428. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.107428 [102] LI J, ZHAO J, DING Y, et al. An improved co-prime parallel array with conjugate augmentation for 2D DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(20): 23400-23411. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3106382 [103] LI L, CHEN Y, ZANG B, et al. A high-precision two-dimensional DOA estimation algorithm with parallel coprime array[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2022, 41(12): 6960-6974. doi: 10.1007/s00034-022-02102-7 [104] ZHENG Z, MU S. Two-dimensional DOA estimation using two parallel nested arrays[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 24(3): 568-571. [105] LI J, ZHANG X. Two-dimensional grid-less angle estimation based on three parallel nested arrays[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 173: 107577. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107577 [106] HE J, LI L, SHU T. 2-D direction finding using parallel nested arrays with full co-array aperture extension[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 178: 107795. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107795 [107] 张岩, 韩子腾, 王昭雷, 等. 基于L型声阵列多重信号分类声源测向研究[J]. 无线电工程, 2024, 54(2): 335-342.ZHANG Y, HAN Z T, WANG Z L, et al. Sound source direction finding based on L-shaped acoustic array multiple signal classification[J]. Radio Engineering, 2024, 54(2): 335-342. [108] 高佳睿. Sub-6 GHz频段微基站阵列天线研究与设计[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2022. [109] 李佳旺. 面向毫米波通信和雷达应用的阵列天线技术研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2022. [110] TAYEM N, KWON H M. L-shape 2-dimensional arrival angle estimation with propagator method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2005, 53(5): 1622-1630. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2005.846804 [111] WANG G, XIN J, ZHENG N, et al. Computationally efficient subspace-based method for two-dimensional direction estimation with L-shaped array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(7): 3197-3212. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2144591 [112] GU J F, WEI P. Joint SVD of two cross-correlation matrices to achieve automatic pairing in 2D angle estimation problems[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2007, 6: 553-556. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2007.907913 [113] LIU D, LIANG J. L-shaped array-based 2D DOA estimation using parallel factor analysis[C]//2010 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation. Jinan, China: IEEE, 2010: 6949-6952. [114] XU L, WU R, ZHANG X, et al. Joint two-dimensional DOA and frequency estimation for L-shaped array via compressed sensing PARAFAC method[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 37204-37213. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2850307 [115] 魏子翔, 崔嵬, 侯建刚, 等. 基于秩减估计器的L型阵列二维波达角估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(8): 1879-1885.WEI Z X, CUI W, HOU J G, et al. Rank reduction estimator based algorithm for estimating 2D-DOA with L-shaped array[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 37(8): 1879-1885. [116] ZHANG Z, WANG W, HUANG Y, et al. Decoupled 2D direction of arrival estimation in L-shaped array[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(9): 1989-1992. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2708698 [117] MATHEWS C P, ZOLTOWSKI M D. Eigenstructure techniques for 2D angle estimation with uniform circular arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on signal processing, 1994, 42(9): 2395-2407. doi: 10.1109/78.317861 [118] 鄢社锋. 优化阵列信号处理(下册): 模态处理与方位估计[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. [119] 邓昌建, 蒋世奇, 蔚泽峰, 等. 球形麦克风阵列时频故障信号定位算法研究[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2017, 31(2): 309-314.DENG C J, JIANG S Q, WEI Z F, et al. Research on location algorithm of time-frequency fault signal based on spherical microphone array[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2017, 31(2): 309-314. [120] 陈卓, 陈伏虎. 潜艇艇艏阵声呐发展趋势分析[J]. 声学与电子工程, 2015(4): 49-52. [121] 张鹏. 大角度扫描共形阵波束综合技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2023. [122] MEYER J, ELKO G. A highly scalable spherical microphone array based on an orthonormal decomposition of the soundfield[C]//2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Orlando, FL, USA: IEEE, 2002: 1781-1784. [123] YAN S, SUN H, SVENSSON U P, et al. Optimal modal beamforming for spherical microphone arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2010, 19(2): 361-371. [124] BATTISTA G, CHIARIOTTI P, CASTELLINI P. Spherical harmonics decomposition in inverse acoustic methods involving spherical arrays[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2018, 433: 425-460. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2018.05.001 [125] CHU Z, YANG Y, HE Y. Deconvolution for 3-dimensional acoustic source identification based on spherical harmonics beamforming[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2015, 344: 484-502. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2015.01.047 [126] YANG Y, CHU Z, SHEN L, et al. Fast fourier-based deconvolution for three-dimensional acoustic source identification with solid spherical arrays[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 107: 183-201. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.01.028 [127] YAN S, HOU C, MA X. From element-space to modal array signal processing[J]. Acta Acustica, 2011, 36(5): 461-468. [128] LIU C, DING Z, LIU X. A low complexity 2D pattern synthesis algorithm for cylindrical array[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 2013(1): 352843. [129] ZHU S, WANG Y, YANG Y. Robust superdirective beamforming for cylindrical arrays based on subarray processing[J]. Acta Acustica, 2018, 43(4): 600-611. [130] PASTORINO M, RANDAZZO A. Real-time SVM-based approach for localization of sources[C]//2004 IEEE International Workshop on Imaging Systems and Techniques(IST). Stresa, Italy: IEEE, 2004: 2-6. [131] ASHOK C, VENKATESWARAN N. Support vector regressionbased DOA estimation in heavy tailed noise environment[C]//2016 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking(WiSPNET). Chennai, India: IEEE, 2016: 99-102. [132] DEHGHANPOUR M, VAKILI V T T, FARROKHI A. DOA estimation using multiple kernel learning SVM considering mutual coupling[C]//2012 Fourth International Conference on Intelligent Networking and Collaborative Systems. Bucharest, Romania: IEEE, 2012: 55-61. [133] TERABAYASHI K, NATSUAKI R, HIROSE A. Ultrawideband direction-of-arrival estimation using complex-valued spatiotemporal neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(9): 1727-1732. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2313869 [134] ZHENG W Q, ZOU Y X, RITZ C. Spectral mask estimation using deep neural networks for inter-sensor data ratio model based robust DOA estimation[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP). South Brisbane, QLD, Australia: IEEE, 2015: 325-329. [135] ADAVANNE S, POLITIS A, VIRTANEN T. Direction of arrival estimation for multiple sound sources using convolutional recurrent neural network[C]//2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference(EUSIPCO). Rome, Italy: IEEE, 2018: 1462-1466. [136] XIANG H, CHEN B, YANG T, et al. Improved de-multipath neural network models with self-paced feature-to-feature learning for DOA estimation in multipath environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(5): 5068-5078. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2977894 [137] YANG Y, CHEN H, ZHANG P. A stacked self-attention network for two-dimensional direction-of-arrival estimation in hands-free speech communication[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2022, 152(6): 3444-3457. doi: 10.1121/10.0016467 [138] LIU Z M, ZHANG C, PHILIP S Y. Direction-of-arrival estimation based on deep neural networks with robustness to array imperfections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(12): 7315-7327. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2874430 [139] CHAKRABARTY S, HABETS E A P. Multi-speaker DOA estimation using deep convolutional networks trained with noise signals[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(1): 8-21. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2901664 [140] WU L, LIU Z M, HUANG Z T. Deep convolution network for direction of arrival estimation with sparse prior[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(11): 1688-1692. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2945115 [141] EMMA O, PETER G, HAIQIANG N. A feedforward neural network for direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2020, 147: 2035-2048. doi: 10.1121/10.0000944 [142] HE W, MOTLICEK P, ODOBEZ J M. Neural network adaptation and data augmentation for multi-speaker direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2021, 29: 1303-1317. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2021.3060257 [143] YUAN Y, WU S, WU M, et al. Unsupervised learning strategy for direction-of-arrival estimation network[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1450-1454. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3096117 [144] NIE W, ZHANG X, XU J, et al. Adaptive direction-of-arrival estimation using deep neural network in marine acoustic environment[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(13): 15093-15105. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3274309 [145] CAO H, WANG W, SU L, et al. Deep transfer learning for underwater direction of arrival using one vector sensor[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2021, 149(3): 1699-1711. doi: 10.1121/10.0003645 [146] ZHU X, DONG H, ROSSI P S, et al. Time-frequency fused underwater acoustic source localization based on contrastive predictive coding[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(13): 13299-13308. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3179405 -




 下载:
下载:







