Deep Learning-Based Method for Key Signal Recognition during Underwater Explosions
-
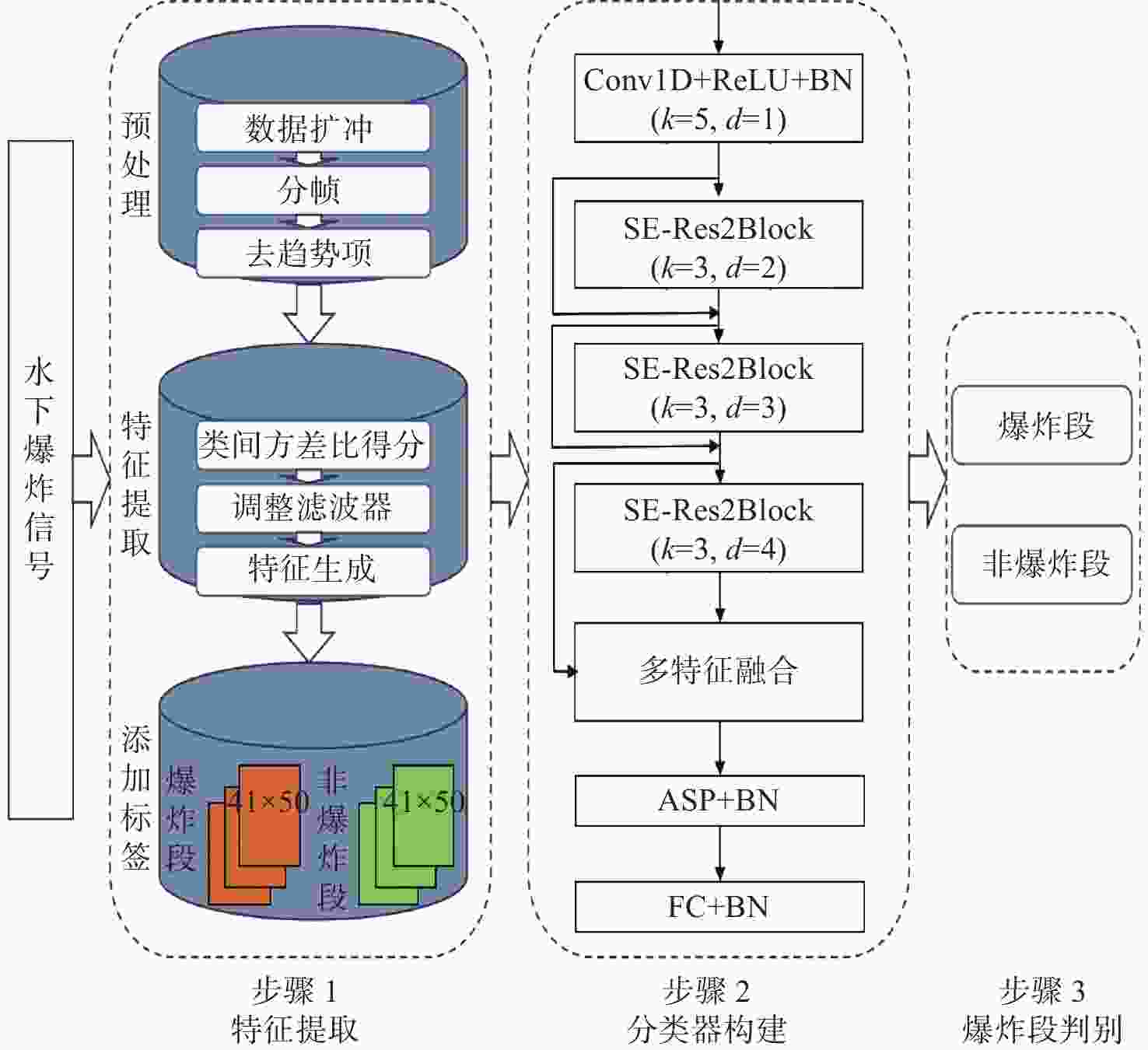
摘要: 水下爆炸试验采集的数据量庞大并掺杂大量无用数据, 为保护数据不受爆炸的影响, 试验时需要优先将关键数据识别并存储。针对此, 文中提出一种将特征提取方法和深度学习模型相结合的关键信号识别模型, 以提升对关键信号识别的准确率。首先, 研究了不同预处理方法对水下爆炸加速度信号趋势项的去除效果, 并用实验证明小波包分解法、经验模态分解法和高通滤波法可较好地提升模型的识别性能; 其次, 为使提取的特征更有利于区分爆炸段与非爆炸段, 提出一种针对水下爆炸加速度信号的基于类间方差比的特征提取方法, 基于水下爆炸加速度信号数据可知, 相比于Log Mel特征, 文中提出的特征用K-means方法分类准确率提升约4.92%; 最后, 引入添加SE-Res2Block模块的ECAPA-TDNN模型, 该模型具有更好的识别准确率, 以文中提出的特征作为输入, 识别准确率达99.31%。Abstract: The amount of data collected from underwater explosion tests is enormous, which is mixed with a large amount of useless data. To protect the data from the effects of the explosion, it is crucial to prioritize the recognition and storage of key data during the test. In response to this, a key signal recognition model that combined feature extraction methods with deep learning models was proposed to improve the accuracy of key signal recognition. Firstly, different preprocessing methods for removing trend components from underwater explosion acceleration signals were studied. Existing test results demonstrated that wavelet packet decomposition, empirical mode decomposition, and high-pass filtering could significantly enhance the model’s recognition performance. Secondly, to make the extracted features more conducive to distinguishing between explosion and non-explosion segments, a feature extraction method based on the inter-class variance ratio for underwater explosion acceleration signals was proposed. According to the underwater explosion acceleration signal data, it was found that compared to Log Mel features, the proposed features improved classification accuracy by approximately 4.92% using the K-means method. Finally, the ECAPA-TDNN model incorporating the SE-Res2Block module was introduced, ensuring better recognition accuracy. With the proposed features as input, the recognition accuracy reached 99.31%.
-
Key words:
- underwater explosion /
- feature extraction /
- deep learning /
- key signal recognition
-
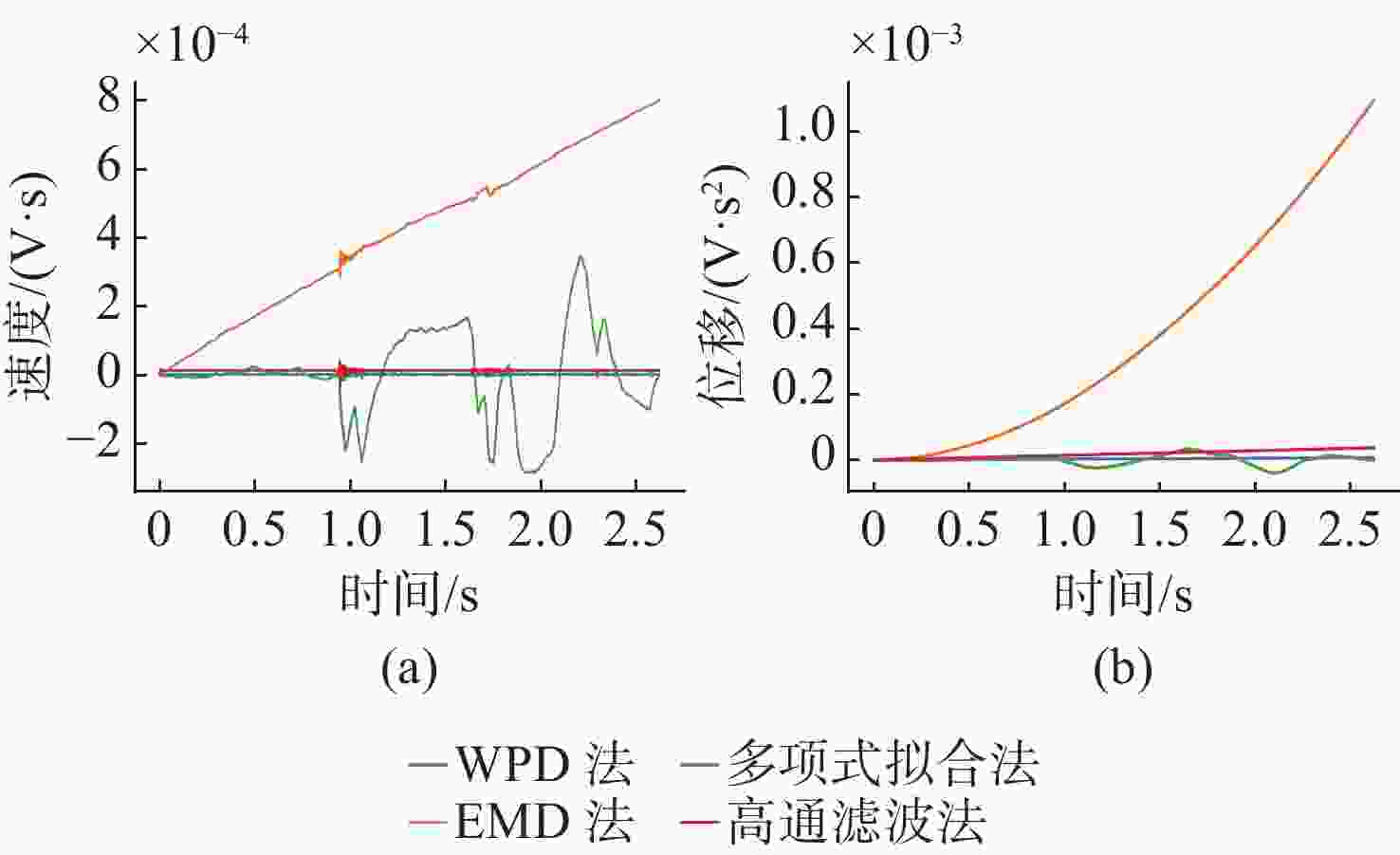
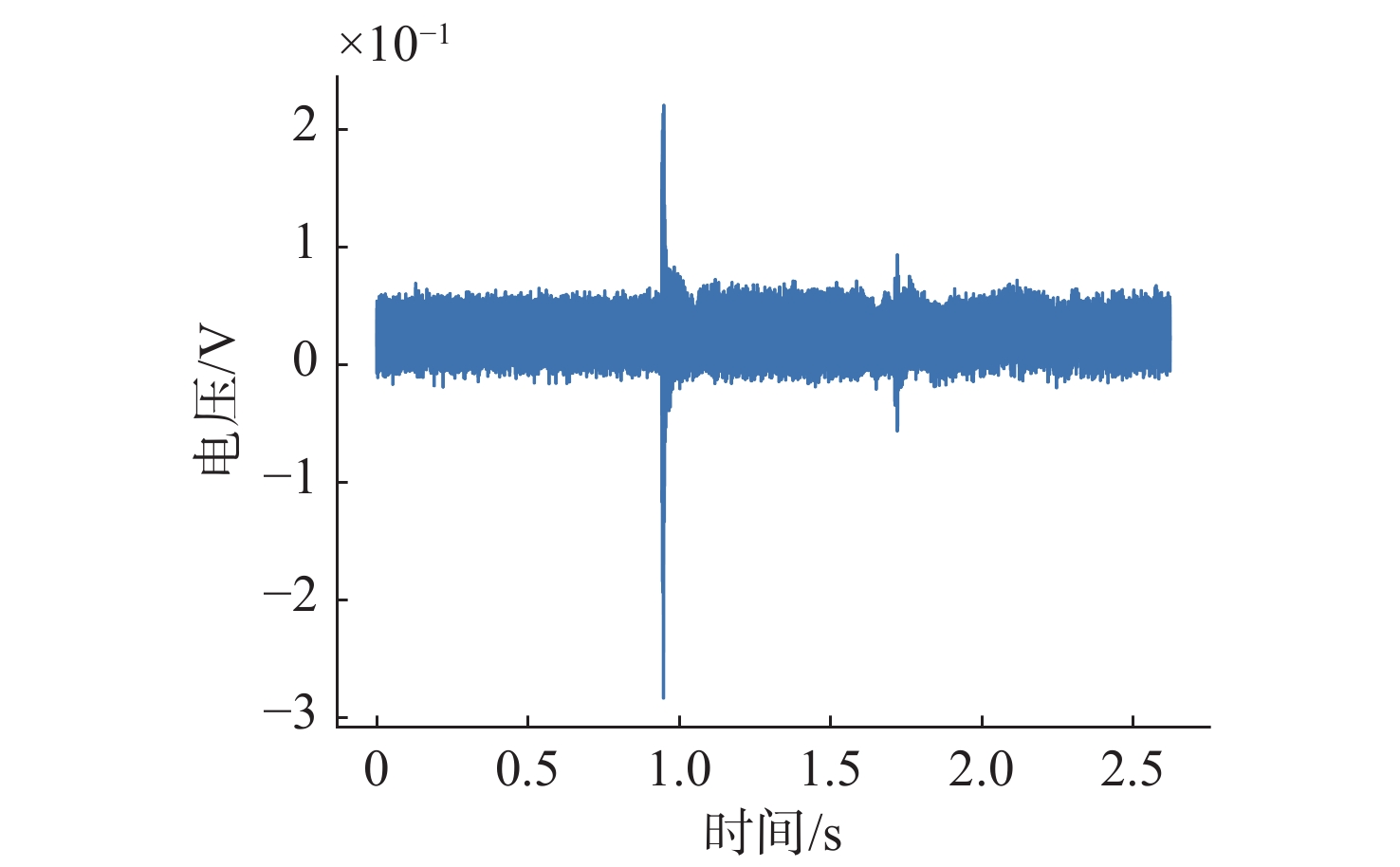
表 1 趋势项去除后加速度信号各评价指标对比
Table 1. Evaluation indicators of acceleration signal after trend item removal
算法名称 5 000点均值 加速度峰值
/V速度峰值
/(V·s)位移峰值
/(V·s2)速度起始
/(V·s)速度结束
/(V·s)位移起始
/(V·s2)位移结束
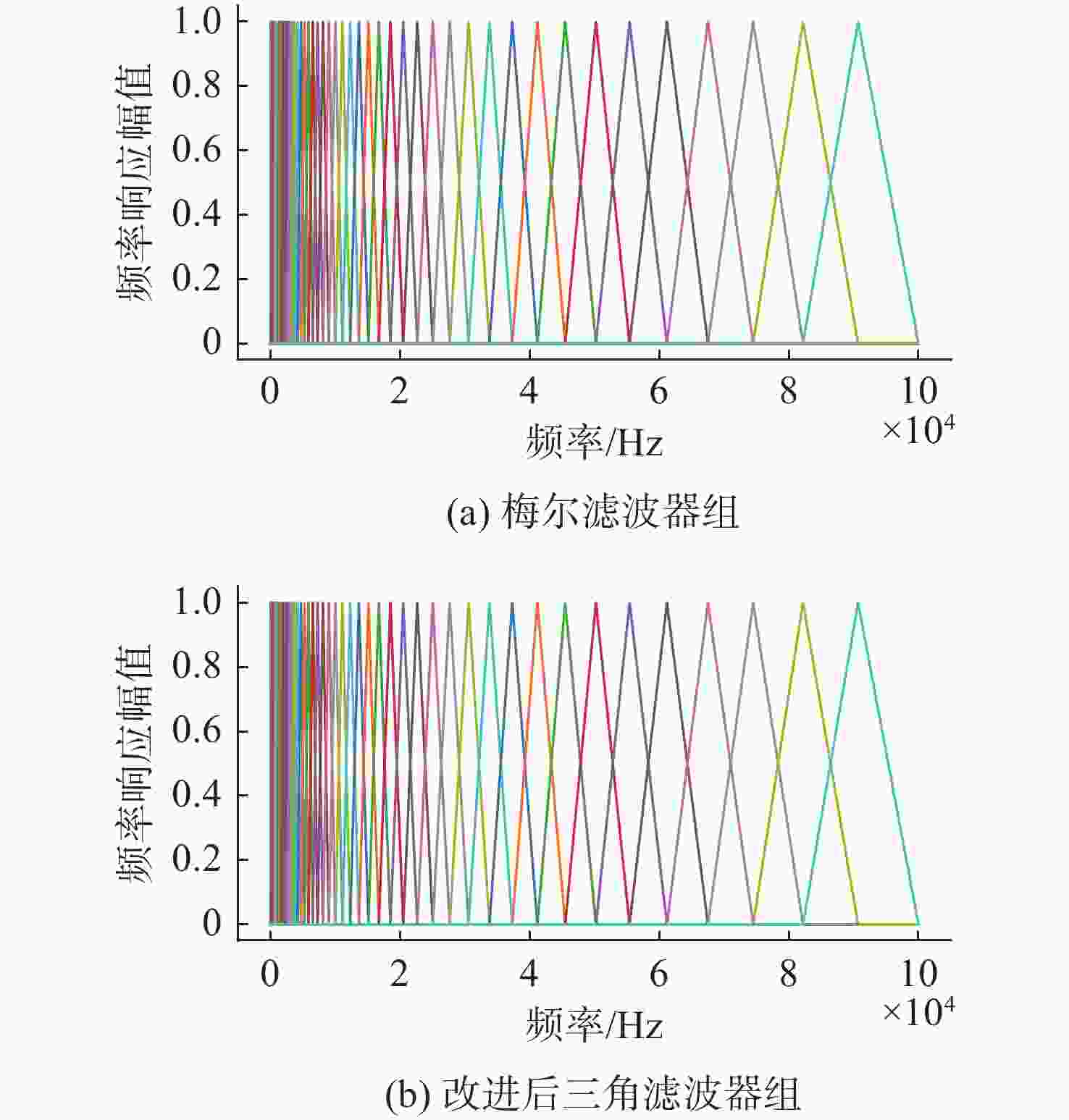
/(V·s2)EMD法 4.36×10−6 7.96×10−4 3.47×10−8 1.08×10−3 2.93×10−1 8.00×10−4 1.09×10−3 高通滤波法 1.39×10−5 1.41×10−5 1.73×10−7 3.70×10−5 3.00×10−1 4.29×10−5 3.72×10−5 WPD法 2.99×10−6 2.86×10−6 3.96×10−8 7.00×10−6 3.02×10−1 4.45×10−5 7.04×10−6 多项式拟合法 −3.19×10−7 −1.05×10−5 −8.17×10−10 1.37×10−7 3.09×10−1 3.47×10−4 3.93×10−5 无处理 3.50×10−4 7.20×10−2 2.92×10−6 9.43×10−2 2.81×10−1 7.24×10−2 9.52×10−1 表 2 2组实验数据在不同数据集的分布
Table 2. Distribution of two experimental data in different data sets
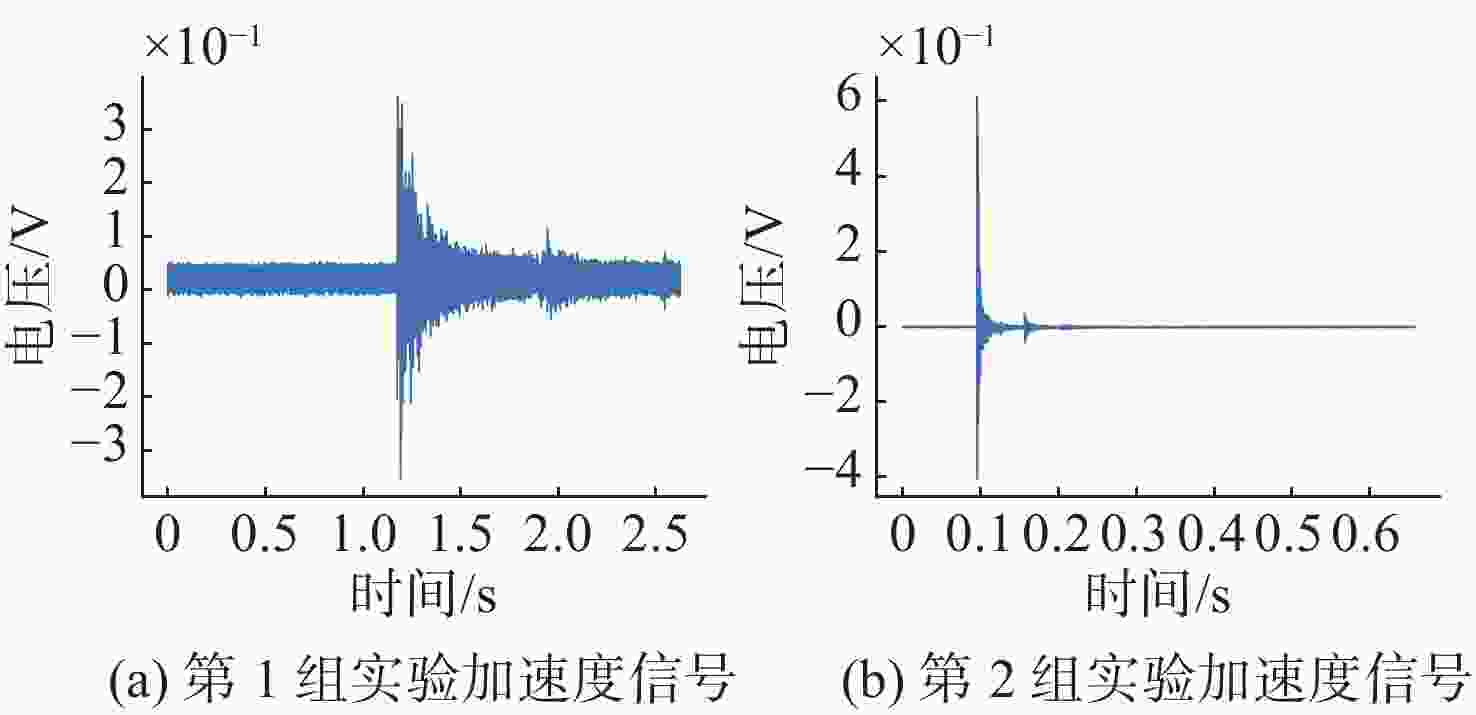
数据集 第1组 第2组 共计 训练集 6 400 12 864 19 264 验证集 1 600 3 820 4 820 测试集 1 000 2 572 3 572 表 3 实验所用不同模型参数对比
Table 3. Parameters of models
模型 结构参数 CNN Conv(Cin=1, Cout=4, k=5, s=2, p=1+ReLU+MaxPool(k=2, s=2))
Conv(Cin=4, Cout=16, k=5, s=2, p=1+ReLU+MaxPool(k=2, s=2))
Conv(Cin=16, Cout=32, k=3, s=2, p=1+ReLU+MaxPool(k=1, s=1))
Conv(Cin=32, Cout=64, k=3, s=2, p=1+ReLU+MaxPool(k=1, s=1))
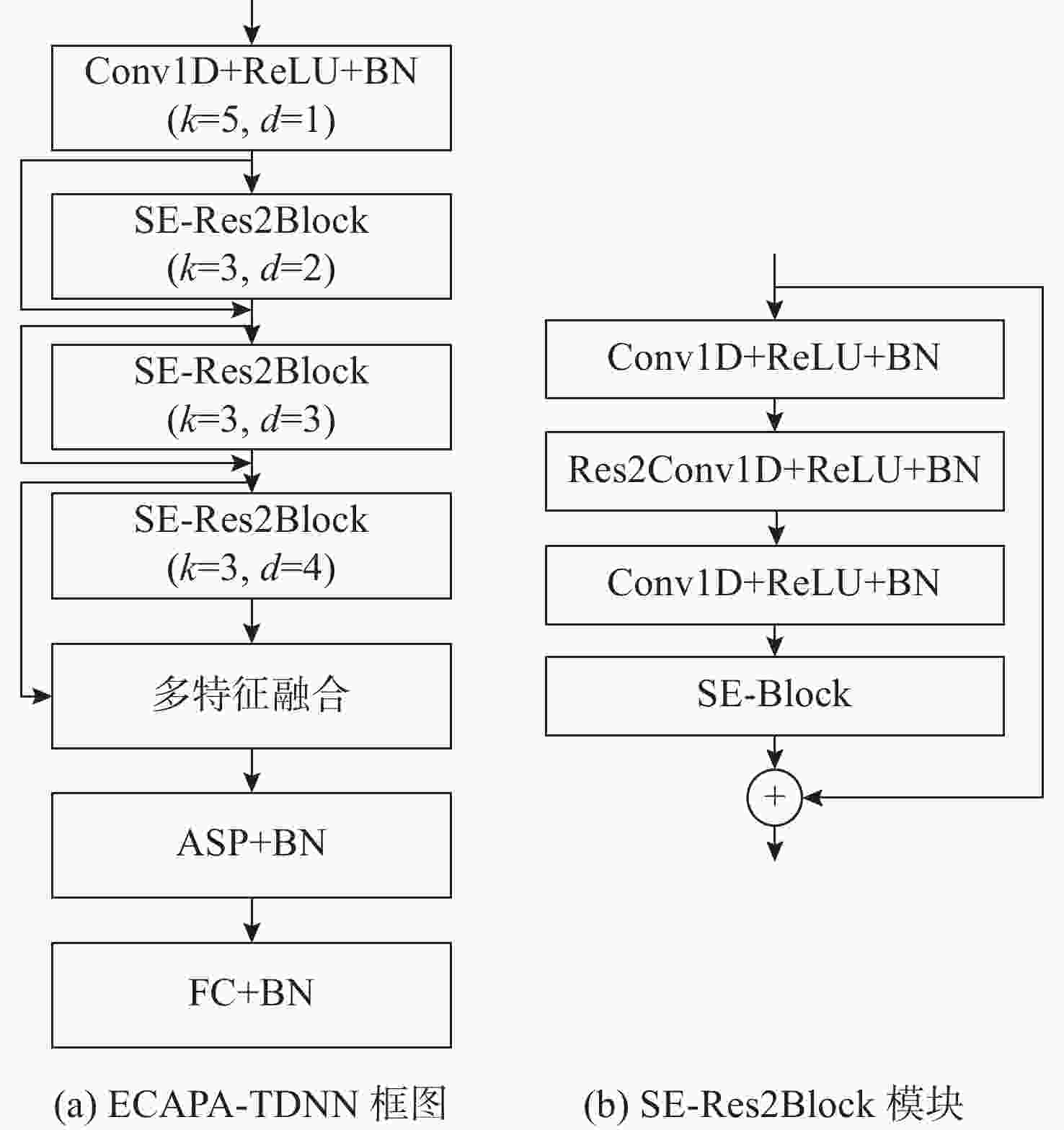
Linear(64$ \times $32, 512)+ReLU+Linear(512, 32)+ReLU+Linear(32, 2)LSTM LSTM(input_dim=50, hidden_dim=128, layer_dim=4, output_dim=2) ResNet18 ResNet18[22](num_classes=2) ECAPA-TDNN ECAPA-TDNN[24](num_classes=2) 表 4 不同特征提取方法识别准确率对比
Table 4. Recognition accuracy comparison of different features extraction combination
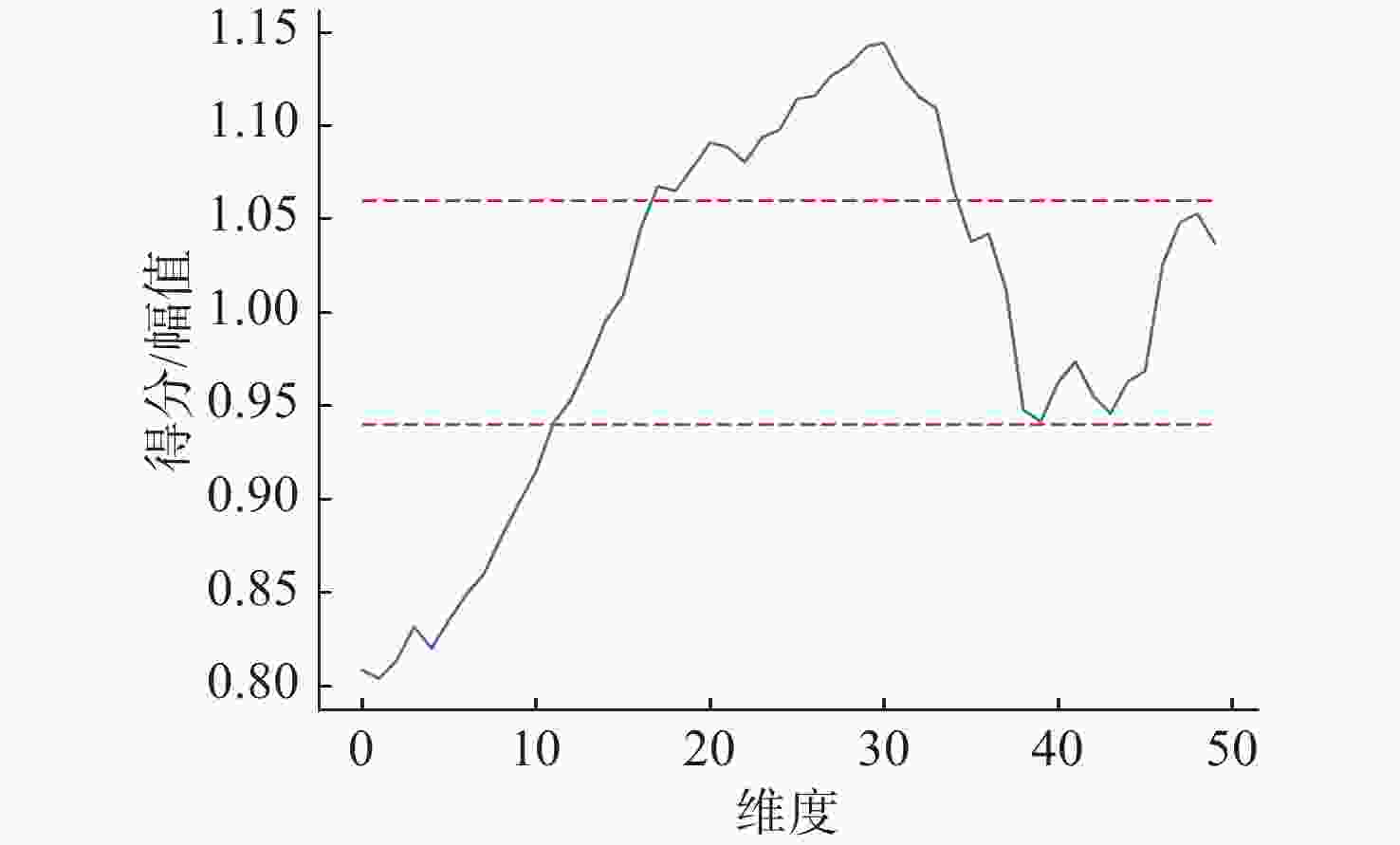
预处理方法 准确率 EMD法 96.25%±0.05% 多项式拟合法 92.75%±1.54% 高通滤波法 96.34%±0.02% WPD法 96.39%±0.05% 无处理 90.34%±1.22% 表 5 50维特征识别准确率
Table 5. Recognition accuracy of 50-dimensional features
模型 准确率 Log Mel特征 文中特征 ECAPA-TDNN 97.28%±0.02% 99.31%±0.09% LSTM 96.45%±0.12% 97.83%±0.02% ResNet18 96.78%±0.02% 97.16%±0.10% CNN 96.39%±0.05% 96.40%±0.04% SVM 96.39%±0.07% 96.72%±0.01% KNN 96.50%±0.05% 96.56%±0.07% K-means 73.80%±2.49% 78.72%±1.02% 表 6 不同特征提取组合的识别准确率对比
Table 6. Recognition accuracy comparison of different features extraction combination
特征+模型 准确率 一维频谱(2 048维)+CNN_1d 93.75%±1.35% PSD(2 048维)+CNN_1d 91.25%±2.24% WPDE(41×12维)+ECAPA-TDNN 95.75%±0.35% 文中特征(41×50维)+ECAPA-TDNN 99.31%±0.09% -
[1] 刘建湖. 舰船非接触水下爆炸动力学的理论与应用[D]. 无锡: 中国船舶科学研究中心, 2002. [2] CHUNG J, SEO Y Y, YOUNG S. Shin dynamic and whipping response of the surface ship subjected to underwater explosion: experiment and simulation[J]. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2020, 15(10): 1129-1140. doi: 10.1080/17445302.2019.1706924 [3] JIN P, XU H L, WANG H C, et al. On the seismic source function of an underwater explosion[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2023, 232(1): 485-503. [4] CHUNG J, SEO Y, SHIN Y S. Dynamic and whipping response of the surface ship subjected to underwater explosion: experiment and simulation[J]. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2019, 15(10): 1129-1140. [5] 杜志鹏, 张磊, 谌勇, 等. 泡沫覆盖层对水下爆炸气泡射流防护机理缩比试验研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(5): 569-576.DU Z P, ZHANG L, CHEN Y, et al. Reduced-scale experiment study on the protective mechanism of foam coating against underwater explosion bubble jet[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 43(5): 569-576. [6] 范志强, 马宏昊, 沈兆武, 等. 水下连续脉冲冲击波的声学特性[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2013, 33(5): 501-506.FAN Z Q, MA H H, SHEN Z W, et al. Acoustic characteristics of underwater continuous pulse shock waves[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2013, 33(5): 501-506. [7] REZAEE M, TARAGHI O A. Improving empirical mode decomposition for vibration signal analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C. 2017, 231(12): 2223-2234. [8] 蒲坚, 崔硕, 黄丹, 等. 山岭隧道爆破振动信号小波包及能量分析[J]. 交通科技, 2018(2): 61-65.PU J, CUI S, HUANG D, et al. Wavelet packet and energy analysis of vibration signals in mountain tunnel blasting[J]. Journal of Traffic Science and Technology, 2018(2): 61-65. [9] ROGÉRIO T, WENDERSON N L, PAULO R A, et al. Digital signal processing for self-vibration monitoring in grinding: A new approach based on the time-frequency analysis of vibration signals[J]. Measurement, 2019, 145: 71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.05.079 [10] 李洪涛. 基于无线数据传输的水下爆炸压力遥测系统硬件设计与实现[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2002. [11] 贾振华, 王文廉. 瞬态压力测试系统中信号识别触发的设计与实现[J]. 火工品, 2016(1): 57-60.JIA Z H, WANG W L. Design and implementation of signal recognition trigger in transient pressure testing system[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2016(1): 57-60. [12] PRIOR M K. An optimization approach to the automatic identification of signals originating from underwater explosions[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2008, 123(5): 3900. [13] ZHA X, PENG H, QIN X, et al. A deep learning framework for signal detection and modulation classification[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19: 4042. [14] ZHONG M, MANUEL C, RAHUL D, et al. Beluga whale acoustic signal classification using deep learning neural network models[J]. J. Acoust. Soc. Am, 2020, 147(3): 1834-1841. doi: 10.1121/10.0000921 [15] JÚLIO d C V F, NATANAEL N d M J, JOSÉ M d S. Deep learning models for passive sonar signal classification of military data[J]. Remote Sens, 2022, 14: 2648. doi: 10.3390/rs14112648 [16] 王乾勋, 闫明, 杜志鹏, 等. 趋势项误差的低频极限特征理论模型与处理方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(12): 239-243.WANG Q X, YAN M, DU Z P, et al. Research on low-frequency limit characteristic theoretical model and processing method of trend item error[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(12): 239-243. [17] 徐卓飞, 刘凯. 基于极值符号序列分析的EMD端点效应处理方法[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2015, 35(2): 309-315, 400.XU Z F, Liu K. Endpoint effect handling method for EMD based on extremum sign sequence analysis[J]. Vibration, Testing and Diagnosis, 2015, 35(2): 309-315, 400. [18] 董晨懿, 陈梦英, 许伟杰, 等. 一种改进的水下爆炸冲击波信号修正方法[J]. 声学技术, 2022, 41(3): 376-381.DONG C Y, CHEN M Y, XU W J, et al. An improved correction method for underwater explosion shock wave signals[J]. Acoustic Technology, 2022, 41(3): 376-381. [19] STEVENS S S, VOLKMANN J, NEWMAN E B. The mel scale equates the magnitude of perceived differences in pitch at different frequencies[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1937, 8(3): 185-190. doi: 10.1121/1.1915893 [20] 伊鑫, 曲爱华. 基于Welch算法的经典功率谱估计的Matlab分析[J]. 现代电子技术, 2010, 33(3): 7-9.YI X, QU A H. Matlab analysis of classical power spectral density estimation based on welch algorithm[J]. Modern Electronic Technology, 2010, 33(3): 7-9. [21] 张志伟, 杨可林, 冯志常, 等. 基于小波包倒谱系数和ECAPA-TDNN的调度说话人确认研究[J]. 山东电力技术, 2023, 50(2): 52-57.ZHANG Z W, YANG K L, FENG Z C, et al. Research on speaker verification in power dispatching based on wavelet packet cepstral coefficient and ECAPA-TDNN[J]. Shandong Electric Power, 2023, 50(2): 52-57. [22] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. [23] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze and excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018: 7132-7141. [24] DESPLANQUES B, THIENPONDT J, DEMUYNCK K. ECAPA-TDNN: Emphasized channel attention, propagation and aggregation in TDNN based speaker verification[EB/OL]. (2020-05-15)[2023-10-10]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.07143v3. [25] 吴夙慧, 成颖, 郑彦宁, 等. K-means算法研究综述[J]. 现代图书情报技术, 2011(5): 28-35.WU S H, CHENG Y, ZHENG Y N, et al. A review of K-means algorithm research[J]. Modern Library and Information Technology, 2011(5): 28-35. -





 下载:
下载: