Control Method of Deep-Sea Vector Propulsion Motors Based on Position-Sensorless and Variable Carrier Frequency
-
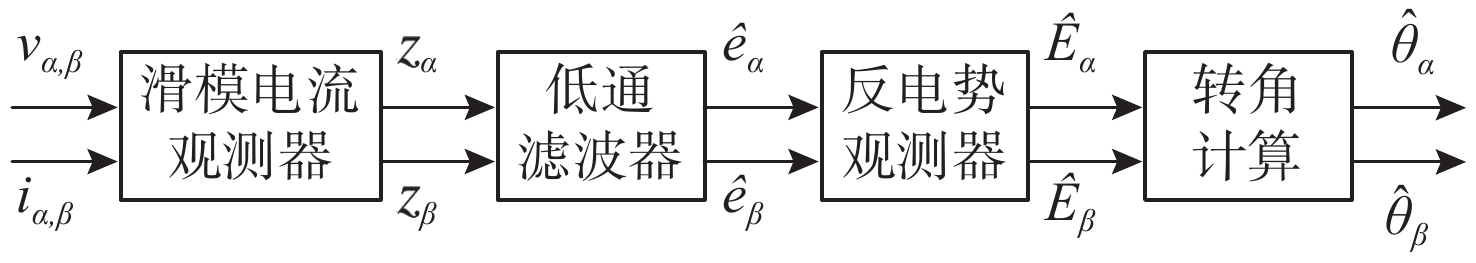
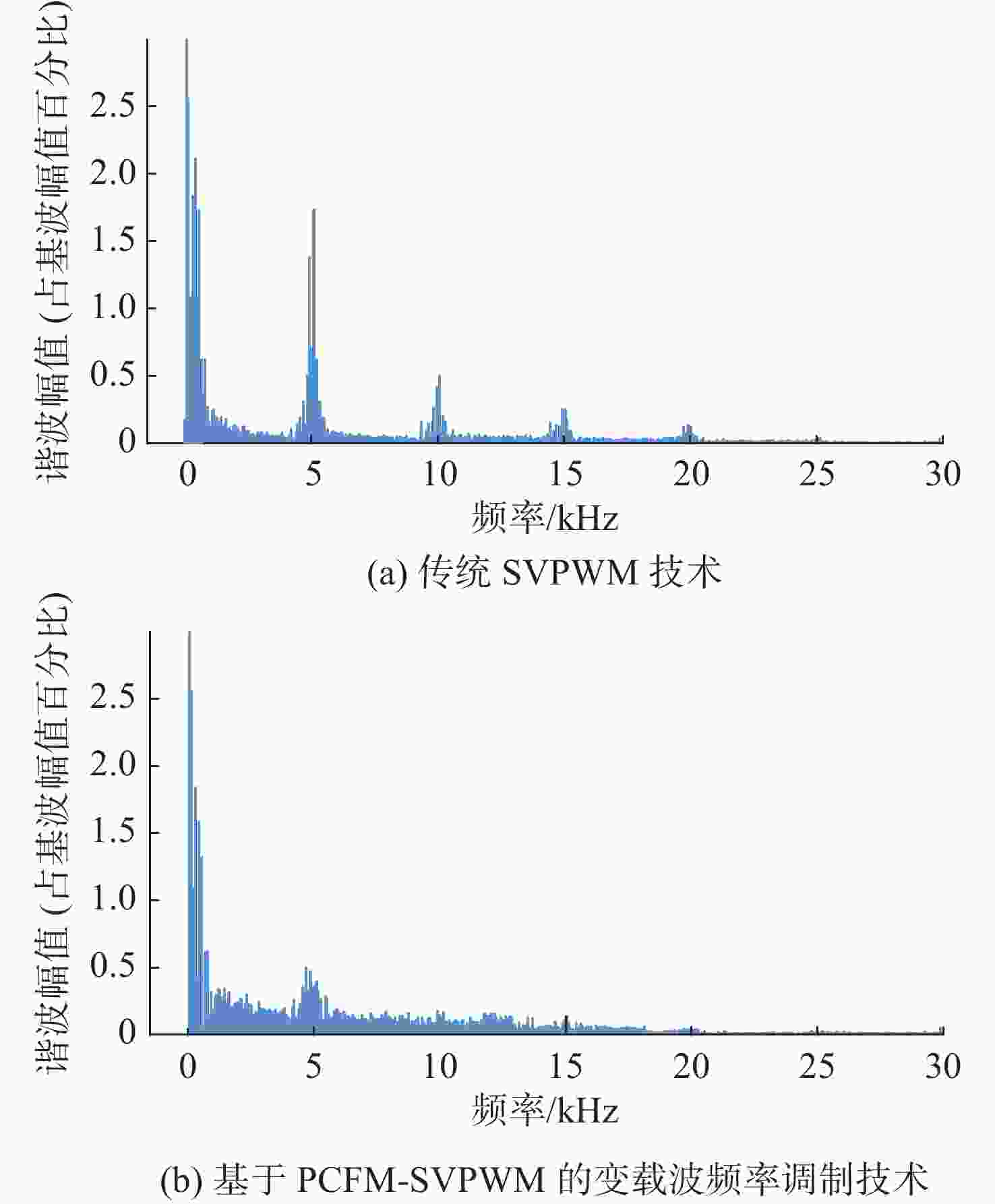
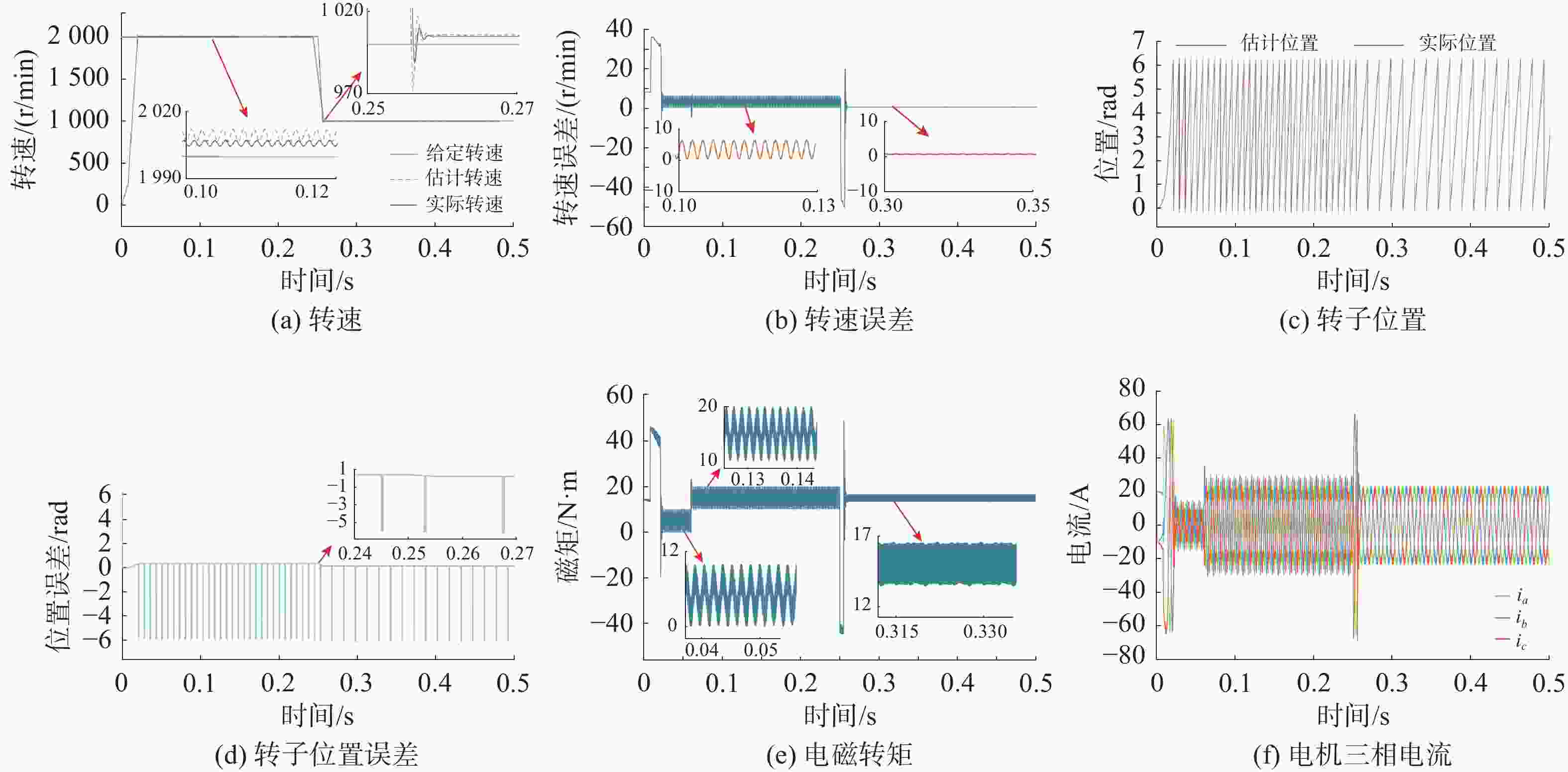
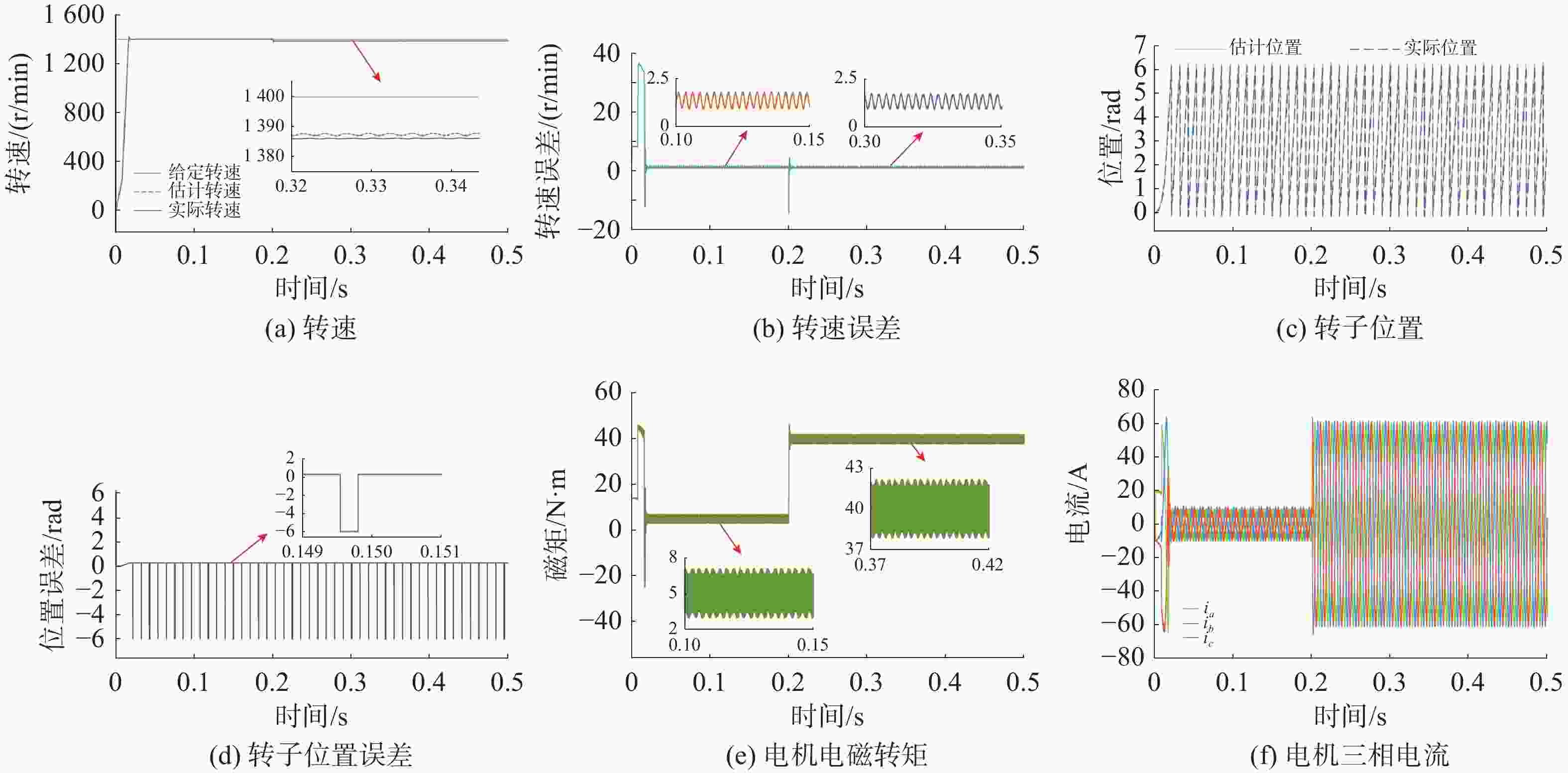
摘要: 为了提高矢量推进电机在深海探索中的稳定性与隐身性, 文中以表贴式永磁同步电机为基础, 结合周期扩频调制技术和改进型滑模观测器无位置控制技术, 提出了基于无位置变载波频率的深海矢量推进电机控制方法。通过电机变载波频率、电机起动变速和负载突变仿真实验, 验证所提控制方法的控制效果, 结果表明所研究控制方法转速估算准确, 对转速有良好的动态跟踪性能, 额定转速工况下转速估算误差率仅为0.32%, 0.5倍额定转速工况下转速估算误差率仅为0.09%, 且具有明显的高频谐波扩频抑制效果和良好的动态抗干扰性能。结合减少位置传感器带来的电机结构简化效果, 文中提出的控制方法可有效降低深海矢量推进电机作业时的故障率, 减少易被探测的高次固定频率谐波, 提高了深海矢量推进电机的可靠性与隐身性, 为深海UUV提供高效可靠的动力保障。Abstract: In order to improve the stability and stealth of vector propulsion motors in deep-sea exploration, a control method of deep-sea vector propulsion motors based on the position-sensorless and variable carrier frequency was derived from surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motors by using periodic spread spectrum modulation technology and position-sensorless control technology of improved sliding mode observer. Through simulations of motors’ variable carrier frequency, motor start-up speed variation, and sudden load change, the control effects of the proposed method were analyzed. The simulation results show that the rotation speed estimation of the studied control method is accurate, and the method has good dynamic tracking performance for rotation speed. The estimation error rate at the rated rotation speed is only 0.32%, and the estimation error rate at 0.5 times the rated rotation speed is only 0.09%. In addition, the proposed control method has an obvious high frequency harmonic spread spectrum suppression effect and good dynamic anti-interference performance. Combined with the simplification effect of reducing the motor structure brought by the position sensor, the control method proposed in this paper can effectively lower the failure rate of the deep-sea vector propulsion motor during operation, reduce the high-order fixed frequency harmonics that are easy to be detected, improve the reliability and stealth of the deep-sea vector propulsion motor, and provide efficient and reliable power guarantee for deep-sea unmanned undersea vehicles.
-
表 1 深海矢量推进电机参数
Table 1. Parameters of deep-sea vector propulsion motor
参数变量 数值 额定转速/(r·min−1) 2 000 极对数 4 定子电感/H 0.0 039 5 定子电阻/Ω 0.0 485 磁链/Wb 0.1 194 转动惯量/(kg·m2) 0.0 056 阻尼系数/(N·m·s) 0.0 000 1 表 2 电机起动变速试验观测转速试验数据分析表
Table 2. Analysis table of observational speed test data for motor starting and variable speed test
运行工况 上升/下降
时间/s超调量
/(r/min)速度
抖振观测
误差误差率
/%额定转速 0.015 15 0.25 6.4 0.32 0.5倍额定转速 0.003 10 0.005 0.9 0.09 -
[1] 史小锋, 党建军, 梁跃, 等. 水下攻防武器能源动力技术发展现状及趋势[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2021, 29(6): 634-647. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2021.06.001SHI X F, DANG J J, LIANG Y, et al. Development status and trend of energy and power technology for underwater attack and defensive weapon[J]. Journal of Undersea Unmanned Systems, 2021, 29(6): 634-647. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2021.06.001 [2] 许峻峰, 徐英雷, 冯江华, 等. 永磁同步电机直接转矩控制中定子磁链的分析[J]. 电气传动, 2005, 35(1): 10-12, 18.XU J F, XU Y L, FENG J H, et al. Analysis of the stator flux linkage in permanent magnet synchronous motor direct torque control[J]. Electric Drive, 2005, 35(1): 10-12, 18. [3] KIVANC O C, OZTURK S B. Sensorless PMSM drive based on stator feedforward voltage estimation improved with MRAS multi-parameter estimation[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2018, 23(3): 1326-1337. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2018.2817246 [4] 尹忠刚, 张瑞峰, 钟彦儒, 等. 基于抗差扩展卡尔曼滤波器的永磁同步电机转速估计策略[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2012, 29(7): 921-927.YIN Z G, ZHANG R F, ZHONG Y R, et al. Speed estimation for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on robust extended Kalman filter[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2012, 29(7): 921-927. [5] 刘金琨, 孙富春. 滑模变结构控制理论及其算法研究与进展[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2007, 24(3): 407-418.LIU J K, SUN F C. Research and development on theory and algorithms of sliding mode control[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2007, 24(3): 407-418. [6] 赵峰, 罗雯, 高锋阳, 等. 基于模糊滑模控制器和两级滤波观测器的永磁同步电机无位置传感器混合控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(8): 1865-1872. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90781ZHAO F, LUO W, GAO F Y, et al. Sensorless hybrid control for permanent magnet synchronous motor using fuzzy sliding mode controller and two-stage filter observer[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(8): 1865-1872. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90781 [7] HAN T G, YANG X, FANG Q B, et al. Observer-based sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motor for electrical vehicle[C]//2016 4th International conference on applied robotics for the power industry. Jinan, China: CARPI, 2016. [8] 郑雪梅, 李秋明, 史宏宇, 等. 用于永磁同步电机的一种非奇异高阶终端滑模观测器[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2011, 28(10): 1467-1472.ZHENG X M, LI Q M, SHI H Y, et al. Higher-order nonsingular terminal-sliding-mode observer for permanent-magnet synchronous motor[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2011, 28(10): 1467-1472. [9] LIANG W, WANG J, LUK C K, et al. Analytical modeling of current harmonic components in PMSM drive with Voltage-Source inverter by SVPWM technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2014, 29(3): 673-680. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2014.2317072 [10] GAMOUDI R, CHARIAG D E, SBITA L. A review of spread-spectrum-based PWM techniques—a novel fast digital implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 33(12): 10292-10307. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2018.2808038 [11] XU Y X, YUAN Q B, ZOU J B, et al. Periodic carrier frequency modulation in reducing low frequency electromagnetic interference of permanent magnet synchronous motor drive system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2015, 51(11): 1-4. [12] 黄惠东. 三电平逆变器PWM谐波高效抑制策略研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. -




 下载:
下载: