Laser Transmission Characteristics of Wake Bubble Curtain
-
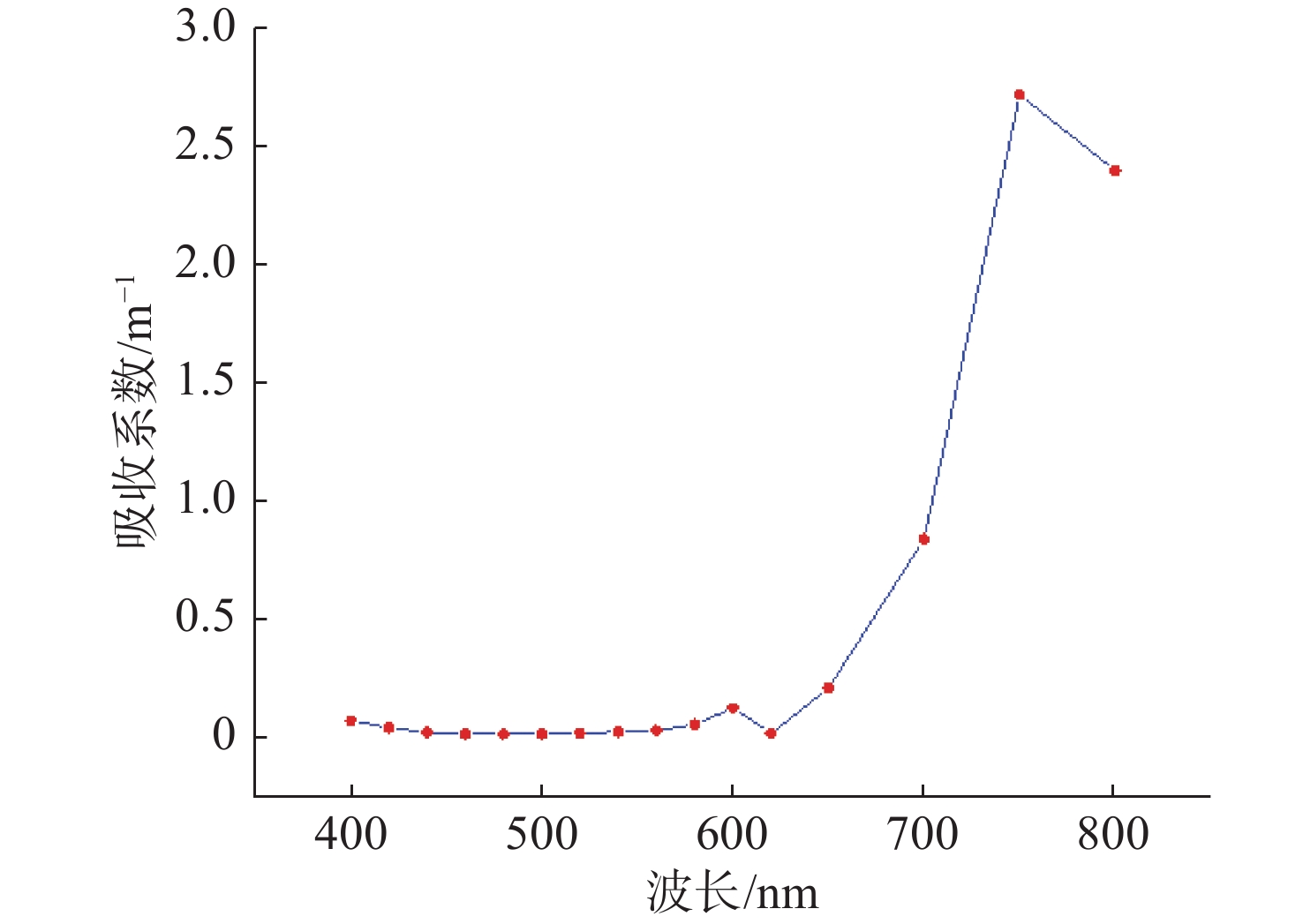
摘要: 舰船在航行过程中会产生尾流区域, 激光穿过气泡尾流区域时会发生散射现象, 通过对散射光的探测和分析, 能够实现检测与识别舰船的目的。文中研究了尾流气泡幕对激光传输特性的影响, 并利用光纤光谱仪探测了尾流气泡幕的光强变化。实验仿真了不同压强下的尾流气泡幕在距离水面5、15和20 cm, 气泡幕厚度分别为10、15 cm时的光强变化, 并探讨了前向散射和后向散射的光强随压强的变化情况。仿真实验结果表明, 随着压强的增大, 光强变化逐渐降低, 气泡浓度与半径也随之增大; 气泡浓度越大, 光强变化越小; 随着压强的增大, 前向散射光强逐渐呈线性降低, 而后向散射光强则会随之增大。Abstract: In the process of navigation, the ship will produce the wake region, and the scattering phenomenon occurs when the laser passes through the wake region of the bubble. Through the detection and analysis of the scattered light, the ship can be detected and identified. In this paper, the influence of the wake bubble curtain on laser transmission characteristics was investigated, and the light intensity changes of the wake bubble curtain were detected based on a fiber optic spectrometer. The experiment simulated the light intensity change of the wake bubble curtain with a thickness of 10 cm and 15 cm under different pressures at 5, 15, and 20 cm away from the water surface and explored the variation of intensity of forward and backward scattered light with pressure. The experimental results show that with the increases in pressure, the variation of light intensity slows down, and the concentration and the radius of the bubble increase. Higher bubble concentration indicates a smaller variation of light intensity. With the increase in pressure, the intensity of forward scattered light decreases linearly, and the intensity of backward scattered light increases.
-
Key words:
- wake bubble curtain /
- scattered light /
- bubble concentration
-
表 1 实验仪器型号及参数
Table 1. Models and parameters of experimental instruments
仪器 型号/参数 微型光谱仪 Flame-S-UV-UIS-ES Oceanview V. 1.6.7 光纤探头 QP600-2-UV-UIS 长2 m He-Ne 激光器 波长632.8 nm 微孔陶瓷管 外径68 mm、内径30 mm、长750 mm、膜孔径10 μm 高压气泵 550W-8L 玻璃水池 高80 cm、宽80 cm、长160 cm、厚12 mm -
[1] 冀邦杰, 王海陆, 严由嵘, 等. 一种利用激光波前变化检测尾流场的方法[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2009, 17(2): 25-28.JI B J, WANG H L, YAN Y R, et al. The invention relates to a method for detecting wake field by using laser wave front change[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2009, 17(2): 25-28. [2] 王羽佳, 宗思光, 张鑫. 基于Mie散射特性的微气泡激光探测仿真与实验研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2022, 42(5): 150-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.05.033WANG Y J, ZONG S G, ZHANG X. Simulation and experimental study of microbubble laser detection based on Mie scattering characteristics[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2022, 42(5): 150-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.05.033 [3] 冀邦杰, 周德善, 张建生. 基于舰船尾流光效应的制导鱼雷[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2000, 8(3): 40-43.JI B J, ZHOU D S, ZHANG J S. Guided torpedo based on ship wake light effect[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2000, 8(3): 40-43. [4] 马治国, 王江安, 石晟玮. 水中气泡激光后向散射衰减特性研究[J]. 激光与红外, 2008(1): 14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2008.01.004MA Z G, WANG J A, SHI S W. Optical of simulated wake in laboratory[J]. Laser and Infrared, 2008(1): 14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2008.01.004 [5] ARNOTT W P, MARSTON P L. Optical glory of small freely rising gas bubbles in water: observed and computed cross-polarized backscattering patterns[J]. JOSA A, 1988, 5(4): 496-506. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.5.000496 [6] LANGLEY D S, MARSTON P L. Forward glory scattering from bubbles[J]. Applied Optics, 1991, 30(24): 3452-8. doi: 10.1364/AO.30.003452 [7] ARNOTT W P, MARSTON P L. Unfolded optical glory of spheroids: backscattering of laser light from freely rising spheroidal air bubbles in water[J]. Applied Optics, 1991, 30(24): 3429-3442. doi: 10.1364/AO.30.003429 [8] TAKAHASHI K, OHUCHI S, SAITO K, et al. Simultaneous determination of the size and concentration of fine bubbles in water by laser-light scattering[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(2): 225-229. [9] 张建生. 实验室模拟尾流的光学研究[J]. 光子学报, 2001(9): 1146-1149.ZHANG J S. Optical study of simulated wake in laboratory[J]. Journal of Photonics, 2001(9): 1146-1149 [10] 张裕士, 田贵才. 微气泡激光散射特性研究[J]. 通化师范学院学报, 2007(4): 3-5.ZHANG Y S, TIAN G C. Study on laser scattering characteristics of micro bubbles[J]. Journal of Tonghua Normal University, 2007(4): 3-5. [11] 张家利, 张建生, 文丽. 舰船尾流气泡后向光散射特性研究[J]. 科技资讯, 2010(33): 8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2010.33.007ZHANG J L, ZHANG J S, WEN Li. Study on back scattering characteristics of ship wake bubbles[J]. Science and technology information, 2010(33): 8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2010.33.007 [12] 孙建鹏, 张建生, 陈焱. 淡水和盐水中模拟气泡幕前向光散射特性[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(1): 31-36.Sun Jian-Peng, Zhang Jian-Sheng, Cheng Yan. Light scattering properties in front of simulated bubble curtain in fresh and salt water[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 44(1): 31-36. [13] 李能能. 船舶尾流模拟气泡的前向光散射特性研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2018, 40(16): 16-18.Li Neng-Neng. Study on forward light scattering charac- teristics of simulated bubbles in ship wake[J]. Ship Sci- ence and Technology, 2018, 40(16): 16-18. [14] 宗思光, 张鑫, 梁善永, 曹静. 多尺度复杂水质尾流气泡的激光探测仿真与实验[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50(5): 71-81.Zun Si-Guang, Zhang Xin, Liang Xiong-san, Cao Jin. Simulation and experiment of multi-scale complex water wake bubble detection by laser[J]. Chinese Laser, 2023, 50(5): 71-81. [15] 吕德华. 基于大气传输的船舶尾流气泡幕成像特性研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2021. [16] 张建生, 刘建康, 冀邦杰, 孙传东. 尾流气泡幕光学特性的数理模型[J]. 光子学报, 2002(8): 1032-1036.Zhang Jian-Sheng, Liu Jian-Kang, Ji Bang-Jian, Sun Chuan-Dong. Mathematical model of optical properties of wake bubble curtain[J]. Journal of Photonics, 2002(8): 1032-1036. [17] 林宏. 海洋悬浮粒子的米氏散射特性及布里渊散射特性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2007. [18] 张建生. 尾流的光学特性研究与测量[D]. 西安: 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所, 2001. -





 下载:
下载: