High-Precision Three-dimensional Reconstruction of Deep-Sea Microtopography Based on Monocular Camera
-
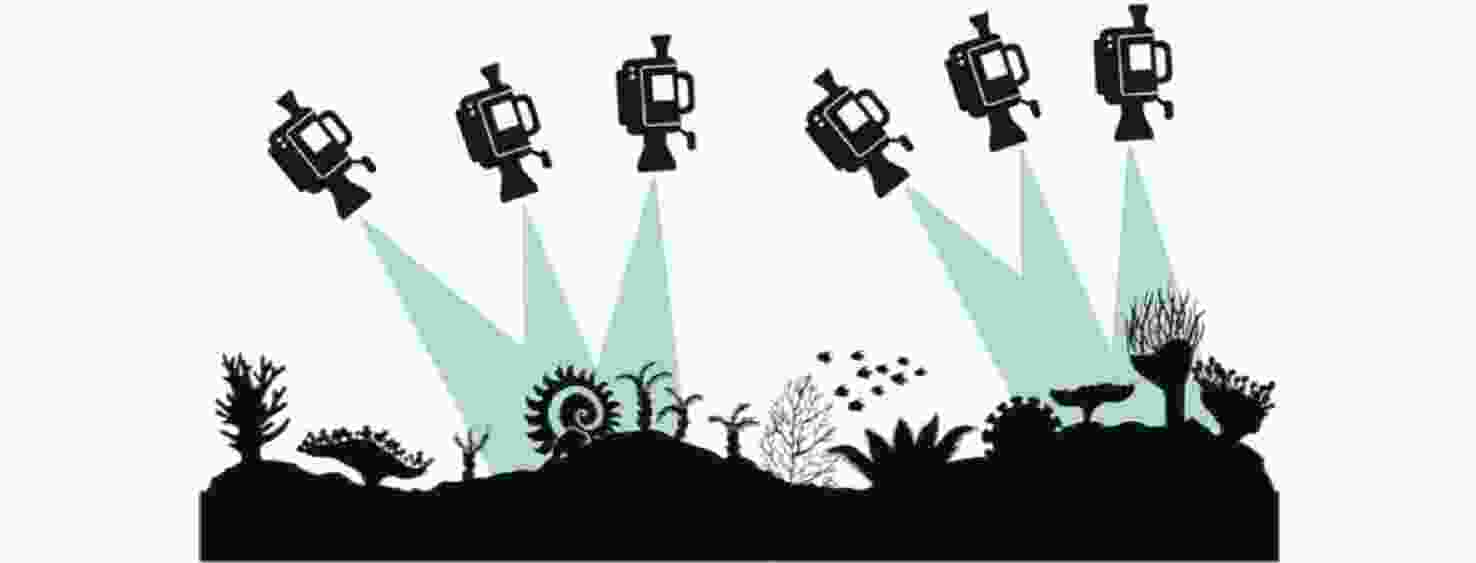
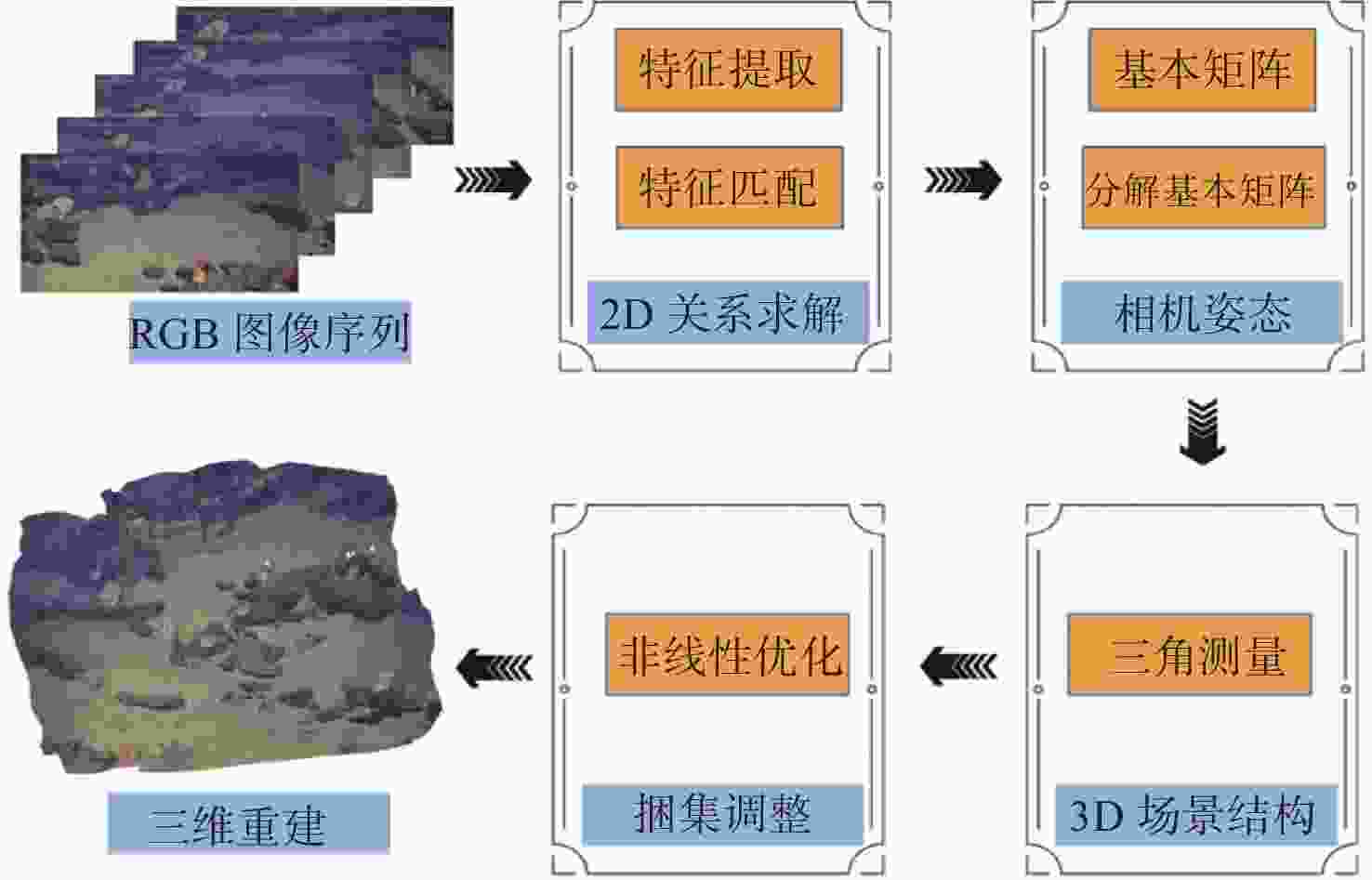
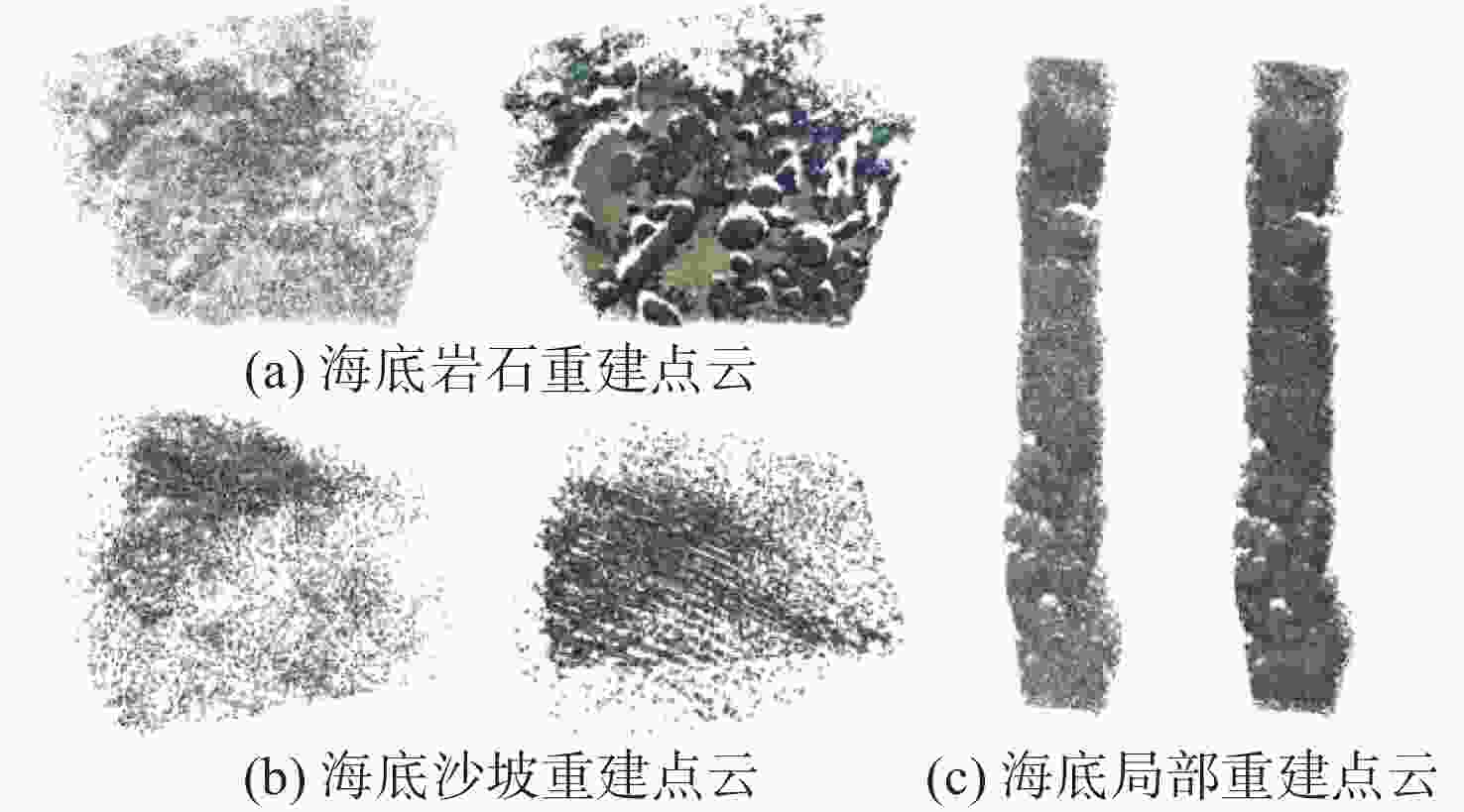
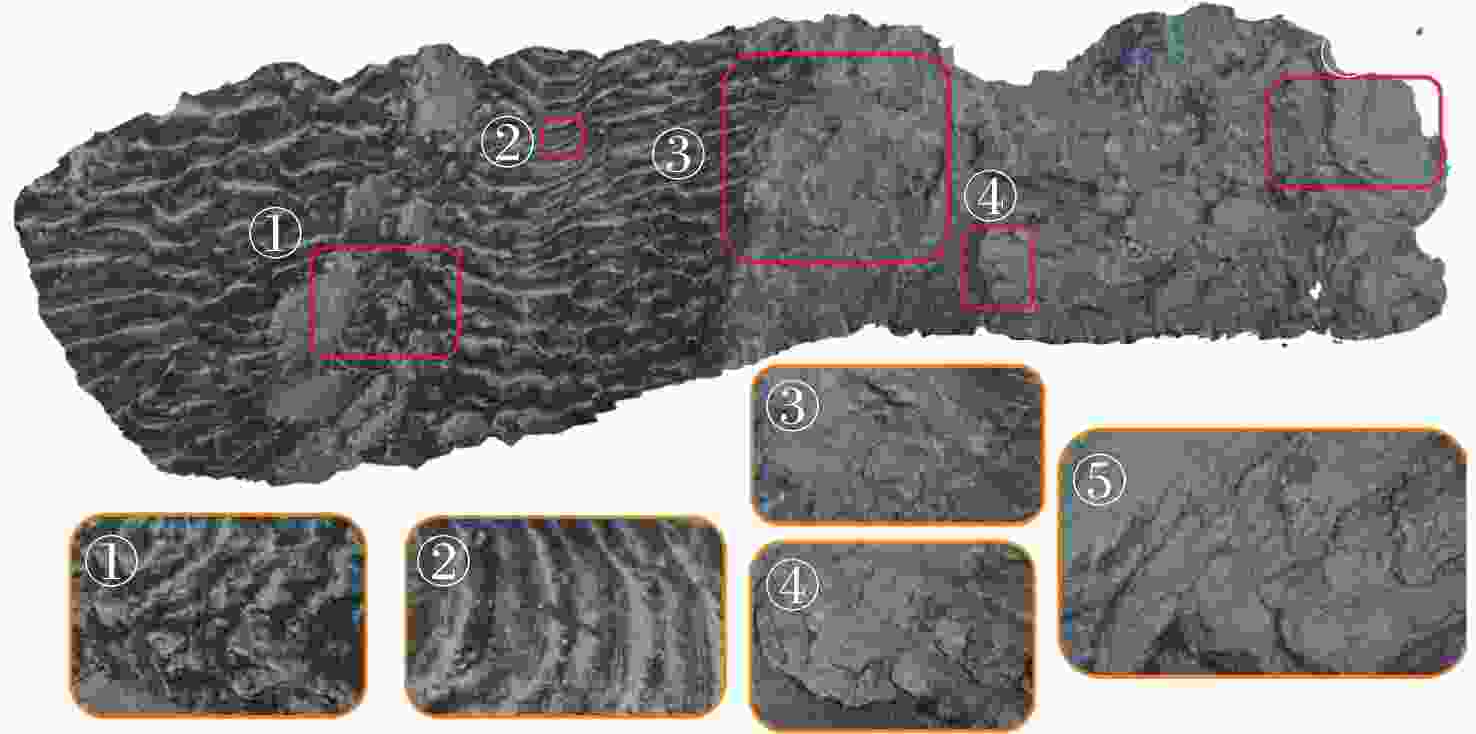
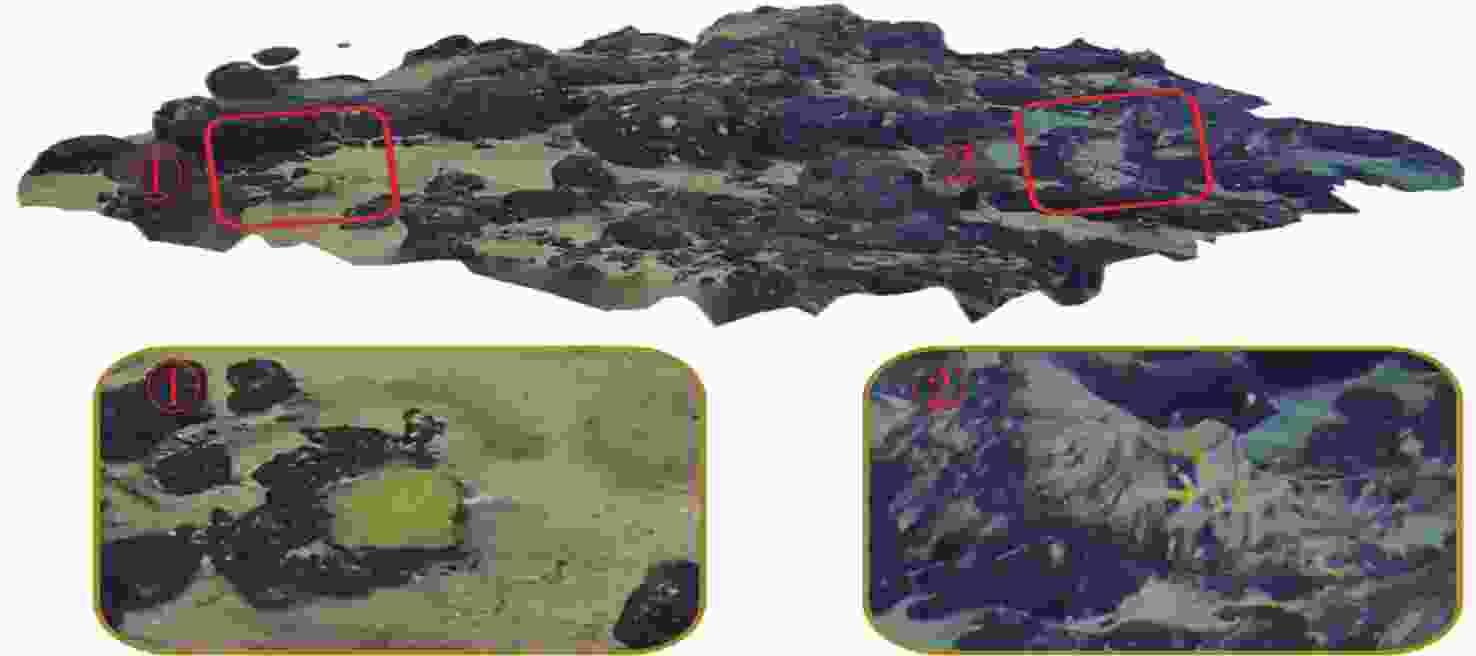
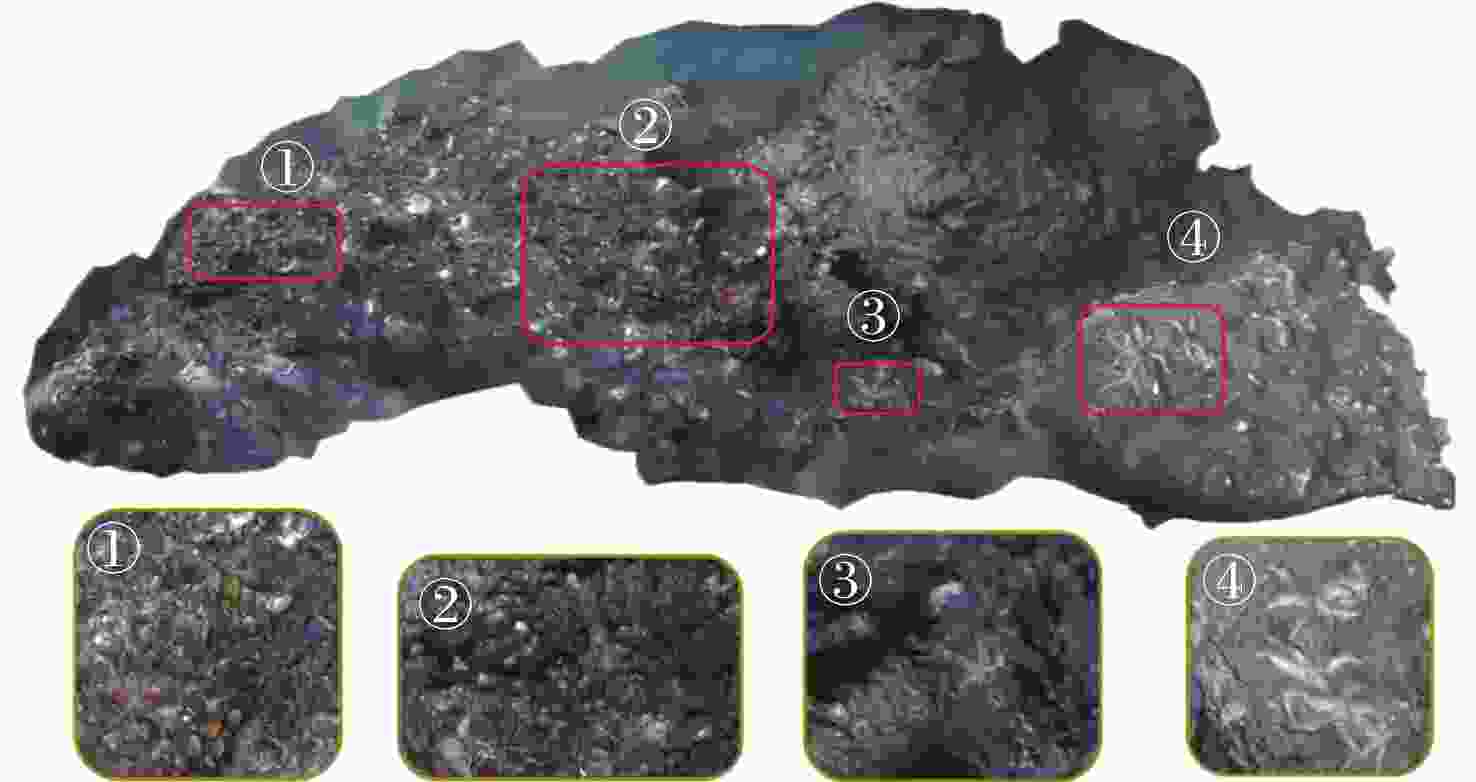
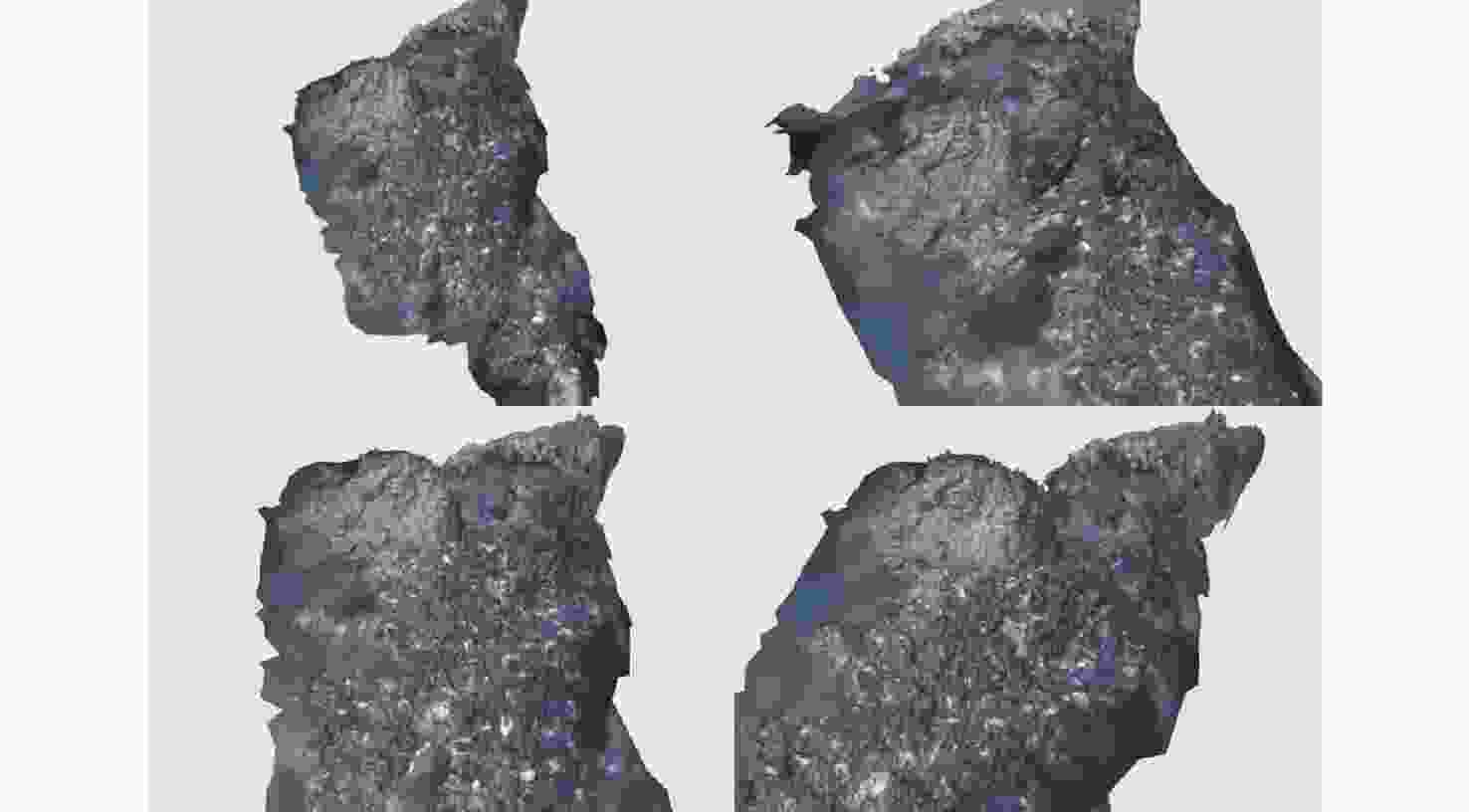
摘要: 在深海矿产资源勘查和极端环境探测中, 利用光学相机搭载水下移动平台获取海底的光学影像资料成为当前深海精细探测的重要方式。文中针对深海微地形地貌的高精度探测需求, 开展了基于单目相机的深海微地形地貌高精度三维重建方法研究。通过水下遥控航行器搭载的单目相机, 获取了我国海域水合物赋存区的大量图像, 基于此, 利用运动恢复结构方法建立了典型海域内沙波区、碳酸盐岩区和冷泉区的海底三维模型, 精细刻画出区域内的地形地貌特征和生物生态信息。研究结果表明, 文中方法可为深海表生矿产资源勘查和极端环境探测提供重要支撑。Abstract: In the exploration of deep-sea mineral resources and detection of extreme environments, the use of optical cameras mounted on mobile underwater platforms to obtain optical image data of the seafloor now becomes an important method of deep-sea fine detection. To meet the demand for high-precision detection of deep-sea microtopography, the high-precision three-dimensional(3D) reconstruction method of deep-sea microtopography based on a monocular camera was studied. The monocular camera mounted on the underwater remotely operated vehicle acquired many images of the hydrate-rich areas in China waters. On this basis, the 3D seafloor models of the sand wave area, carbonate rock area, and cold spring area in the typical sea area were constructed using the structure from motion(SFM) method, and the topographic and geomorphological features and bio-ecological information were finely delineated. The results show that this method can provide important support for the exploration of deep-sea epigenetic mineral resources and the detection of extreme environments.
-
表 1 重建结果相关参数
Table 1. Relevant parameters for reconstruction results
点云模型 稀疏重建
点云数密集重建后
点云数平均重投影
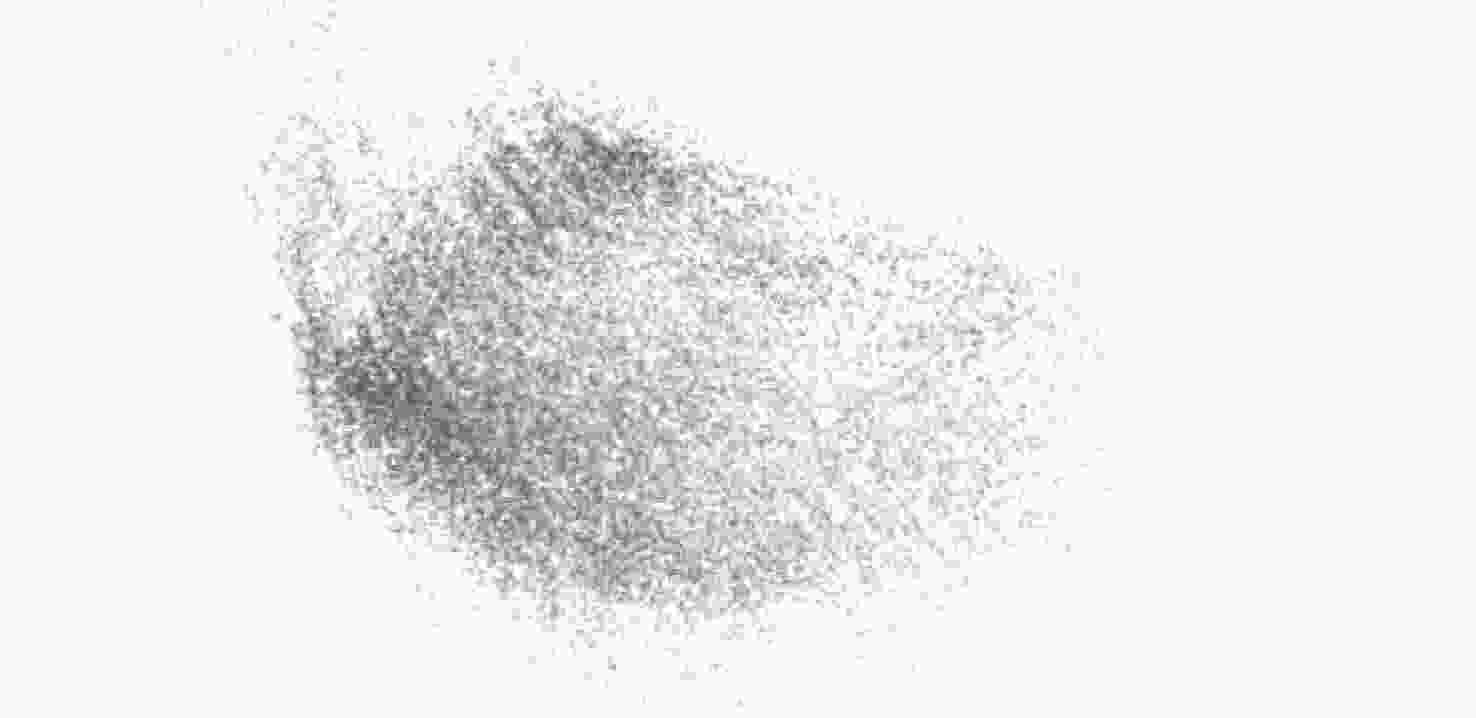
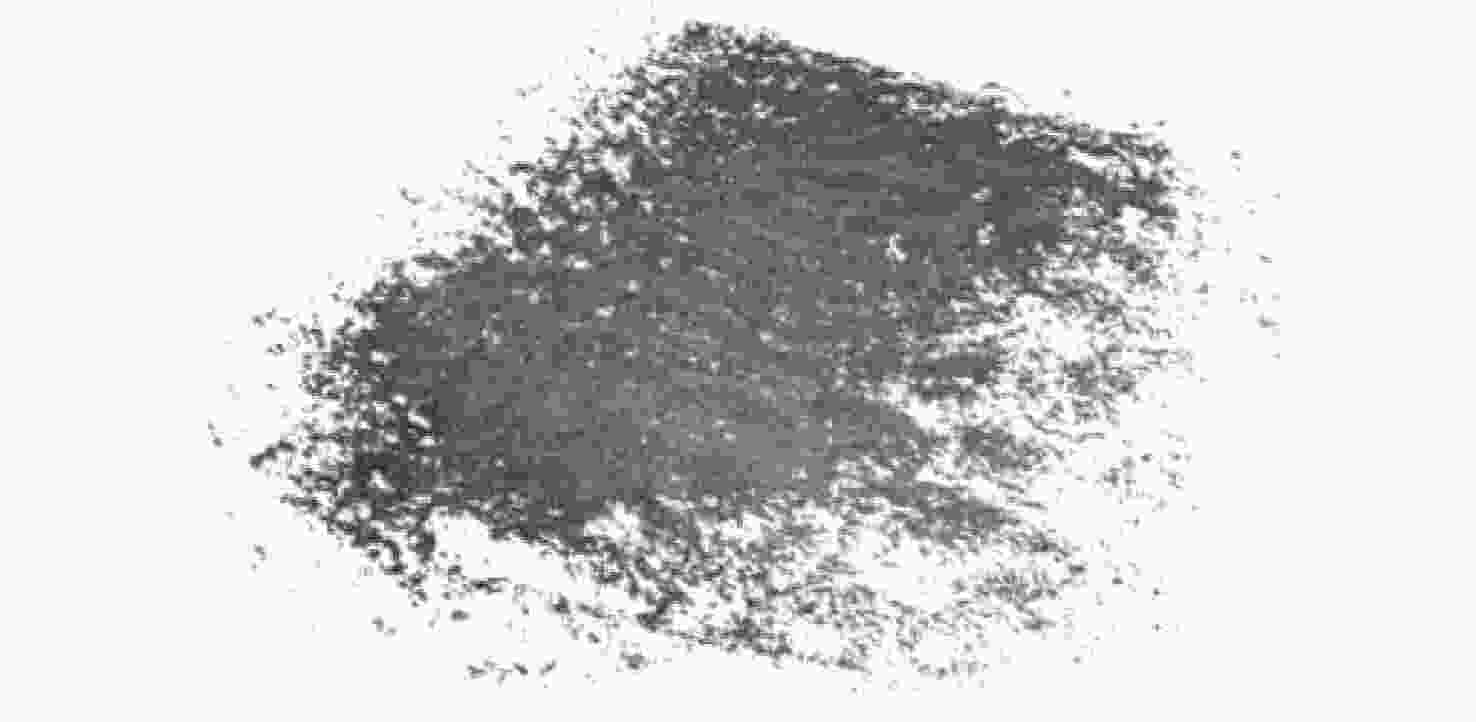
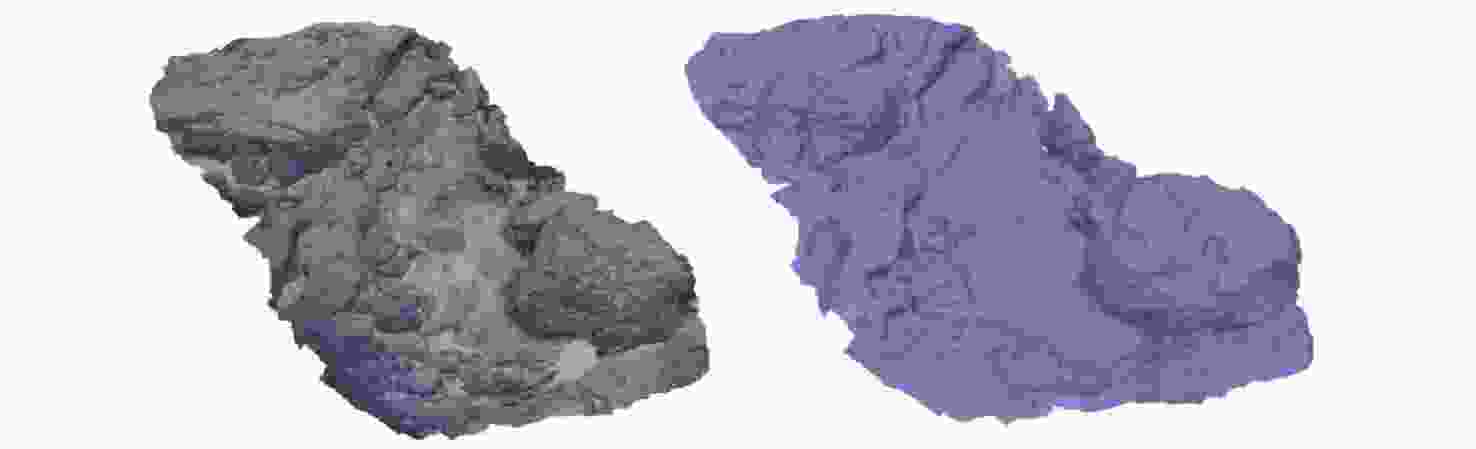
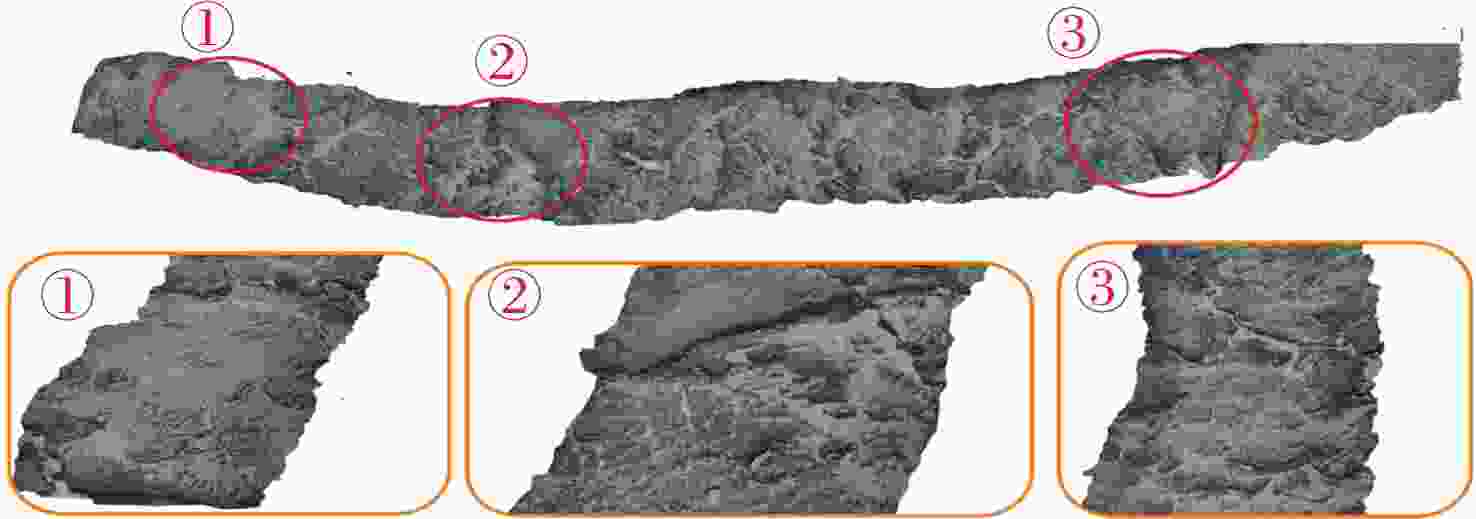
误差海底岩石重建点云 44 839 961 746 0.18 海底沙坡重建点云 22 053 760 421 0.21 海底局部重建点云 94 612 1 346 101 0.12 表 2 不同算法的三维重建评估指标
Table 2. 3D reconstruction evaluation indexes for different algorithms
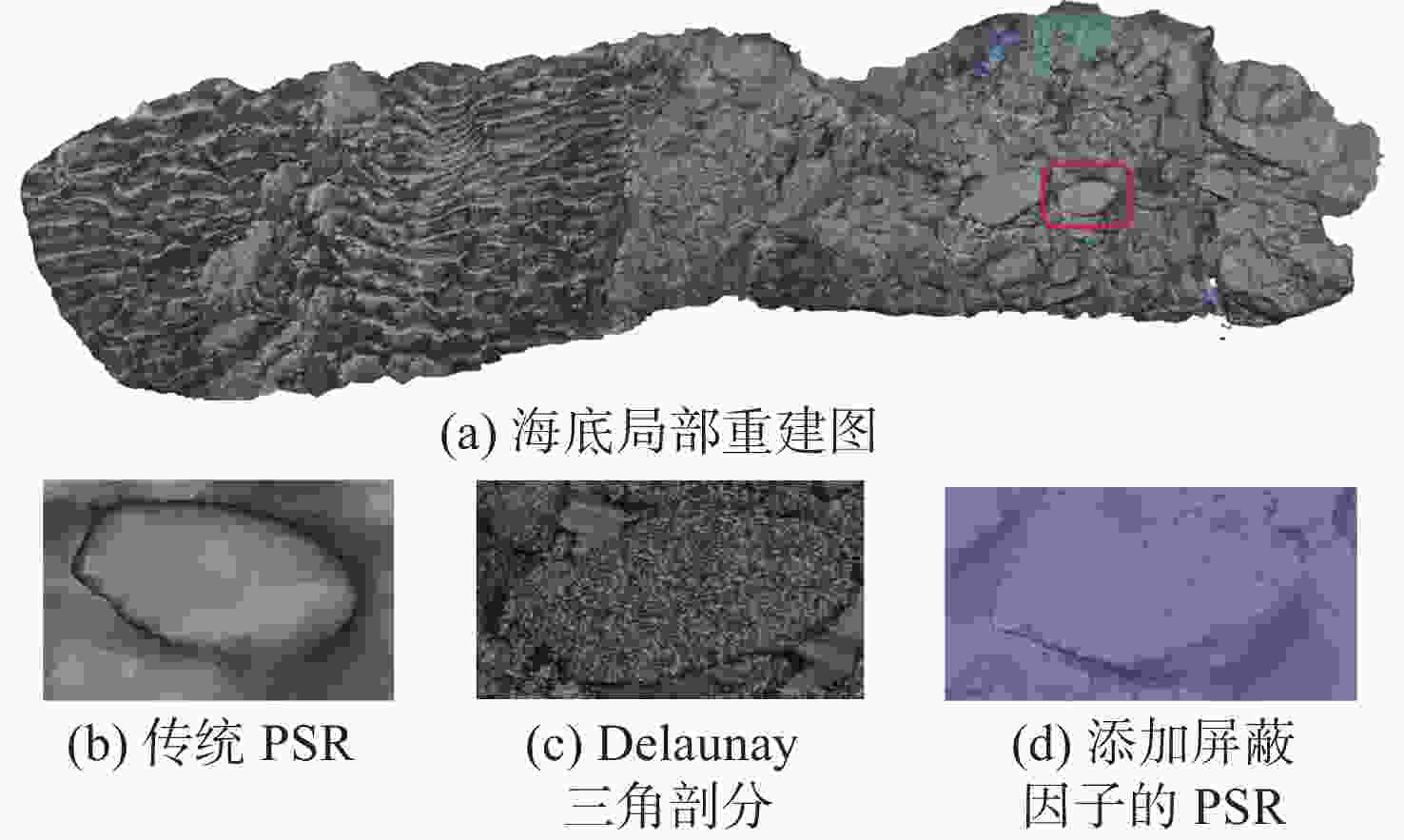
重建评估指标 传统PSR Delaunay
三角剖分添加屏蔽
因子的PSR最大偏差/mm 0.16 0.13 0.11 平均偏差距离/mm 0.08 0.07 0.06 标准偏差/mm 0.09 0.06 0.07 均方根误差/mm 0.11 0.08 0.06 重建所需时间/s 680 322 486 -
[1] 王新伟, 孙亮, 王敏敏, 等. 水下二维及三维距离选通成像去噪技术研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(2): 15-25.Wang Xinwei, Sun Liang, Wang Minmin, et al. Deblurring methods for underwater 2D and 3D range-gated imaging[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(2): 15-25. [2] 范承成, 德晓薇, 郭金家, 等. 基于三角位移法姿态矫正的激光线扫描海底地形三维测绘[J]. 光学精密工程, 2022, 30(10): 1170-1180. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223010.1170Fan Chengcheng, De Xiaowei, Guo Jinjia, et al. 3D mapping of submarine topography by laser line scanning based on pose correction by triangular displacement method[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(10): 1170-1180. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223010.1170 [3] 徐国权, 李广英, 万建伟, 等. 脉冲调制激光雷达水下成像系统[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51(3): 264-271.Xu Guoquan, Li Guangying, Wan Jianwei, et al. Underwater imaging system of pulse modulated lidar[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(3): 264-271. [4] 谢亮亮, 屠大维, 张旭, 等. 深海原位激光扫描双目立体视觉成像系统[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2020, 41(6): 106-114.Xie Liangliang, Tu Dawei, Zhang Xu, et al. Deep sea in-situ binocular stereo vision imaging system with laser scanning[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2020, 41(6): 106-114. [5] Bayley D T I, Mogg A O M. A protocol for the largescale analysis of reefs using structure from motion photogrammetry[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2020, 11(11): 1410-1420. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13476 [6] Ham H, Wesley J, Hendra H. Computer vision based 3D reconstruction: A review[J]. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2019, 9(4): 2394. [7] Gonçalves J A, Henriques R. UAV photogrammetry for topographic monitoring of coastal areas[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 104: 101-111. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.02.009 [8] Ryan J C, Hubbard A L, Box J E, et al. UAV photogrammetry and structure from motion to assess calving dynamics at Store Glacier, a large outlet draining the Greenland ice sheet[J]. The Cryosphere, 2015, 9(1): 1-11. doi: 10.5194/tc-9-1-2015 [9] Woodget A S, Carbonneau P E, Visser F, et al. Quantifying submerged fluvial topography using hyperspatial resolution UAS imagery and structure from motion photogrammetry[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2015, 40(1): 47-64. doi: 10.1002/esp.3613 [10] Niethammer U, James M R, Rothmund S, et al. UAV-based remote sensing of the Super-Sauze landslide: Evaluation and results[J]. Engineering Geology, 2012, 128: 2-11. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.03.012 [11] Castillo C, Pérez R, James M R, et al. Comparing the accuracy of several field methods for measuring gully erosion[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2012, 76(4): 1319-1332. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2011.0390 [12] Robert K, Huvenne V A I, Georgiopoulou A, et al. New approaches to high-resolution mapping of marine vertical structures[J]. Scientific reports, 2017, 7(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x [13] Teague J, Miles J, Connor D, et al. Exploring offshore hydrothermal venting using low-cost ROV and photogrammetric techniques: A case study from Milos Island, Greece[EB/OL]. (2017-10-03)[2023-05-01]. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints201710.0014.v2. [14] Wright A E, Conlin D L, Shope S M. Assessing the accuracy of underwater photogrammetry for archaeology: A comparison of structure from motion photogrammetry and real time kinematic survey at the east key construction wreck[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2020, 8(11): 849. doi: 10.3390/jmse8110849 [15] Burns J H R, Delparte D, Gates R D, et al. Integrating structure-from-motion photogrammetry with geospatial software as a novel technique for quantifying 3D ecological characteristics of coral reefs[EB/OL]. PeerJ, (2016-08-01)[2023-07-03]. https://www.docin.com/p-1693845315.html [16] 李硕, 刘健, 徐会希, 等. 我国深海自主水下机器人的研究现状[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2018, 48(9): 1152-1164. doi: 10.1360/N112017-00264Li Shuo, Liu Jian, Xu Huixi, et al. Research status of autonomous underwater vehicles in China[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2018, 48(9): 1152-1164. doi: 10.1360/N112017-00264 [17] Furukawa Y, Ponce J. Accurate, dense, and robust multiview stereopsis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 32(8): 1362-1376. [18] Kazhdan M, Bolitho M, Hoppe H. Poisson surface reconstruction[C]//Proceedings of the Fourth Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing(SGP). Cagliari, Sardinia, Italy: [s.n.], 2006: 61-70. [19] 何家雄, 钟灿鸣, 姚永坚, 等. 南海北部天然气水合物勘查试采及研究进展与勘探前景[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(12): 1-14. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2020.127He Jiaxiong, Zhong Canming, Yao Yongjian, et al. The exploration and production test of gas hydrate and its research progress and exploration prospect in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geological Frontiers, 2020, 36(12): 1-14. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2020.127 [20] 张伟, 梁金强, 何家雄, 等. 南海北部陆坡泥底辟/气烟囱基本特征及其与油气和水合物成藏关系[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(7): 11-23. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2017.07002Zhang Wei, Liang Jinqiang, He Jiaxiong, et al. Characteristics of mud diapir and gas chimney and their relationship with reservoir forming for petroleum and national gas hydrate on northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geological Frontiers, 2017, 33(7): 11-23. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2017.07002 -





 下载:
下载: