Underwater Detection Method of Highly Conductively Targets Based on Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Method
-
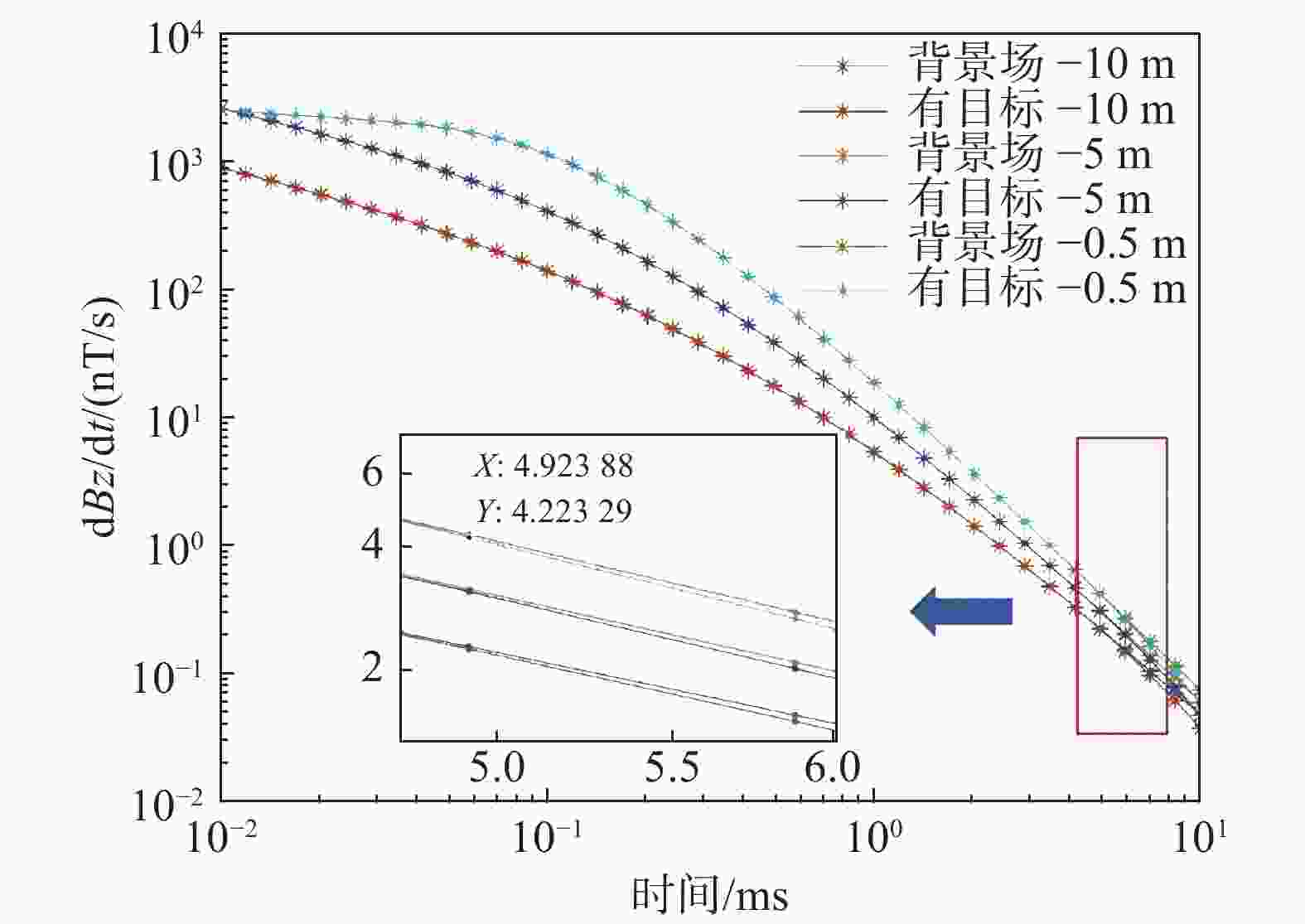
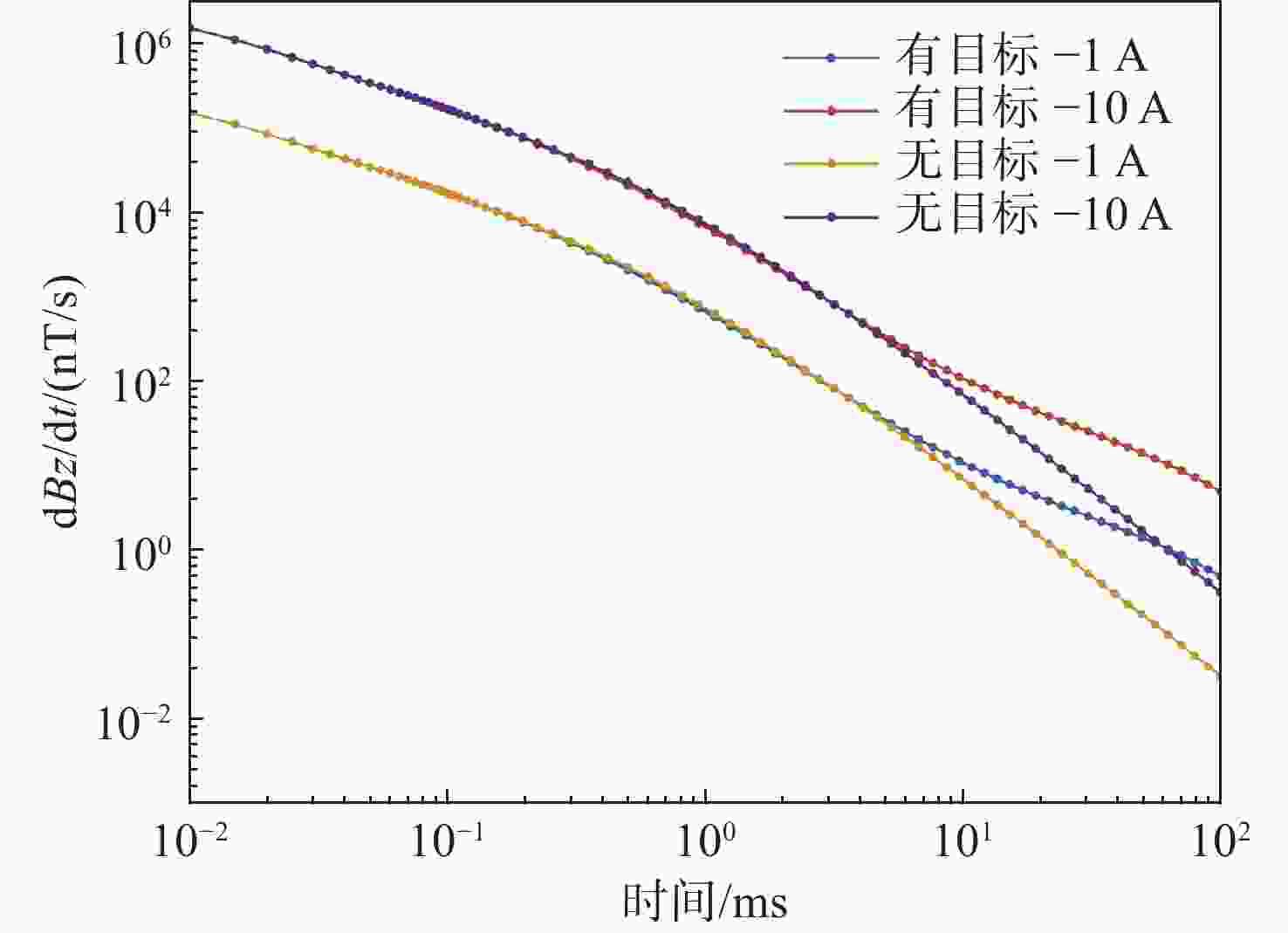
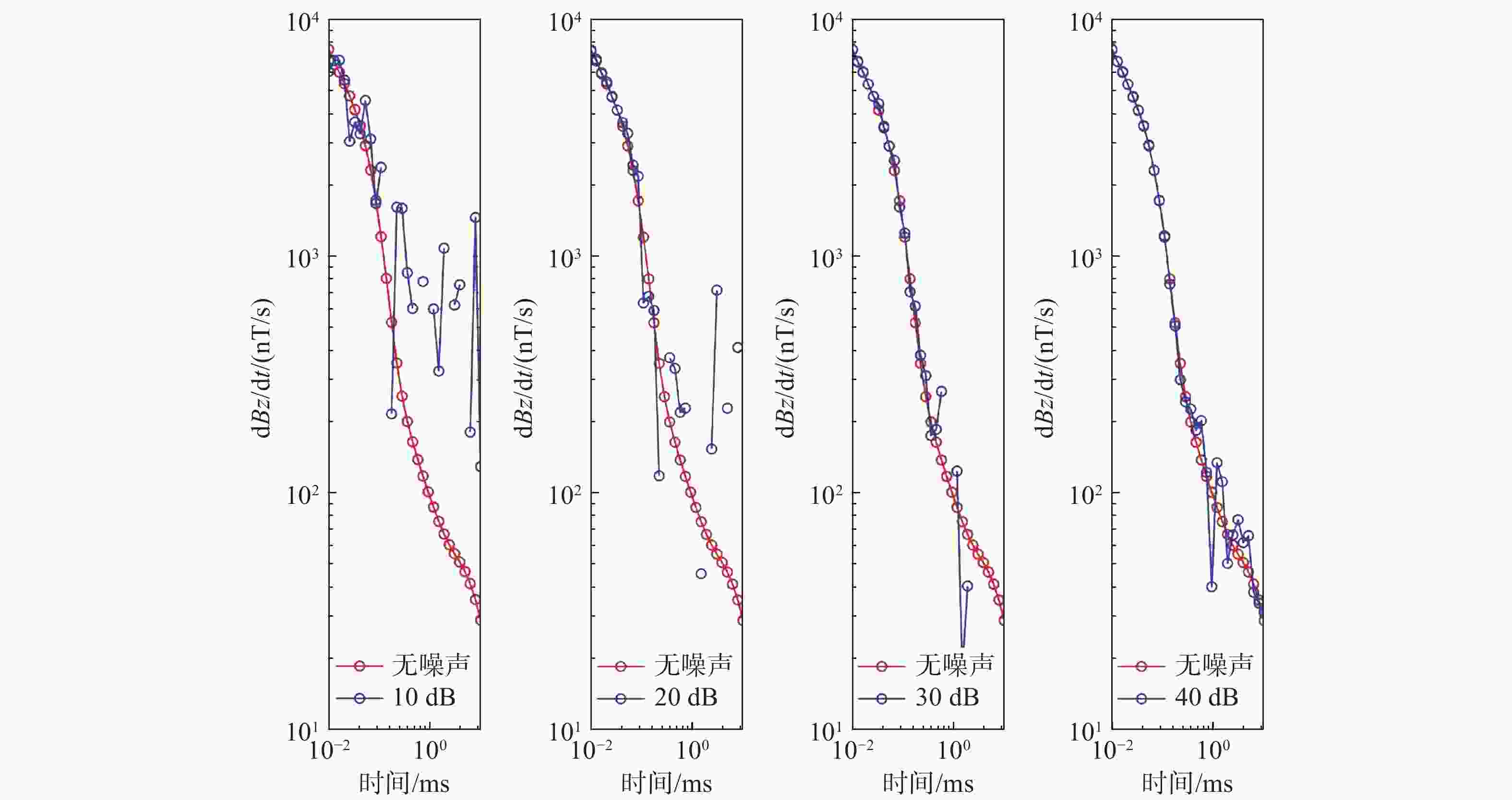
摘要: 随着声、磁隐身技术的快速发展, 主流的声探测和被动磁探测效能大幅降低。经典的航空瞬变电磁法凭借主动探测、对高导体敏感及探测速度快等优势, 在水下高导体目标探测领域极具潜力。文中从航空瞬变电磁法原理出发, 基于圆形中心回线装置形式求得时间域垂直磁场响应公式, 通过构建海水—高导电层—海水—海底岩石层状模型, 研究了不同目标层深度及不同收发高度下一维模型中垂直磁场响应特征; 并基于三维时域有限体积法对水下高导长方体进行正演计算, 获得接收线圈中心处dBz/dt的衰减曲线。一、三维仿真结果均表明: 当海水中存在高导电率目标体时, 其垂直磁场响应特征与无目标存在时有明显差异。反演成像中, 利用高斯白噪声合成不同信噪比的仿真数据, 结合OCCAM反演算法对水下目标体进行一维计算, 对比不同信噪比下水中目标检测效果。结果显示: 当信噪比大于等于10 dB时, 水中存在的高导电层可以被有效检测; 当达到40 dB时, 高导电层的深度及厚度信息也有较好地判断。最后, 在40 dB的信噪比下, 将高导电层电阻率值按比例减小, 发现该方法仍对目标层的深度信息有明显的反应。综合以上正演及反演计算过程, 有效验证了该方法在水下高导体探测领域的可行性。Abstract: With the rapid development of acoustic and magnetic stealth technology, the effectiveness of mainstream acoustic detection and passive magnetic detection has been greatly reduced. The classical airborne transient electromagnetic method(ATEM), with the advantages of active detection, sensitivity to highly conductive targets, and high detection speed, has great potential in the field of underwater detection of highly conductive targets. Based on the principle of the airborne transient electromagnetic method, this paper obtained the vertical magnetic field response formula in the time domain based on the form of a circular central loop device and studied the vertical magnetic field response characteristics in the one-dimensional model with different depths of the target layer and different transmitting and receiving heights by constructing the layered model of seawater-highly conductive layer–seawater–seabed rock. Based on the three-dimensional time domain finite volume method, the forward calculation of the underwater cuboid with high conductivity was carried out, and the attenuation curve of dBz/dt at the center of the receiving coil was obtained. The one-dimensional and three-dimensional simulation results all show that the vertical magnetic field response characteristics are significantly different when there is a target with high conductivity in seawater, compared with the condition with no target. In the inversion imaging, the simulation data of different signal-to-noise ratios(SNRs) were synthesized by Gaussian white noise, and the one-dimensional calculation of underwater targets was carried out in combination with OCCAM inversion algorithm, so as to compare the detection effect of underwater targets under different SNRs. Inversion results show that when the SNR is greater than or equal to 10 dB, the highly conductive layer in the water can be effectively detected; when it reaches 40 dB, the depth and thickness information of the highly conductive layer can also be well judged. Finally, at an SNR of 40 dB, the resistivity value of the high conductive layer is reduced proportionally, and it is found that this method still has a significant response to the depth information of the target layer. According to the above forward and inversion calculation processes, the feasibility of this method in the field of underwater detection of highly conductive targets is effectively verified.
-
表 1 层状模型参数表
Table 1. Parameter table of layered model
层序 电阻率/(Ω·m) 厚度/m 备注 第1层 0.250 00 4.5 海水层 第2层 0.000 05 1.0 高导电层 第3层 0.250 00 294.5 海水层 第4层 200.000 00 $\infty $ 海底层 -
[1] 成建波, 孙心毅. 航空磁异常探潜技术发展综述[J]. 声学与电子工程, 2018(3): 4. [2] 殷长春, 张博, 刘云鹤, 等. 航空电磁勘察技术发展现状及展望[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8): 2637-53. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150804 [3] 钱建兵, 李貅, 戚志鹏, 等. 航空瞬变电磁合成孔径成像方法探潜应用研究[C]//国家安全地球物理丛书(八)—遥感地球物理与国家安全. 大连: 第八届国家安全地球物理学术讨论会, 2012: 227-233. [4] 齐耀光. 基于矩阵束的航空瞬变电磁去噪方法研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016. [5] Nabighian M N, Corbett J. Electromagnetic methods in applied geophysics: Volume 1, theory[M]. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysics, 1988. [6] 李华林, 雷达, 杨良勇, 等. 航空瞬变电磁激电效应特性研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020(5): 1953-61. doi: 10.6038/pg2020DD0403 [7] Haber E, Schwarzbach C, Shekhtman R. Modeling electromagnetic fields in the presence of casing[C]//2016 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting. Dallas, Texas: 2016 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, 2016: 959-964. [8] Luan X, Zhang W, Di Q, et al. Direct synthesis of time domain pseudo-random 3D electromagnetic response with a band-limited source[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2022, 200: 104624. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2022.104624 [9] Yee K. Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving maxwell’s equations in isotropic media[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1966, 14(3): 302-307. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1966.1138693 [10] 柳建新, 童孝忠, 郭荣文, 等. 大地电磁测深法勘探[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. [11] 刘小军, 王家林, 于鹏. 基于二次场的二维大地电磁有限元法数值模拟[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 35(8): 1114-9. [12] Constable S C, Parker R L, Constable C G. Occam’s inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data[J]. Geophysics, 1987, 52(3): 289-300. doi: 10.1190/1.1442303 [13] 陈润滋, 安志国, 杨良勇. 基于MATLAB语言的二维大地电磁OCCAM快速反演[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(4): 1461-68. doi: 10.6038/pg2018BB0518 [14] 屈文璋, 安志国. 时移音频大地电磁监测数值模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(4): 1595-604. doi: 10.6038/pg2020DD0312 -





 下载:
下载: