Underwater Potential Characteristics of Static Electric Field Related to Ship Corrosion
-
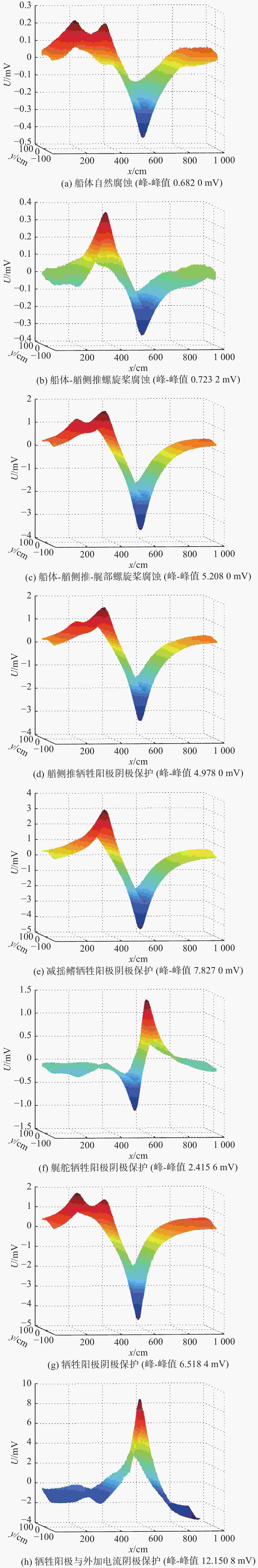
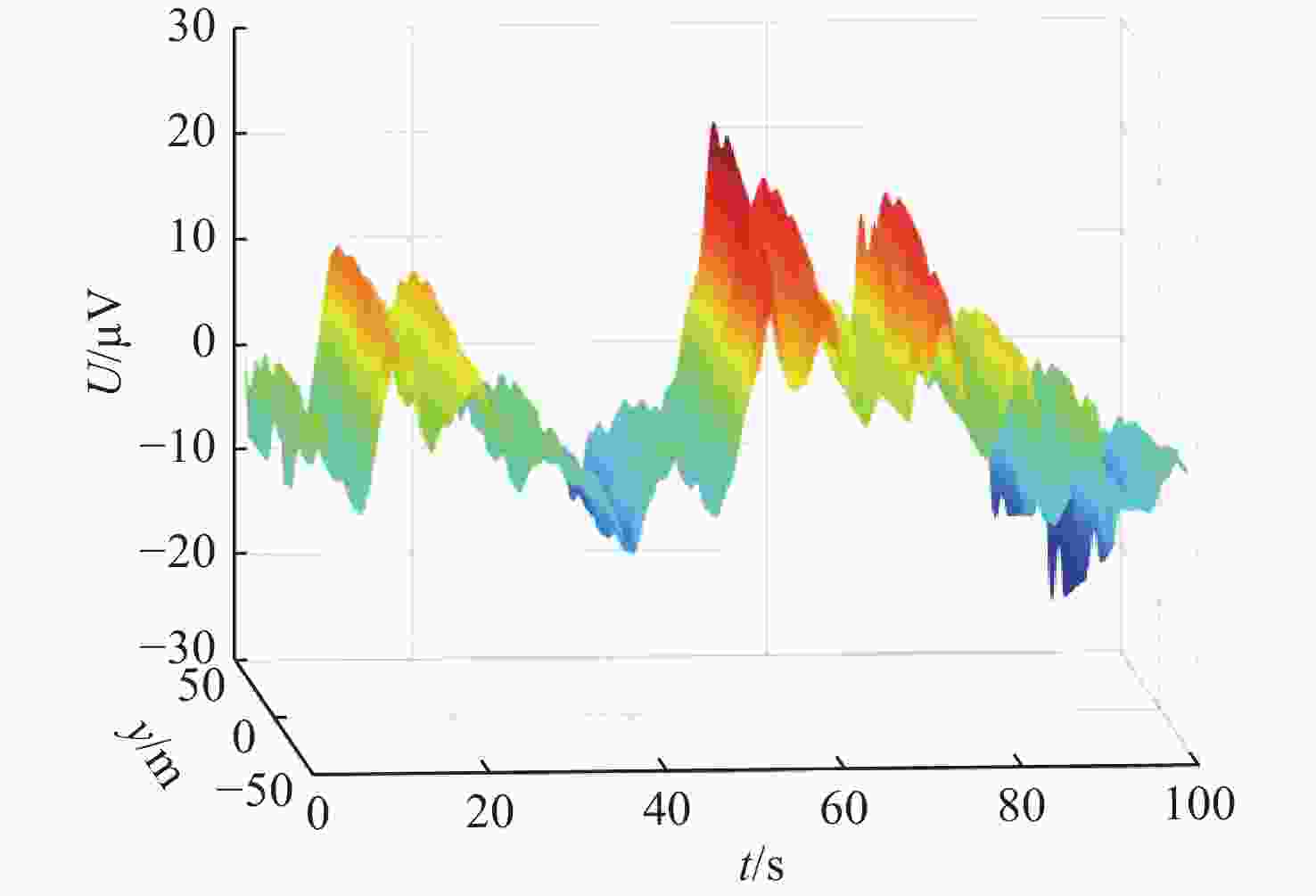
摘要: 为深入分析舰船静电场信号特征, 在船模试验和海上平面电位测量阵列实测数据的基础上, 对舰船腐蚀相关静态电场水下电位特征进行研究。首先根据船模试验分析了阴极保护系统工作下的舰船静电场信号特征, 发现阴极保护系统对静电场信号的量级影响较大; 其次对海上实测数据获得的典型舰船水下电位信号进行时域和频域上的分析, 结果表明, 静电场能量主要集中在0~0.1 Hz频段内; 最后根据水下电位分布规律, 发现以12 dB作为检测门限时, 在240 m以浅深度, 相邻传感器之间的距离不大于320 m时, 传感器阵列才能准确探测水面等效源强度为10 A·m的舰船电场。Abstract: In order to deeply analyze the characteristics of the ship’s static electric field signals, the underwater potential characteristics of static electric field related to ship corrosion were studied based on the ship model test and the measured data of the planar potential measurement array at sea. Firstly, based on the ship model test, the characteristics of the ship’s static electric field signals under the cathodic protection system were analyzed, and it was found that the cathodic protection system had a great influence on the magnitude of static electric field signals. Secondly, the time domain and frequency domain of underwater potential signals of typical ships obtained from the measured data at sea were analyzed. The results show that the static electric field energy is mainly concentrated in the frequency band of 0-0.1 Hz. Finally, according to the distribution rule of underwater potential, it is found that when 12 dB is taken as the detection threshold, and the distance between adjacent sensors is no more than 320 m at a shallow depth of 240 m, the sensor array can accurately detect the ship’s electric field with a surface equivalent source intensity of 10 A·m.
-
-
[1] 龚沈光, 卢新城. 舰船电场特性初步分析[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2008, 20(2): 1-4. [2] 张玉涛, 王巍. 舰船静电场特性分析[J]. 船电技术, 2018, 38(6): 15-17. doi: 10.13632/j.meee.2018.06.003Zhang Yutao, Wang Wei. Research on ship’s static electric field[J]. Marine Electric & Electronic Technology, 2018, 38(6): 15-17. doi: 10.13632/j.meee.2018.06.003 [3] 王瑾. 舰船水下电场测量[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2007, 2(5): 45-49.Wang Jin. Measurement of underwater electric field for ships[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2007, 2(5): 45-49. [4] Fabio S. Advanced mine capability[R]. Ghedi, BS, Italy: RWM Italia S. p. A., 2012: 1-65. [5] 姜润翔, 史建伟, 龚沈光. 船舶极低频电场信号特性分析[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2014, 26(1): 5-8.Jiang Runxiang, Shi Jianwei, Gong Shenguang. Analysis of signal characteristics of ship’s extremely low frequency electrical field[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2014, 26(1): 5-8. [6] Daya Z A, Hutt D L, Richards T C. Maritime electromagnetism and DRDC management research[R]. Canada: Defence R&D Canada-Atlantic, 2005: 1-80. [7] 杨清学. 外加电流阴极保护装置在舰船防腐中的应用研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2016, 38(10): 181-183.Yang Qingxue. Impressed current cathodic protection on the application of the ship[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2016, 38(10): 181-183. [8] 蒋治国, 陈聪, 危玉倩. 舰船自然腐蚀时腐蚀相关电场场源等效方法研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2020, 32(1): 14-19.Jiang Zhiguo, Chen Cong, Wei Yuqian. Study on equivalent method of field source for natural corrosion-related-electric field of ships[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2020, 32(1): 14-19. [9] 姜润翔, 林春生, 龚沈光. 基于点电荷模型的舰船静电场反演算法研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(3): 545-551.Jiang Runxiang, Lin Chunsheng, Gong Shenguang. Electrostatic electric field inversion method for ship based on point charge source model[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(3): 545-551. -





 下载:
下载: