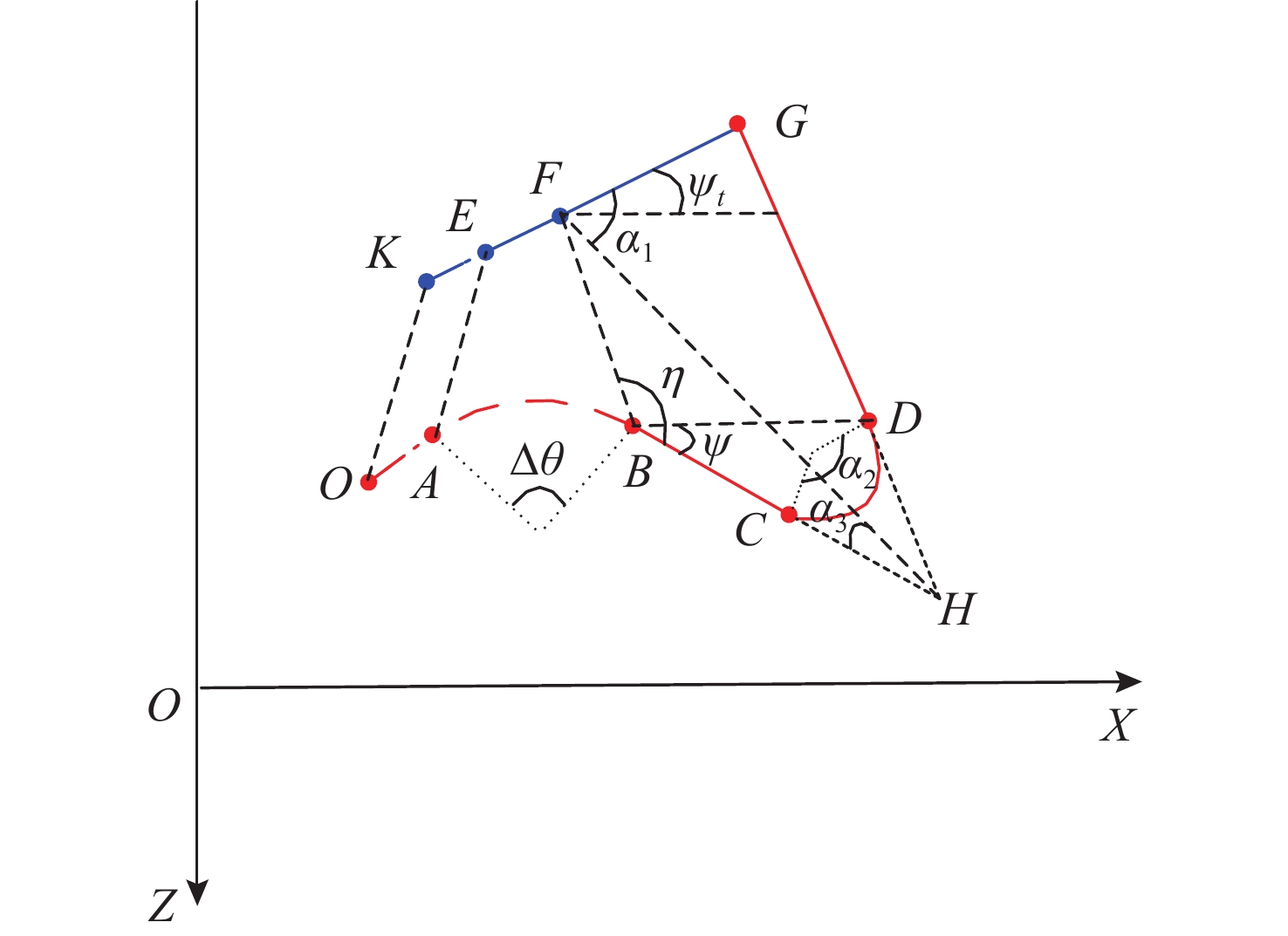
A Vertical Hit Method for Striking the Middle of a Large Undersea Vehicle
-
摘要: 受探测系统目标瞄准点在大型水下航行器上随机漂移的影响, 工程应用中经常会出现高速攻击型无人水下航行器(UUV)在大型水下航行器前后两侧垂直穿过而导致目标脱靶的情况。针对上述问题, 文中提出一种新的垂直命中导引方法, 利用探测系统多周期数据实现垂直命中大型水下航行器中间部位的目的, 并进行了统计仿真, 仿真结果表明该方法对制导参量敏感程度较低, 对UUV与目标航行器相对阵位的适应能力强, 在现有制导参量精度要求条件下能够满足垂直命中工程要求, 考虑命中部位时, 可垂直命中大型水下航行器中间部位, 垂直命中概率有明显提高。文中提出的方法具有合理性和可行性, 能够提高对大型水下航行器的毁伤效果。Abstract: Due to the random drift of the target aiming point of the detection system on large undersea vehicles, high-speed attack-type unmanned undersea vehicles(UUVs) often cross the front and rear sides of large undersea vehicles vertically in engineering applications, resulting in target miss. To address the above issues, this article proposed a new vertical hit guidance method that utilized multi-cycle data from the detection system to achieve vertical hits in the middle of a large undersea vehicle. In addition, statistical simulation was conducted. The simulation results show that this method has a relatively low sensitivity to guidance parameters and strong adaptability to the relative position of UUVs and the target vehicle. It can meet the requirements of vertical hit engineering under the existing guidance parameter accuracy requirements. When the hit location is considered, the middle of the large undersea vehicle can be hit vertically, and there is a significant increase in the probability of vertical hit. The method proposed in the article is reasonable and feasible and can improve the damage effect on large undersea vehicles.
-
表 1 误差设置情况表
Table 1. The error setting
误差参量 误差类型 A B C 目标航向角均方误差/(°) 0 5/3(≈1.6) 3.0 目标速度均方误差/m 0 0.5 1.0 目标距离均方误差/m 0 2/3(≈0.6) 2.0 目标方位角均方误差/(°) 0 1/3(≈0.3) 0.5 表 2 不考虑探测系统多周期数据动态亮点移位仿真结果
Table 2. The simulation results without considering the dynamic bright spot shift of the multi-cycle data of the detection system
误差
类型脱靶量/m 命中角与90º之差的绝对值/(°) 深度差/m 水平面垂直命中概率/% 水平面和垂直面垂直命中概率/% 平均值 均方差 平均值 均方差 平均值 均方差 不考虑命中部位 考虑命中部位 不考虑命中部位 考虑命中部位 误差A 1.34 1.20 1.45 1.22 0.37 0.01 100 53 100 51 误差B 3.27 2.65 1.96 1.40 0.57 0.43 100 49 96 46 误差C 6.38 5.20 2.68 1.91 0.80 0.64 94.5 44 82 40 表 3 考虑探测系统多周期数据动态亮点移位仿真结果
Table 3. The simulation results with considering the dynamic bright spot shift of the multi-cycle data of the detection system
脱靶量/m 命中角与90º之差的绝对值/(°) 深度差/m 水平面垂直命中概率/% 水平面和垂直面垂直命中概率/% 平均值 均方差 平均值 均方差 平均值 均方差 不考虑命中部位 考虑命中部位 不考虑命中部位 考虑命中部位 误差A — — 1.46 1.25 0.38 0.015 — 86 — 85 误差B — — 1.98 1.42 0.58 0.46 — 82 — 81 误差C — — 2.71 1.93 0.83 0.66 — 79 — 76 -
[1] 詹致祥. 鱼雷制导规律及命中精度[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 1995. [2] 聂卫东, 高智勇, 刘艳波. 轻型反潜鱼雷最优垂直命中末弹道设计[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2012, 20(1): 1-8.NIE W D, GAO Z Y, LIU Y B. Optimization design of perpendicular hit terminal trajectory for lightweight antisubmarine torpedo[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2012, 20(1): 1-8. [3] 张秦南, 李建辰, 缪雪佳. 鱼雷实现垂直命中的最优导引技术研究[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2000, 8(1): 18-21. [4] 井炜, 严卫生. 一种优化的鱼雷垂直命中最优导引律的研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2005, 26(3): 138-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2005.03.043JING W, YAN W S. A kind of optimum guide law for a torpedo hitting a target vertically[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2005, 26(3): 138-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2005.03.043 [5] 张安民, 杨世兴, 李志舜, 等. 利用遗传算法的垂直命中导引律研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2004, 25(3): 276-279. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2004.03.005ZHANG A M, YANG S X, LI Z S, et al. Perpendicular impact guidance law based on genetic algorithm[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2004, 25(3): 276-279. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2004.03.005 [6] 陈路伟. 萤火虫算法在鱼雷垂直命中导引方法中的仿真研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2020, 40(6): 89-91.CHEN L W. Simulation study of firefly algorithm in torpedo perpendicular hit guidance method[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2020, 40(6): 89-91. [7] 王澍初, 吕汉兴, 萧昌美, 等. 垂直命中机动目标的鱼雷三维拦截导引律设计[J]. 兵工学报, 2001, 22(2): 284-287. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2001.02.038WANG S C, LÜ H X, XIAO C M, et al. 3D guidance law for a torpedo impacting vertically on the target[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2001, 22(2): 284-287. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2001.02.038 [8] 张西勇, 李宗吉, 王树宗. 基于变结构控制的反鱼雷鱼雷拦截弹道建模与仿真[J]. 弹道学报, 2013, 25(3): 34-37, 58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2013.03.007ZHANG X Y, LI Z J, WANG S Z. Modeling and simulation of anti-torpedo torpedo intercepting trajectory based on variable structure control[J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2013, 25(3): 34-37, 58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2013.03.007 [9] 刘洋, 李宗吉, 张西勇. 基于变结构控制的反鱼雷鱼雷导引律设计[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2013, 21(1): 39-42.LIU Y, LI Z J, ZHANG X Y. Design of guidance law for anti-torpedo torpedo based on variable structure control[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2013, 21(1): 39-42. [10] 刘宇, 原建平, 侯朝焕. 水下自导武器导引律研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2008, 29(4): 483-486. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2008.04.021LIU Y, YUAN J P, HOU Z H. Research on the guidance law of underwater autoguide weapon[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2008, 29(4): 483-486. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2008.04.021 [11] 井炜, 严卫生, 高剑, 等. 无级变速鱼雷的最优垂直命中导引律研究[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2006(9): 1024-1026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-8728.2006.09.005JING W, YAN W S, GAO J, et al. Research on optimal and perpendicular impact guidance law for underwater vehicles with infinitely variable speeds[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2006(9): 1024-1026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-8728.2006.09.005 [12] 刘正平, 徐德民, 王晓娟. 一种新的鱼雷垂直命中目标的制导方法[J]. 船舶工程, 2001(5): 47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6982.2001.05.014LIU Z P, XU D M, WANG X J. A new guiding and controlling method for perpendicular target impact of the underwater autonomous vehicle[J]. Ship Engineering, 2001(5): 47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6982.2001.05.014 [13] 罗凯, 马远良. 一种垂直命中导引律制导参量的获取方法[J]. 兵工学报, 1998(3): 223-226. [14] 程善政, 何心怡. 一种可用于鱼雷导引的高冲突数据融合处理方法[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2014, 34(12): 186-188.CHENG S Z, HE X Y. Highly conflicting data fusion processing method in torpedo guidance[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2014, 34(12): 186-188. [15] 曹庆刚, 毛秋丹, 房毅. 某型潜艇尾流自导鱼雷命中概率方法研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2015, 35(3): 132-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1672-9730.2015.03.037CAO Q G, MAO Q D, FANG Y. The hitting probability's methods of x-model wake homing torpedo[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2015, 35(3): 132-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1672-9730.2015.03.037 -





 下载:
下载: