Review of Numerical Calculation Research on Underwater Supercavitation Flow
-
摘要:
超空泡技术能够减小航行体阻力、提高航速, 是水下高速航行体的关键技术之一。文中对国内外水下超空泡数值计算研究状况进行了综述, 介绍了水下超空泡数值计算方法, 主要包括理论模型求解方法及数值仿真方法。其中理论模型求解方法从势流理论出发, 分别发展了主要针对二维水翼的自由流线理论、线性理论及可进行三维超空泡形状计算的独立膨胀原理。目前大部分超空泡数值仿真基于计算流体动力学有限体积法。其中多相流和湍流模型对仿真结果影响显著, 通过结合空化、声学模型等, 能够突破势流理论的限制, 在考虑多相流、传质以及黏性情况下进行不同构形水下航行体超空泡流动及载荷预报。文中同时基于超空泡计算的自然空化数、通气参数、来流条件和几何构型4个典型影响因素, 介绍了数值计算研究的相关进展, 这些影响因素的变化均会改变超空泡整体形态, 其中通气参数和来流条件还会影响超空泡尾部闭合模式。
Abstract:Supercavity technology is one of the key technologies for underwater high-speed vehicles as it can reduce their resistance and increase their speed. In this paper, the current development of numerical calculation in supercavitation flow is reviewed. First, the numerical calculation methods are introduced, including modeling and numerical simulation methods. The modeling methods are based on the potential flow theory, which develops into the free streamline theory and linear theory for two-dimensional hydrofoils, and Logvinovich’s principle, which can be used to calculate the three-dimensional shape of the supercavity. The numerical simulation method is based on computational fluid dynamics. The finite volume method is typically used for the supercavity problem. The multiphase flow and turbulence model significantly affect the simulation results, and the limitation of the potential flow theory is overcome by combining the cavitation model and acoustic model. The supercavitation flow and load are predicted for undersea vehicles with different configurations considering the effects of multiphase flow, mass transfer, and viscosity. Finally, the recent developments in numerical research are introduced with regard to several key factors, including the natural cavitation number, ventilation and inflow conditions, and vehicle shape. These factors affect the shape of the supercavity, and the ventilation parameters and inflow conditions affect the closure mode. This paper provides a reference for subsequent research on the numerical calculations of underwater supercavitation flow.
-
Key words:
- supercavity /
- numerical calculation /
- cavitation /
- underwater drag reduction
-
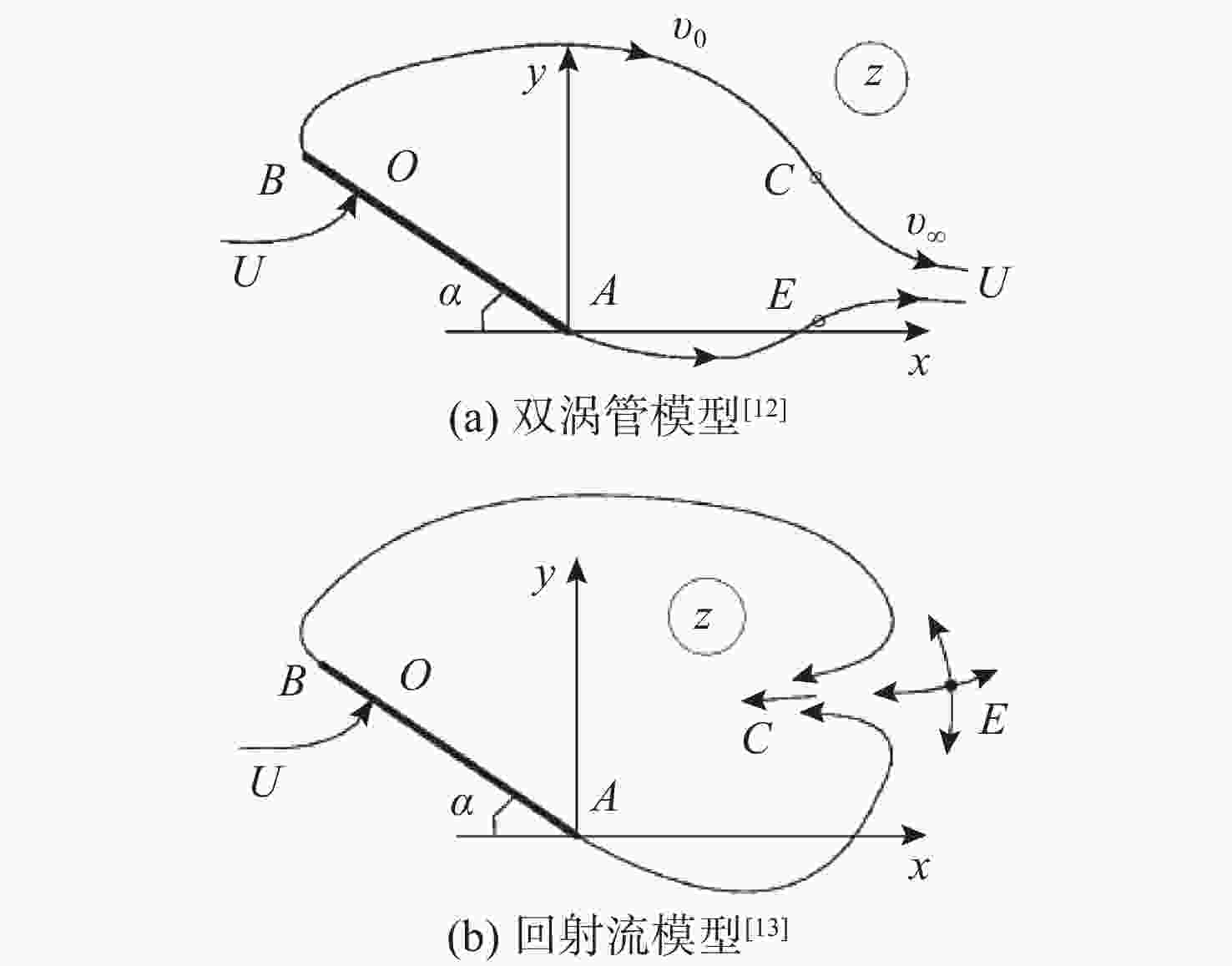
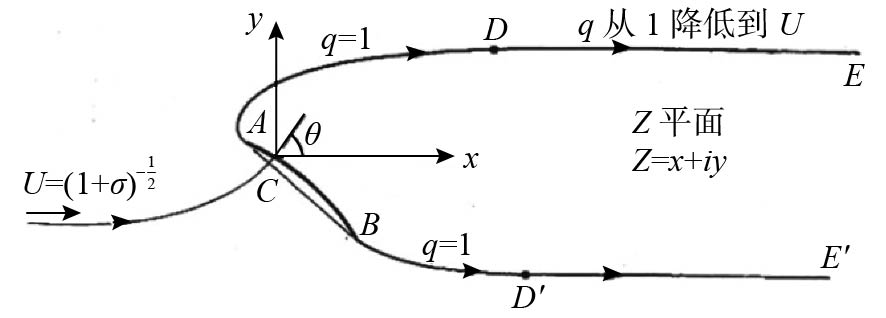
图 1 非零空化数自由流线模型[10]
Figure 1. Free streamline model under non-zero cavitation number condition
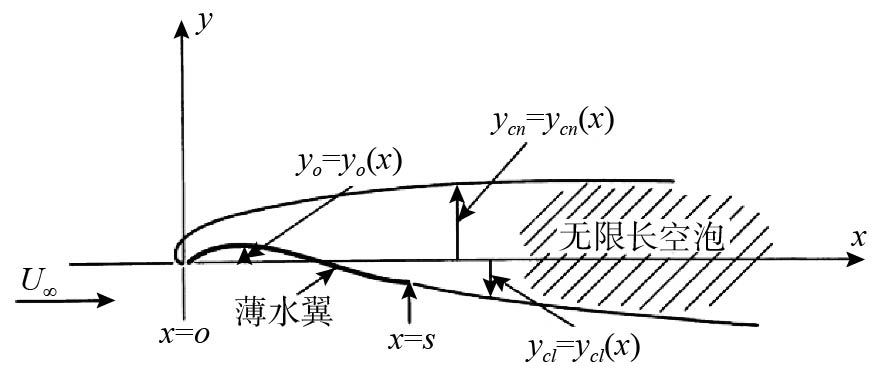
图 4 Auslaender的近自由面水翼模型[18]
Figure 4. Auslaender’s near free surface hydrofoil model
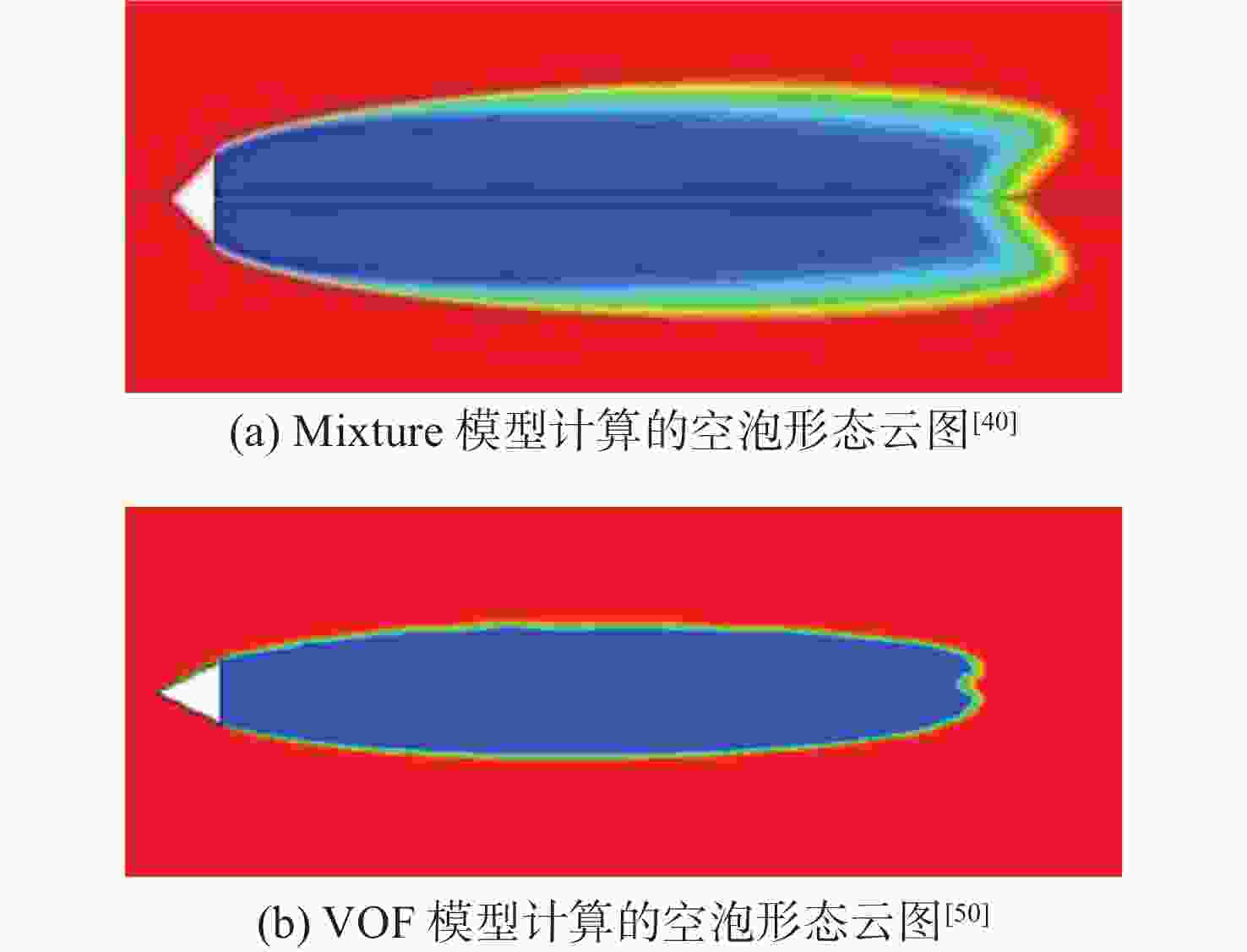
图 6 Euler-Euler模型计算的超空泡形态等值面图[53]
Figure 6. Iso-surface of supercavity morphology simulated by Euler-Euler model
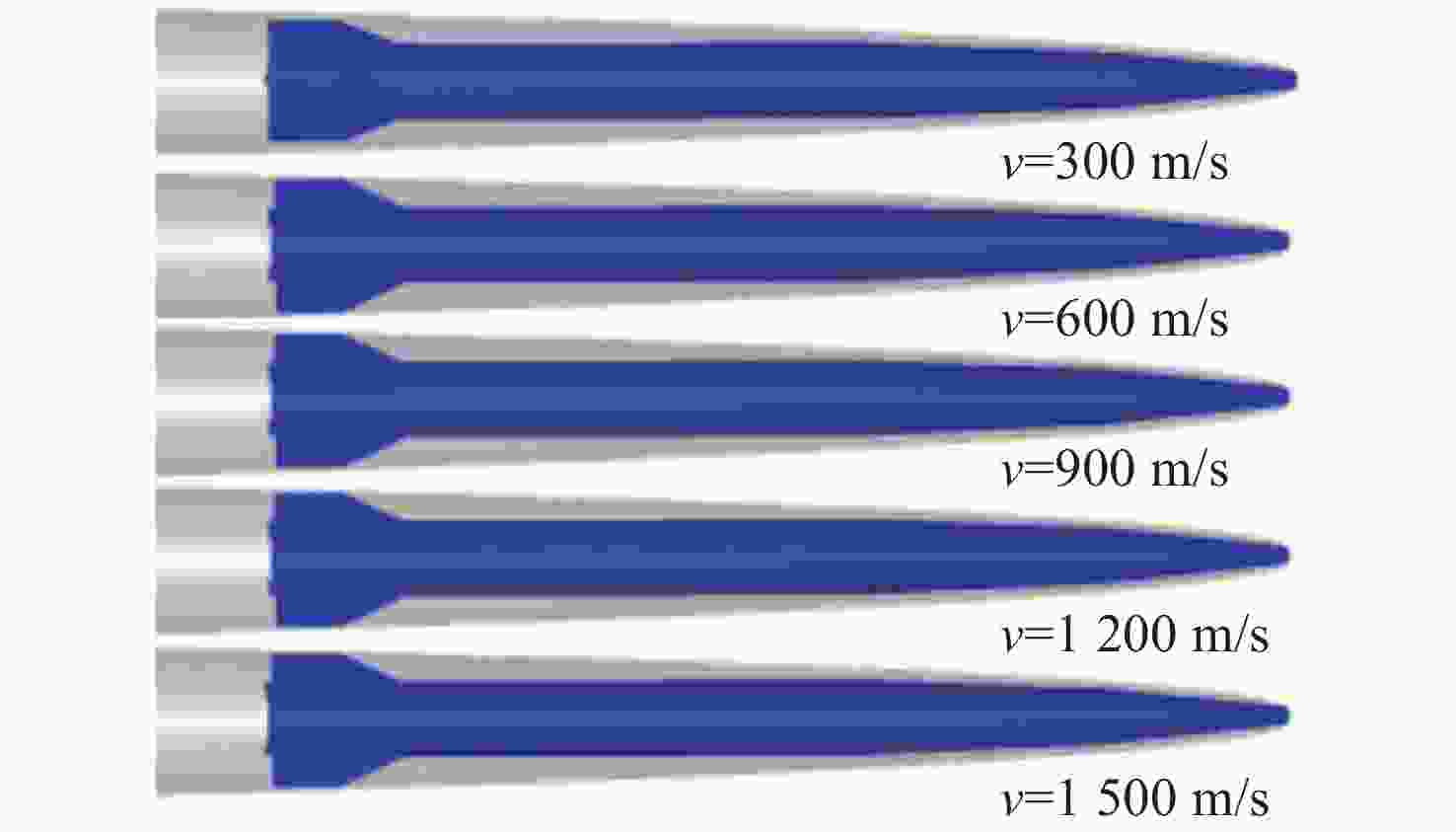
图 7 RANS方法预报的不同速度下的超空泡形态等值面图[58]
Figure 7. Iso-surface of supercavity morphology with different flow speed using RANS method
图 8 LES模型预报超空泡尾部涡管及脱落现象[64]
Figure 8. Tail vortex and shedding of supercavity using LES model
图 9 DES模型相体积分数等值面预报的尾鳍附近空泡壁面波动[70]
Figure 9. Cavity fluctuation near the tail fin predicted by phase volume fraction iso-surface using DES model
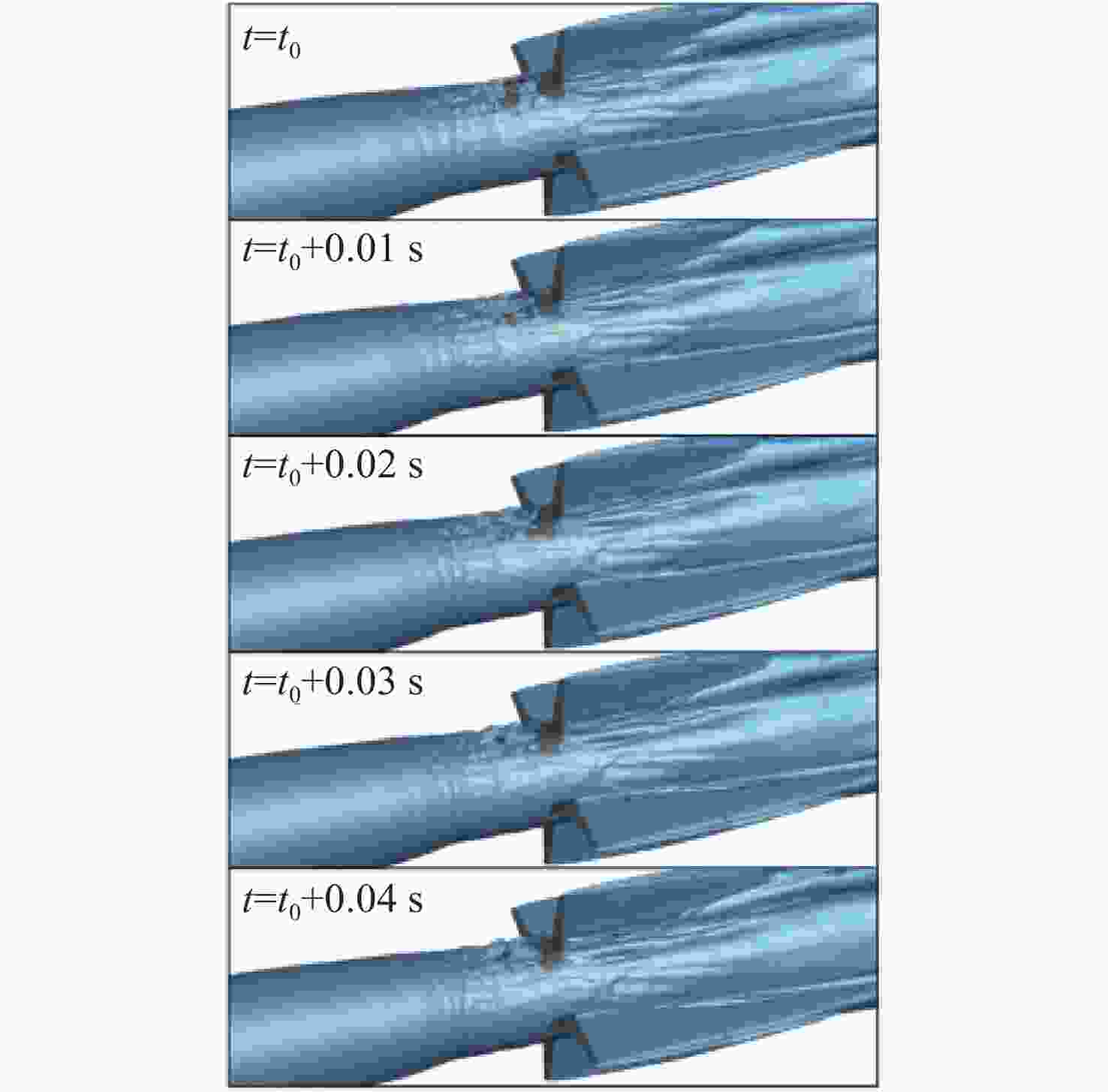
图 10 不同通气率下空泡内部涡量云图[104]
Figure 10. Vorticity field inside cavity under different ventilation rates
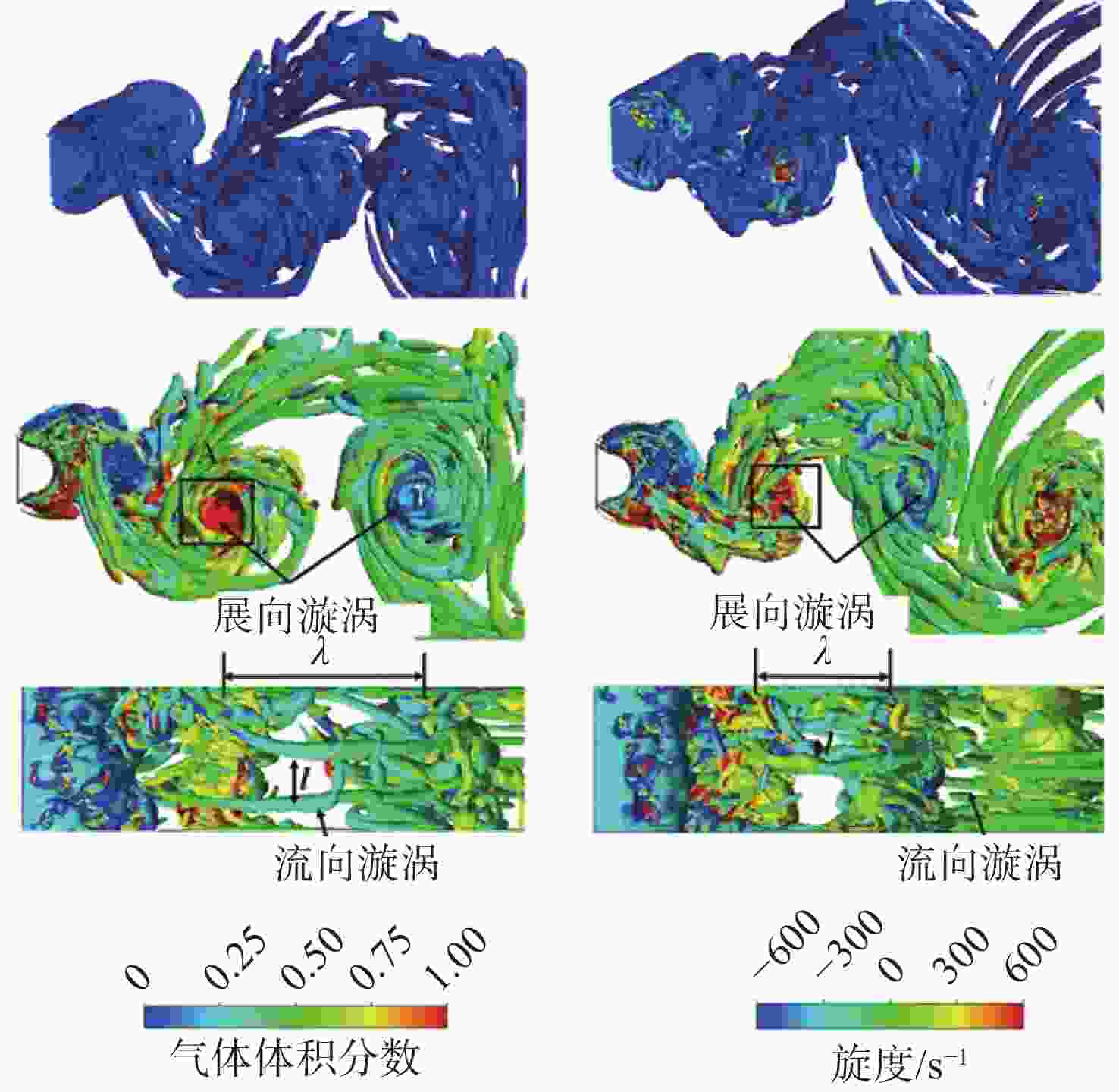
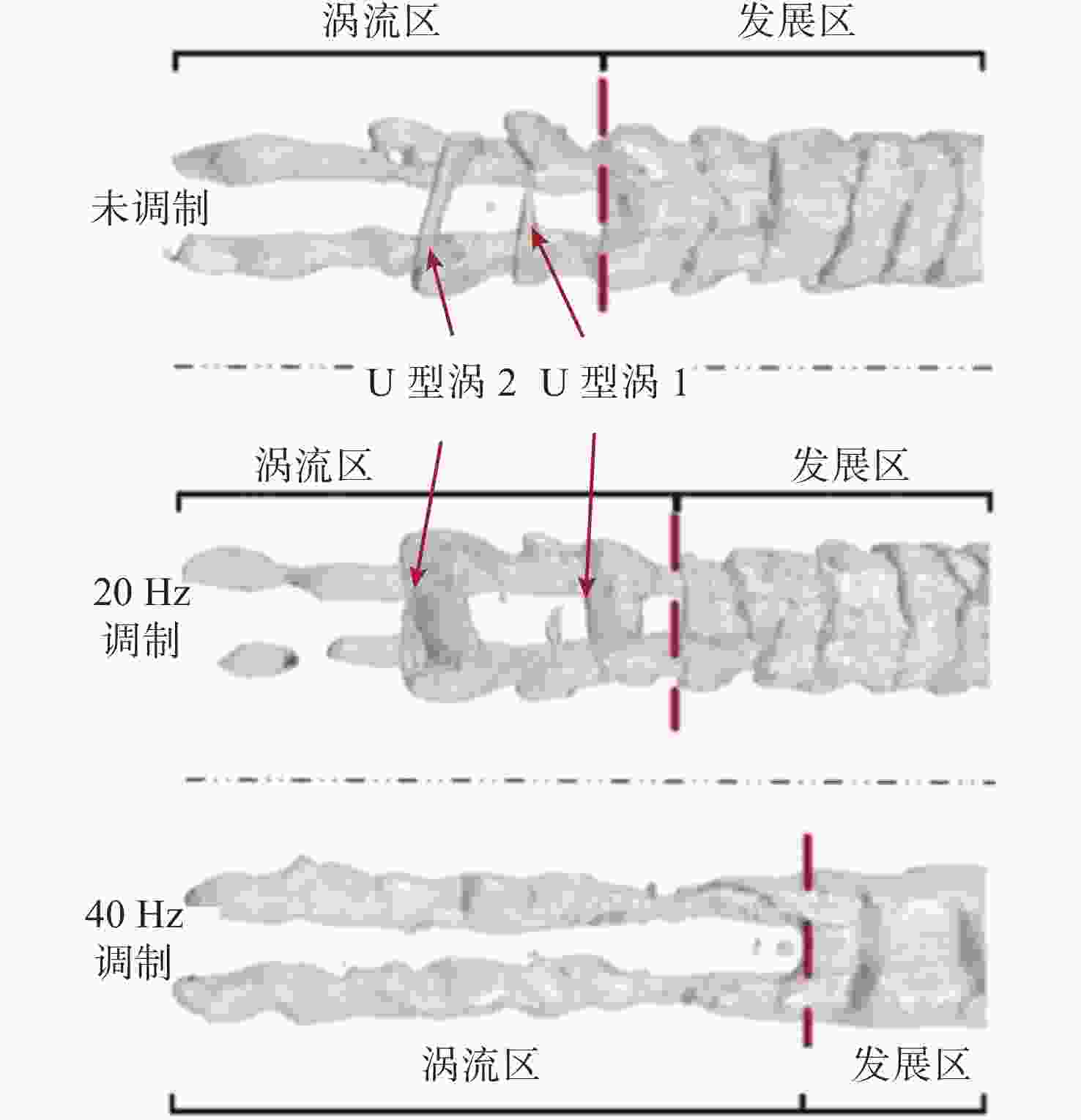
图 11 不同调制频率空泡尾部涡结构[83]
Figure 11. Vortex at cavity tail under different modulated frequencies
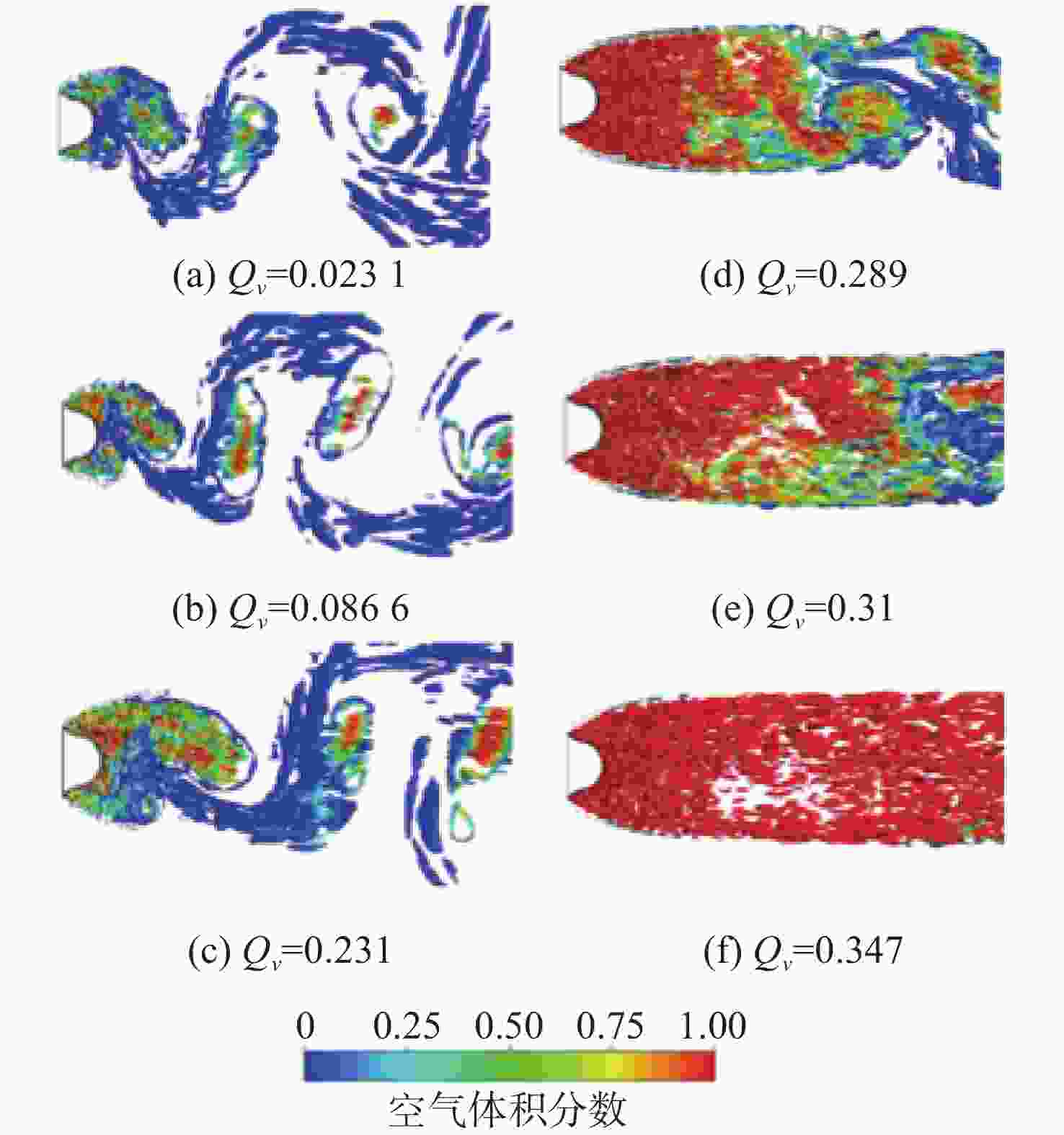
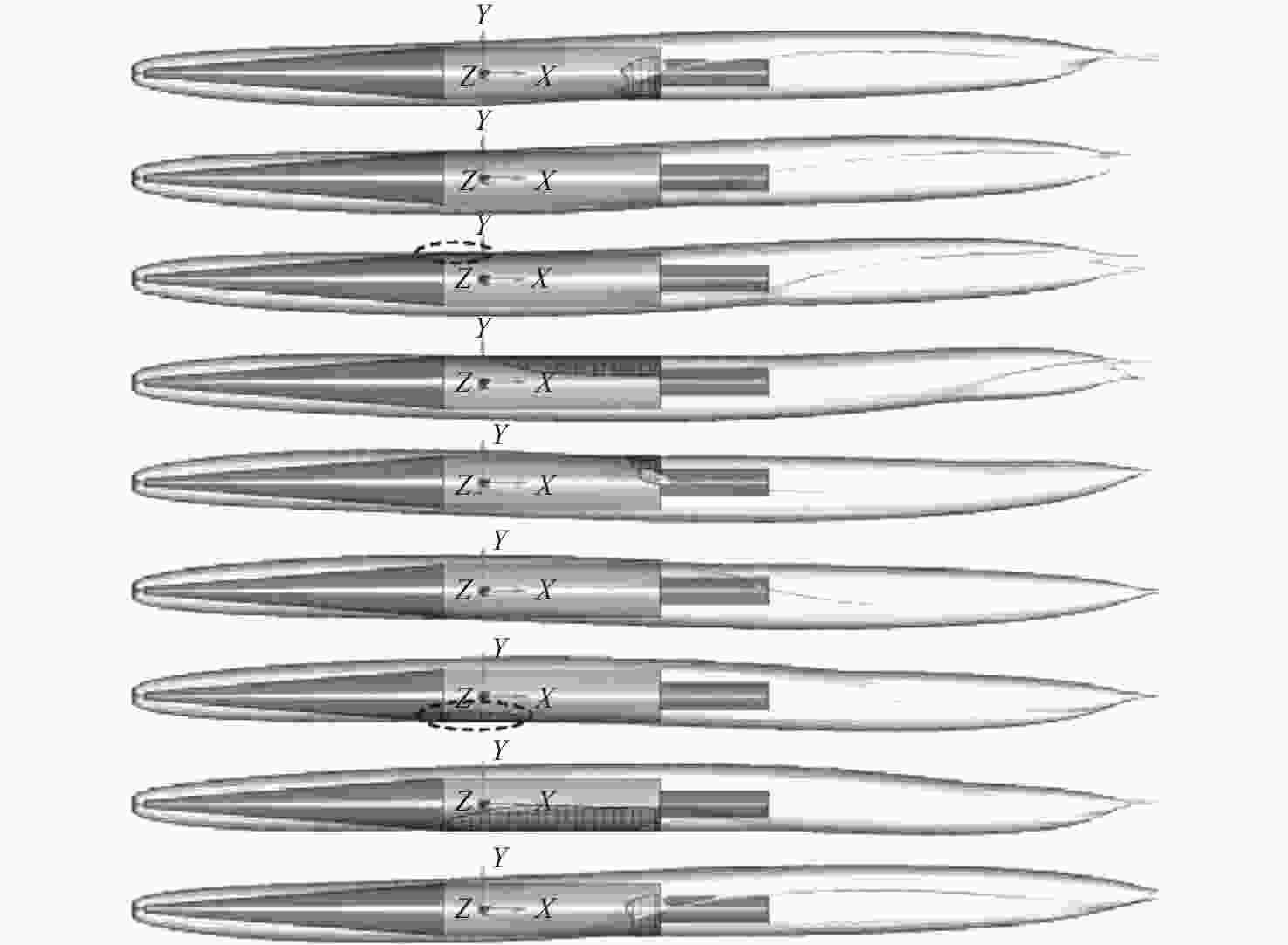
图 12 由相体积分数等值面表示的周期性来流对超空泡影响[116]
Figure 12. Influence of periodic flow on supercavity shown by iso-surface of phase volume fraction
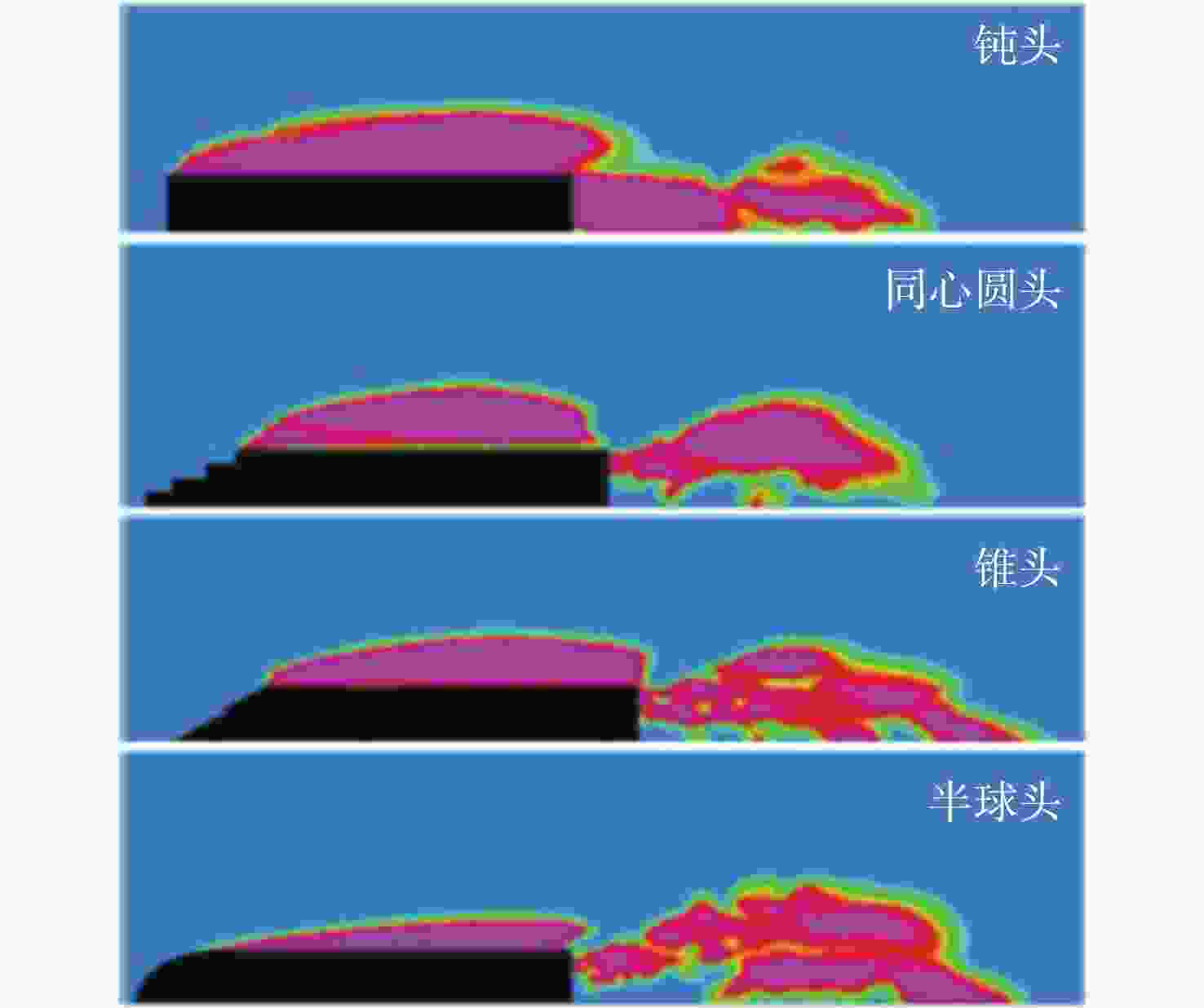
图 13 不同头部形状对超空泡云图形态影响[131]
Figure 13. Influence of different head shapes on supercavity morphology
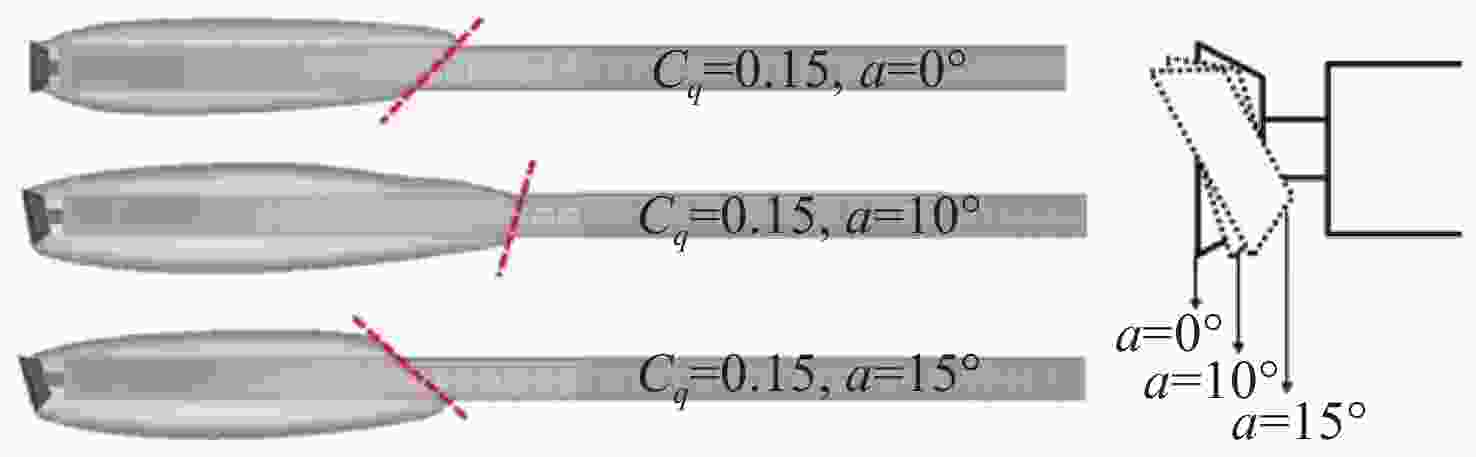
图 14 不同空化器攻角下超空泡形态[133]
Figure 14. Supercavity morphology under different cavitator attack angles
-
[1] 周景军. 通气超空泡流动及航行体流体动力数值模拟研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2011. [2] Kuklinski R, Henoch C, Castano J. Experimental study of ventilated cavities dynamic test model[C]//Fouth International Symposium on Cavitation. Pasadena: California institute of Technology, 2001. [3] 王晓娟, 张纪华, 张宇文. 通气量突变对通气超空泡形态影响的试验研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2012, 30(2): 222-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2012.02.014Wang Xiaojuan, Zhang Jihua, Zhang Yuwen. Experimental study of supercavity shape undersudden change of ventilation[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2012, 30(2): 222-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2012.02.014 [4] Karn A, Arndt R E, Hong J. Dependence of supercavity closure upon flow unsteadiness[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2015(68): 493-498. [5] Karn A, Arndt R E, Hong J. Gas entrainment behaviors in the formation and collapse of a ventilated supercavity[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2016(79): 294-300. [6] 陈诚, 袁绪龙, 任耀, 等. 通气对超空泡航行体自由运动的弹道特性影响试验研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2019, 37(4): 691-696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2019.04.007Chen Cheng, Yuan Xulong, Ren Yao, et al. Experimental study on influence of ventilation on trajectory characteristics of free motion of supercavitating vehicle[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2019, 37(4): 691-696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2019.04.007 [7] Yang Y, Wang M, Liu P, et al. An experimental investigation of ventilated supercavity under the action of tail jet[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022(266): 112921. [8] Levi-Civita T. Scie e leggi de resistenza[J]. Rend. Circolo Mat. Palermo, 1907, 23: 1-37. doi: 10.1007/BF03013504 [9] Roshko A. A new hodograph for free-streamline theory: NACA-TN-3168[R]. Washington: NACA, 1954. [10] Wu T. A free streamline theory for two-dimensional fully cavitated hydrofoils[R]. Pasadena, CA: California Institute of Technology, 1955. [11] Riabouchinsky D. On steady fluid motions with free surfaces[J]. Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, 1920(19): 206-215. [12] Tulin M P. Supercavitating flows-small perturbation theory[J]. Journal of Ship Research, 1964(8): 16-37. [13] Gilbarg D. Jets and cavities[J]. Encyclopedia of Physics, 1960(3, 9): 311-445. [14] Zhukovsky N E. Modification of the Kirchhoff method for determining two-dimensional flow at constant velocity given on an unknown streamline[J]. Matematichesky Sbornik, 1890, 15: 121-276. [15] Tulin M P, Burkart M P. Linearized theory for flows about lifting foils at zero cavitation number. The US Government Science and Technology Report[R/OL]. (2022-08-29)[2023-01-26]. https://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/ntis-science-report_other_thesis/020711575338.html. [16] Geurst J A. Linearized theory for partially cavitated hydrofoils[J]. International Shipbuilding Progress, 1959, 6(60): 369-384. doi: 10.3233/ISP-1959-66004 [17] Geurst J A. Linearized theory for fully cavitated hydrofoils[J]. International Shipbuilding Progress, 1960, 7(65): 17-27. doi: 10.3233/ISP-1960-76502 [18] Auslaender J. The linearized theory for supercavitating hydrofoils operating at high speeds near a free surface[R]. Arlington, Virginia: Hydronautics Inc Laurel Md, 1961. [19] Parkin B R, Grote R S. Inverse methods in the linearized theory of fully cavitating hydrofoils[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1964(86): 641-654. [20] 董世汤. 超空泡和局部空泡水翼的线性化理论[J]. 中国造船, 1964(2): 9-28. [21] Logvinovich G V. Hydrodynamics of free-boundary flows[M]. Jerusalem: Israel Program for Scientific Translations, 1972. [22] Serebryakov V V. The circular model for calculation of axisymmetric supercavitation flows[J]. Hydromechanics, 1974(27): 25-29. [23] Paryshev E V. Mathematical modeling of unsteady cavity flows[C]//Fifth International Symposium On Cavitation. Osaka, Japan: Osaka University, 2003. [24] Paryshev E V. Approximate mathematical models in high-speed hydrodynamics[J]. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2006, 55(1): 41-64. [25] 张学伟, 张亮, 王聪, 等. 基于Logvinovich独立膨胀原理的超空泡形态计算方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2009, 30(3): 361-365. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2009.03.021Zhang Xuewei, Zhang Liang, Wang Cong, et al. A calculation method for supercavity shape based on the logvinovich independence principle of the cavity section expansion[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2009, 30(3): 361-365. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2009.03.021 [26] 宋书龙, 万亚民, 李建辰, 等. 一种基于独立膨胀原理的三维超空泡形态计算方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(1): 51-58.Song Shulong, Wan Yamin, Li Jianchen, et al. A calculation method of three-dimensional supercavity shape based on the principle of independent expansion[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(1): 51-58. [27] Nouri N M, Eslamdoost A, Shienejad A, et al. Calculation of 2d velocity field in supercavitating flow by combination of slender body theory and bem[C]//4th Iasme/Wseas Int. Conf. on Fluid Mechanics and Aerodynamics. Elounda, Greece: World Scientific and Engineering Academy and Society, 2006. [28] Shafaghat R, Hosseinalipour S M, Vahedgermi A. Determination of supercavity shape for axisymmetric cavitators at different non-zero attack angles using boundary element method[J]. Journal of Mechanics, 2012, 28(2): 383-389. doi: 10.1017/jmech.2012.43 [29] Lyu H G, Sun P N, Colagrossi A, et al. Towards SPH simulations of cavitating flows with an EoSB cavitation model[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2023, 39(2): 722158. doi: 10.1007/s10409-022-22158-x [30] 张新明, 周超英, Islam Shams, 等. 用格子Boltzmann方法数值模拟三维空化现象[J]. 物理学报, 2009, 58(12): 8406-8414.Zhang Xinming, Zhou Chaoying, Islam Shams, et al. Three-dimensional cavitation simulation using lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Acta Phys. Sin., 2009, 58(12): 8406-8414. [31] Peng C, Tian S, Li G, et al. Simulation of laser-produced single cavitation bubbles with hybrid thermal Lattice Boltzmann method[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 149: 119136. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.119136 [32] Peng C, Tian S, Li G, et al. Simulation of multiple cavitation bubbles interaction with single-component multiphase Lattice Boltzmann method[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 137: 301-317. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.03.096 [33] Shan M L, Zhu C P, Zhou X, et al. Investigation of cavitation bubble collapse near rigid boundary by lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2016, 28(3): 442-450. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60647-9 [34] 黄彪, 黄瀚锐, 刘涛涛, 等. 通气空泡流动特性研究现状及进展[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2020, 38(4): 724-745. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2019.0084Huang Biao, Huang Hanrui, Liu Taotao, et al. Research progress and prospects of ventilated cavitating flows characteristics[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2020, 38(4): 724-745. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2019.0084 [35] Manninen M, Taivassalo V, Kallio S. On the mixture model for multiphase flow[R]. Espoo, Finland: Technical Research Centre of Finland, 1996. [36] 陈鑫, 鲁传敬, 吴磊. 通气空泡流的多相流模型与数值模拟[J]. 水动力学研究与进展(A辑), 2005, 20(S1): 916-920.Chen Xin, Lu Chuanjing, Wu Lei. A multiphase model on simulating a ventilated cavitating flow[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics A, 2005, 20(S1): 916-920. [37] Javadpour S M, Farahat S, Ajam H, et al. Experimental and numerical study of ventilated supercavitation around a cone cavitator[J]. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 53(5): 1491-1502. doi: 10.1007/s00231-016-1893-3 [38] 仲霄, 王树山, 马峰. 通气空泡内部流动特征数值仿真[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2014, 22(1): 1-6.Zhong Xiao, Wang Shushan, Ma Feng. Numerical simulation on the internal flow characteristics in ventilated cavity[J]. Torpedo technology, 2014, 22(1): 1-6. [39] Radzyuk A Y, Kulagin V A, Istyagina E B, et al. Numerical simulation of supercavitation in the constrained flow[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 315(3): 032027. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/315/3/032027 [40] Gopala K T, Lokesharun D, Saravanan R, et al. Cfd based shape optimization of axisymmetric cavitators in supercavitating flows[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Recent Trends in Mechanical and Materials Engineering. Chennai, India: American Institute of Physics, 2020. [41] 刘如石, 郭则庆, 张辉. 尾部形状对超空泡射弹尾拍运动影响的数值研究[EB/OL]. (2022-11-04)[2023-01-31]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C45S0n9fL2suRadTyEVl2pW9UrhTDCdPD64UTFRAXGf5onBVQOTpzMUn1NONudQgUyfZuUj9BMRSRdktPw-DiBjP&uniplatform=NZKPT. [42] Thang N T, Ngoc D. Numerical study of the natural-cavitating flow around underwater slender bodies[J]. Fluid Dynamics, 2019, 54: 835-849. doi: 10.1134/S0015462819060120 [43] Kim S, Lee J, Lee H, et al. Effect of rotating, non-axisymmetric cavitator on supercavity size[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2022, 36(7): 3437-3447. doi: 10.1007/s12206-022-0622-8 [44] Hirt C W, Nichols B D. Volume of fluid(VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries[J]. Journal of computational physics, 1981, 39(1): 201-225. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(81)90145-5 [45] Roohi E, Zahiri A P, Passandideh-Fard M. Numerical simulation of cavitation around a two-dimensional hydrofoil using VOF method and LES turbulence modelp[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2013, 37(9): 6469-6488. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2012.09.002 [46] Pendar M R, Roohi E. Investigation of cavitation around 3D hemispherical head-form body and conical cavitators using different turbulence and cavitation models[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2016, 112: 287-306. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.12.010 [47] Jiang C X, Li S L, Li F C, et al. Numerical study on axisymmetric ventilated supercavitation influenced by dragreduction additives[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017(115): 62-76. [48] 向敏, 刘波, 谢泽阳, 等. 近自由面超空泡航行体多相流特性分析[EB/OL]. (2022-08-22)[2023-02-27]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C45S0n9fL2suRadTyEVl2pW9UrhTDCdPD657q3h1OCdd59PSRDGX5w-0oqV0775UNmnenfrcfSHO4gUH2LNWzZ2Y&uniplatform=NZKPT. [49] 魏海鹏, 符松. 不同多相流模型在航行体出水流场数值模拟中的应用[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(4): 48-52.Wei Haipeng, Fu Song. The research of multiphase models applied for flow field numerical simulation of vehicle exiting water[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(4): 48-52. [50] Pendar M R, Roohi E. Investigation of cavitation around disk and conical cavitators using different sets of turbulence and cavitation models[C]//4th International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering. Bali, Indonesia: ICAME, 2015. [51] 周景军, 于开平, 杨明. 低弗鲁德数条件下通气超空泡泄气机理数值模拟[J]. 工程力学, 2011, 28(1): 251-256.Zhou Jingjun, Yu Kaiping, Yang Ming. Numerical simulation of gas leakage mechanism of ventilated supercavity under the condition of low froude number[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2011, 28(1): 251-256. [52] 杨明, 于开平, 周景军, 等. 通气超空泡洞壁影响及其比尺效应数值模拟[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2011, 43(7): 23-27. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2011.07.005Yang Ming, Yu Kaiping, Zhou Jingjun, et al. Numerical simulation of the wall effect and scale effect of ventilated supercavity[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2011, 43(7): 23-27. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2011.07.005 [53] Zhou S, Li D, Huang C, et al. Ventilated supercavity shapes and hydrodynamic characteristics of bow rudder layout[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2022, 124: 103192. [54] Xu H Y, Luo K, Huang C, et al. Variation characteristics of formation and development of ventilated supercavity at low froude numbers[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2021, 55(8): 934. [55] 周景军, 于开平. 空化器倾斜角对超空泡流影响的三维数值仿真研究[J]. 船舶力学, 2011, 15(z1): 74-80.Zhou Jingjun, Yu Kaiping. Three dimensional numerical simulation on the influence of cavitator inclination angle to supercavity flow[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2011, 15(z1): 74-80. [56] Park S, Rhee S H. Computational analysis of turbulent super-cavitating flow around a two-dimensional wedge-shaped cavitator geometry[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2012, 70: 73-85. [57] Choi J K, Ahn B K, Kim H T. A numerical and experimental study on the drag of a cavitating underwater vehicle in cavitation tunnel[J]. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 2015, 7(5): 888-905. doi: 10.1515/ijnaoe-2015-0062 [58] Lu R, Pan G, Tan K, et al. Numerical simulation of cavitation and damping force characteristics for a high-speed supercavitation vehicle[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(11): 1171. doi: 10.3390/jmse9111171 [59] 王威, 侯瀚程, 何广华, 等. 超空泡航行体三相流动演化特性[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2022, 43(1): 48-54.Wang Wei, Hou Hancheng, He Guanghua, et al. Evolution characteristics of the three-phase cavity flow around a ventilated vehicle[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2022, 43(1): 48-54. [60] 赵怡, 刘平安, 苗成林. 非稳态超空泡流动的数值模拟[J]. 四川兵工学报, 2015, 36(1): 64-67.Zhao Yi, Liu Pingan, Miao Chenglin. Numerical simulation of unsteady cavitating flow[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2015, 36(1): 64-67. [61] Pendar M R, Roohi E. Detailed investigation of cavitation and supercavitation around different geometries using various turbulence and mass transfer models[C]//9th International Symposium on Cavitation(CAV2015). Lausanne, Switzerland: Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, 2015. [62] Pendar M R, Roohi E. LES investigation of cavitating characteristics around a 3D sphere[C]//The 18th Marine Industry Conference of the Country. Kish, Iran: [s.n.], 2016. [63] 张木, 谭俊杰, 易文俊, 等. 空化器参数对超空泡初生位置影响大涡模拟[J]. 弹道学报, 2016, 28(1): 87-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2016.01.016Zhang Mu, Tan Junjie, Yi Wenjun, et al. Large eddy simulation analysis on effect of cavitator parameteron supercavity primary position[J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2016, 28(1): 87-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2016.01.016 [64] Wang Z, Huang B, Zhang M, et al. Numerical investigation of ventilated cavitating vortex shedding over a bluff body[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 159: 129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.03.087 [65] Kunz R F, Lindau J W, Kaday T A, et al. Unsteady RANS and detached eddy simulations of cavitating flow over a hydrofoil[C]//Fifth international symposium on cavitation. Osaka, Japan: CAV, 2003. [66] Kinzel M, Lindau J, Peltier L, et al. Detached-eddy simulations for cavitating flows[C]//18th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference. Miami, FL, U.S.: AIAA, 2007. [67] Kinzel M P, Krane M H, Kirschner I N, et al. A numerical assessment of the interaction of a supercavitating flow with a gas jet[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 136: 304-313. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.03.042 [68] Gao G H, Zhao J, Ma F, et al. Numerical study on ventilated supercavitation reaction to gas supply rate[J]. In Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 418: 1781-1785. [69] Zhou J J, Dong C P, Xiang Q R. Evaluation on the application of two-fluid multiphase model to supercavity[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 275: 417-428. [70] Choe Y, Kim C. Computational investigation on ventilated supercavitating flows and its hydrodynamic characteristics around a high-speed underwater vehicle[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 249: 110865. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110865 [71] Kubota A, Kato H, Yamaguchi H, et al. Unsteady structure measurement of cloud cavitation on a foil section using conditional sampling technique[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1989, 111(2): 204-210. doi: 10.1115/1.3243624 [72] Kubota A, Kato H, Yamaguchi H. A new modelling of cavitating flows: A numerical study of unsteady cavitation on a hydrofoil section[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1992, 240(1): 59-96. [73] Merkle C L. Computational modelling of the dynamics of sheet cavitation[C]//3rd International Symposium on Cavitation. Grenoble, France: [s.n.], 1998. [74] Kunz R F, Boger D A, Stinebring D R, et al. A preconditioned Navier-Stokes method for two-phase flows with application to cavitation prediction[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2000, 29(8): 849-875. [75] Singhal A K, Athavale M M, Li H, et al. Mathematical basis and validation of the full cavitation model[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2002, 124(3): 617-624. doi: 10.1115/1.1486223 [76] Schnerr G H, Sauer J. Physical and numerical modeling of unsteady cavitation dynamics[C]//Fourth international conference on multiphase flow. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: [s.n.], 2001. [77] Yuan W, Sauer J, Schnerr G H. Modeling and computation of unsteady cavitation flows in injection nozzles[J]. Mécanique & industries, 2001, 2(5): 383-394. [78] Owis F M, Nayfeh A H. Computations of the compressible multiphase flow over the cavitating high-speed torpedo[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2003, 125(3): 459-468. doi: 10.1115/1.1568358 [79] Gerber A G. A CFD model for devices operating under extensive cavitation conditions[C]//Proceedings of the ASME 2002 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. New Orleans, Louisiana, USA: ASME, 2002: 341-349. [80] Zwart P J, Gerber A G, Belamri T. A two-phase flow model for predicting cavitation dynamics[C]//Fifth International Conference on Multiphase Flow. Yokohama, Japan: The Japanese Society for Multiphase Flow, 2004. [81] Howe M S, Colgan A M, Brungart T A. On self-noise at the nose of a supercavitating vehicle[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2009, 322: 772-784. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2008.11.019 [82] 张风珍, 李桂娟, 王纪会, 等. 超空泡航行体空化噪声特性仿真分析[C]//2016年中国造船工程学会水中目标特性学组学术交流会. 大连: 中国造船工程学会, 2016. [83] Sun T, Ding Y, Huang H, et al. Numerical study on the effects of modulated ventilation on unsteady cavity dynamics and noise patterns[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2021, 33(12): 123307. doi: 10.1063/5.0067559 [84] Ramesh S S, Lim K M, Khoo B C. An axisymmetric hypersingular boundary integral formulation for simulating acoustic wave propagation in supercavitating flows[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2012, 331: 4313-4342. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2012.04.031 [85] Ramesh S S, Lim K M, Zheng J, et al. Numerical analysis of flow induced noise propagation in supercavitating vehicles at subsonic speeds[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2014, 135: 1752-1763. doi: 10.1121/1.4865919 [86] Skidmore G M, Lindau J W, Brungart T A, et al. Finite Volume, computational fluid dynamics-based investigation of supercavity pulsations[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2017, 139: 091301. doi: 10.1115/1.4036596 [87] Passandideh-Fard M, Roohi E. Transient simulations of cavitating flows using a modified volume-of-fluid(VOF) technique[J]. International Journal of Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2008, 22(1-2): 97-114. doi: 10.1080/10618560701733657 [88] Gugulothu S K. Computational modeling on supercavitating flow over axisymmetric cavitators[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 210: 107515. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107515 [89] 金大桥, 王聪, 魏英杰, 等. 水下射弹自然超空泡减阻特性的数值模拟[J]. 工程力学, 2010, 27(6): 202-208.Jin Daqiao, Wang Cong, Wei Yingjie, et al. Numerical simulation on drag reduction of natural supercavitation induced by underwater projectile[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2010, 27(6): 202-208. [90] Jiang C X, Shuai Z J, Zhang X Y, et al. Numerical study on evolution of axisymmetric natural supercavitation influenced by turbulent drag-reducing additives[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 107: 797-803. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.07.040 [91] 张木, 易文俊, 谭俊杰, 等. 带尾翼水下自然超空泡射弹数值模拟研究[J]. 计算力学学报, 2013, 30(1): 161-165,172. doi: 10.7511/jslx201301027Zhang Mu, Yi Wenjun, Tan Junjie, et al. Numerical investigation of underwater natural supercavitating projectiles operating with the empennages[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2013, 30(1): 161-165,172. doi: 10.7511/jslx201301027 [92] Kadivar E, Kadivar E, Javadi K. et al. The investigation of natural supercavitation flow behind three-dimensional cavitators: Full cavitation model[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2017, 45: 165-178. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2016.12.017 [93] 孙士明, 颜开, 陈伟政. 超空泡航行体通气规律数值仿真[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2014, 22(2): 81-86.Sun Shiming, Yan Kai, Chen Weizheng. Numerical simulation of ventilation law for supercavitating vehicle[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2014, 22(2): 81-86. [94] Moeny M J, Krane M H, Kirschner I N, et al. Jet-supercavity interaction: insights from experiments[C]//9th International Symposium on Cavitation(CAV2015). Lausanne, Switzerland: Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2015. [95] Karn A, Rosiejka B. Air entrainment characteristics of artificial supercavities for free and constrained closure models[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2017, 81: 364-369. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.10.003 [96] Xu C, Zhao X, Khoo B C. Numerical investigation of ventilated cavitating flow from high to low cavitation numbers[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266: 112782. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112782 [97] 杨武刚, 张宇文, 阚雷. 高速水下航行体超空化通气参数数值研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2007, 27(4): 198-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2007.04.060Yang Wugang, Zhang Yuwen, Kan Lei. Numerical research on the ventilation parameters of underwater supercavitating high speed vehicle[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2007, 27(4): 198-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2007.04.060 [98] 黄海龙, 黄文虎, 王聪, 等. 数值模拟通气角度对超空泡形态特性影响分析[J]. 工程力学, 2007, 24(z2): 195-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2007.z2.022Huang Hailong, Huang Wenhu, Wang Cong, et al. Numerical analysis of the influence of angle of ventilation on the shapes of supercavity[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2007, 24(z2): 195-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2007.z2.022 [99] Rashidi I, Pasandideh-Fard M, Passandideh-Fard M, et al. Numerical and experimental study of a ventilated supercavitating vehicle[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2014, 136(10): 101301. doi: 10.1115/1.4027383 [100] Nouri N M, Riahi M, Valipour A, et al. Analytical and experimental study of hydrodynamic and hydroacoustic effects of air injection flow rate in ventilated supercavitation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 95: 94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2014.11.013 [101] Kim S H, Kim N. Hydrodynamics and modeling of a ventilated supercavitating body in transition phase[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2015, 27(5): 763-772. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(15)60538-8 [102] Cao L, Karn A, Arndt R E, et al. Numerical investigations of pressure distribution inside a ventilated supercavity[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2017, 139(2): 021301. doi: 10.1115/1.4035027 [103] Fronzeo M A, Kinzel M, Lindau J. Artificially ventilated cavities: Evaluating the constant-pressure approximation[C]//Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting. Waikoloa, Hawaii: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2017. [104] Wang Z, Huang B, Zhang M, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of ventilated cavitating flow structures with special emphasis on vortex shedding dynamics[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2018, 98: 79-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2017.08.014 [105] Lindau J, Skidmore G, Brungart T, et al. Finite volume computation of the mitigation of cavity pulsation[C]//9th International Symposium on Cavitation(CAV2015). Lausanne, Switzerland: Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2015. [106] An H, Pan H, Yang P. CFD-based numerical study on drag reduction of ventilated supercavities combined with gas layer of the surface vehicle with struts[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 262: 112334. [107] Lv Y, Zhang M, Liu T, et al. Physical and numerical study on the transition of gas leakage regime of ventilated cavitating flow[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 239: 109861. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109861 [108] Pham V D, Hong J W, Hilo A K, et al. Numerical study of hot-gas ventilated supercavitating flow[J]. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 2022, 14: 100470. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnaoe.2022.100470 [109] Kawakami E, Arndt R E. Investigation of the behavior of ventilated supercavities[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2011, 133(9): 091305. doi: 10.1115/1.4004911 [110] Wang W, Zhang Z, He G, et al. Numerical analysis of the effects of periodic gust flow on the wake structure of ventilated supercavities[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 2021, 20(1): 34-45. doi: 10.1007/s11804-021-00192-4 [111] 何广华, 杨豪, 王威, 等. 周期性来流扰动对通气超空泡航行体流体动力特性的影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(10): 16-22. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2022.10.003He Guanghua, Yang Hao, Wang Wei, et al. Influence of periodic inflow disturbance on the hydrodynamic characteristics of ventilated supercavitating vehicles[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(10): 16-22. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2022.10.003 [112] Kim J H, Ahn B K. Numerical simulation of supercavitating flows using a viscous-potential method[C]//9th International Symposium on Cavitation(CAV2015). Lausanne, Switzerland: Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2015. [113] Wang Z, Huang B, Wang G, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of ventilated cavitating flow with special emphasis on gas leakage behavior and re-entrant jet dynamics[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 108: 191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.07.063 [114] Karn A, Arndt R E, Hong J. An experimental investigation into supercavity closure mechanisms[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 789: 259-284. [115] Jafarian A, Pishevar A. Numerical simulation of steady supercavitating flows[J]. Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 9(6): 2981-2992. doi: 10.29252/jafm.09.06.26209 [116] 王威, 王聪, 李聪慧, 等. 周期性阵风流对通气航行体超空泡形态及流体动力特性影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(13): 208-214.Wang Wei, Wang Cong, Li Conghui, et al. Effects of periodic gust flow on super-cavitation morphology and hydrodynamic characteristics of a ventilated vehicle[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(13): 208-214. [117] 王威, 王聪, 宋武超, 等. 侧滑角对超空泡航行体转弯运动沾湿区域的影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(12): 135-141.Wang Wei, Wang Cong, Song Wuchao, et al. Influence of sideslip angle on wetted area in turning motion of a supercavitating vehicle[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(12): 135-141. [118] Huang R, Shao S, Arndt R E, et al. Numerical study of the behaviors of ventilated supercavities in a periodic gust flow[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2020, 142(6): 061403. doi: 10.1115/1.4046110 [119] Zou W, Yu K P, Arndt R E, et al. On the shedding of the ventilated supercavity with velocity disturbance[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2013, 57: 223-229. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2012.09.013 [120] Sun T, Ding Y, Liu Y, et al. Numerical modeling and investigation of the effect of internal waves on the dynamic behavior of an asymmetric ventilated supercavity[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 233: 109193. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109193 [121] Moltani A A, PasandidehFard M, Erfanian M R. Experimental and numerical study of free surface effect on the ventilated cavitating flow around a surface vehicle model[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 268: 113413. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113413 [122] 许海雨, 罗凯, 黄闯, 等. 低弗劳德数通气超空泡初生及发展演变特性[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2021, 13(8): 628-640.Xu Haiyu, Luo Kai, Huang Chuang, et al. Numerical investigation of supercavity geometry and gas leakage behavior for the ventilated supercavities with the twin-vortex and the re-entrant jet modes[J]. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 2021, 13(8): 628-640. [123] 王科燕, 邓飞, 张衡, 等. 超空泡航行器扩张尾裙流体动力特性试验研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2016, 50(1): 53-58. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201601009Wang Keyan, Deng Fei, Zhang Heng, et al. Experimental research on hydrodynamic characteristics of supercavitating vehicle expansion sterns[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2016, 50(1): 53-58. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201601009 [124] 施红辉, 孙亚亚, 周杨洁, 等. 水下航行体表面凹槽数对超空泡流场影响的数值模拟[J]. 弹道学报, 2017, 29(1): 44-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2017.01.008Shi Honghui, Sun Yaya, Zhou Yangjie, et al. Numerical study of the supercavitation flow-field around underwater vehicle with different surface-grooves[J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2017, 29(1): 44-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2017.01.008 [125] Jiang Y H, Zou Z H, Li J, et al. Numerical analysis of a ventilated supercavity under periodic motion of the cavitator[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2021, 33(6): 1216-1229. doi: 10.1007/s42241-021-0103-z [126] 陈鑫, 鲁传敬, 吴磊. 通气超空泡的形态特性研究[J]. 弹道学报, 2005, 17(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2005.01.001Chen Xin, Lu Chuanjing, Wu Lei. The investigation on morphology of ventilated supercavity[J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2005, 17(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2005.01.001 [127] 王海斌, 张嘉钟, 魏英杰, 等. 空泡形态与典型空化器参数关系的研究——小空泡数下的发展空泡形态[J]. 水动力学研究与进展(A辑), 2005, 20(2): 251-257.Wang Haibin, Zhang Jiazhong, Wei Yingjie, et al. Study on relations between cavity form and typical cavitor parameters[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics: A, 2005, 20(2): 251-257. [128] Jia L P, Wang C, Wei Y J, et al. Numerical simulation of artificial ventilated cavity[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. B, 2006, 18(3): 273-279. [129] 蒋增辉, 于开平, 张嘉钟, 等. 不同尾部超空泡航行体阻力特性数值模拟研究[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2007(5): 14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1300.2007.05.004Jiang Zenghui, Yu Kaiping, Zhang Jiazhong, et al. Numerical simulation of drag characters of supercavity vehicles with various afterbodies[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2007(5): 14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1300.2007.05.004 [130] Ahn B K, Kim H T, Lee C S. Experimental and numerical studies on super-cavitating flow of axisymmetric cavitators[C]//International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering. Shanghai, China: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2010. [131] Mansour M Y, Mansour M H, Mostafa N H, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation of supercavitating flow development over different nose shape projectiles[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 45(4): 1370-1385. [132] Prichard R, Strasser W, Eldredge T. Cavitation number as a function of disk cavitator radius: a numerical analysis of natural supercavitation[C]//ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. Salt Lake City, Utah, Usa: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2019. [133] Kim D H, Paramanantham S S, Park W G. Numerical analysis of multi-phase flow around supercavitating body at various cavitator angle of attack and ventilation mass flux[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(12): 4228. doi: 10.3390/app10124228 -




 下载:
下载: