Feature Selection of Scale Target Recognition by Underwater Acoustic Homing Weapons Based on Random Forest
-
摘要:
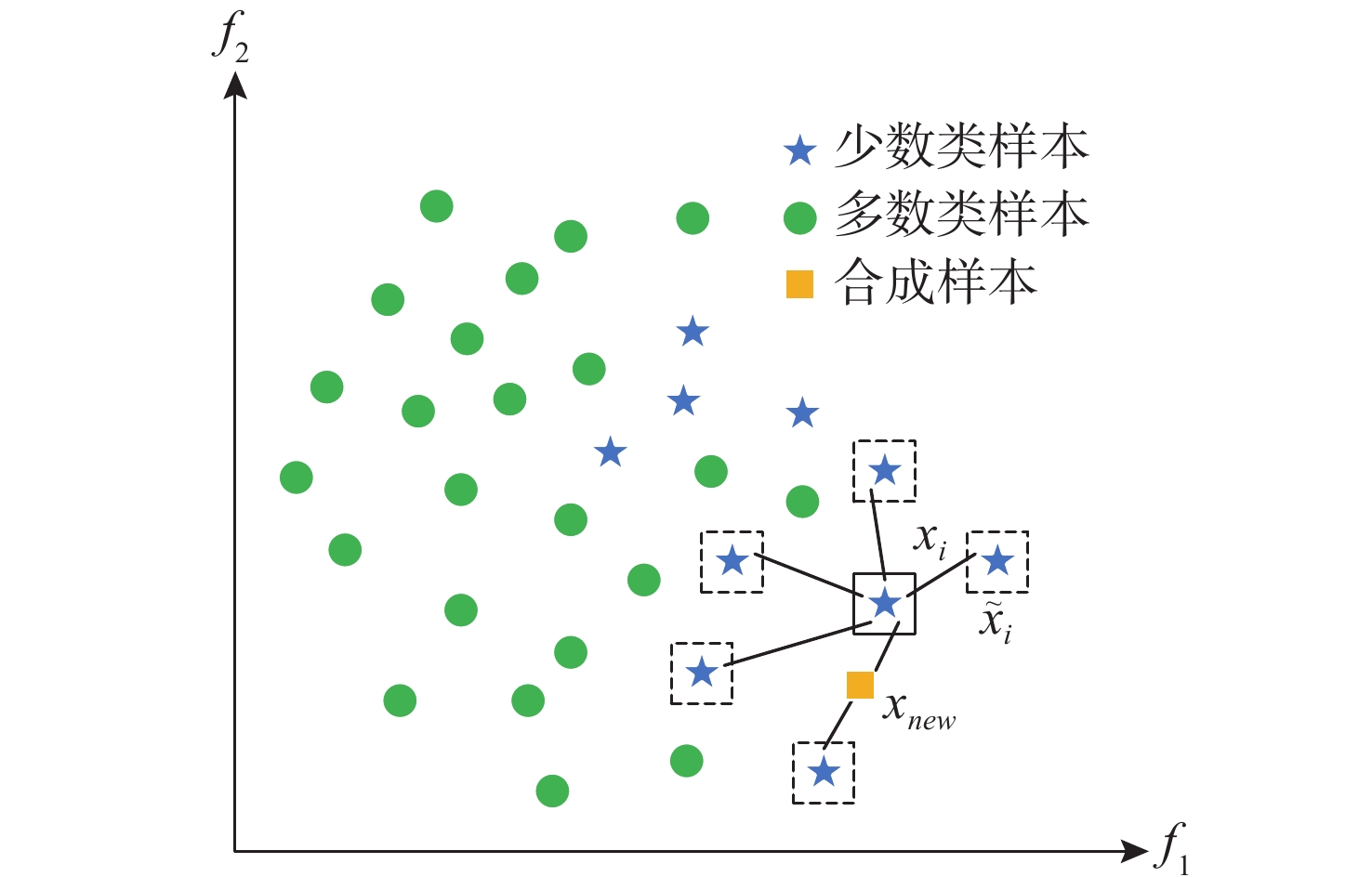
水下声自导武器在进行水下尺度目标识别时, 通常需要从水下目标回波中提取不同维度特征, 并将其进行组合形成互补的特征集合以提高识别率。然而, 由于特征的应用场景不同, 将所有特征全部引入会导致特征集维度较高, 特征之间可能包含冗余信息, 导致识别难度增加。文中针对水下声自导武器主动识别问题中特征集维度高、需要进行选择的问题, 提出了一种基于随机森林的特征寻优算法。同时, 针对水下声自导武器主动回波数据量少且种类不平衡的问题, 在特征域采用合成少数类过采样技术。利用实航数据将文中方法选择的特征子集输入分类器进行测试, 结果表明, 该方法可获得较好的特征子集, 能够有效提高识别率。 Abstract: When underwater acoustic homing weapons identify underwater scale targets, it is necessary to extract different dimensional features from underwater target echoes and combine the features to form a complementary feature set to improve the recognition accuracy. However, due to the different application scenarios of different features, introducing all features leads to a high dimension of the feature set and may contain redundant information among each other, which will increase the difficulty of recognition. In the active recognition problem of underwater acoustic homing weapons, the feature set has a high dimension and needs to be selected. To solve these problems, a feature selection algorithm based on random forest(RF)was proposed in this paper. At the same time, to solve the problem of small amounts and unbalanced types of active echo data of underwater acoustic homing weapons, the synthetic minority oversampling technique was adopted in the feature domain. The feature subsets selected by the proposed method were put into the classifiers for testing by using real data. The results show that the proposed method can obtain better feature subsets and effectively improve the recognition accuracy. -
表 1 二分类混淆矩阵
Table 1. Two-class confusion matrix
真实情况 预测结果 正例 反例 正例 $ TP $(真正例) $ FN $(假反例) 反例 $ FP $(假正例) $ TN $(真反例) 表 2 KNN分类结果
Table 2. Classification results of KNN
评价指标 原始数据集 扩容数据集 均值变化量 ACC 0.965±0.023 0.975±0.018 0.010 AUC 0.932±0.035 0.989±0.024 0.057 F1 0.843±0.118 0.976±0.018 0.133 表 3 SVM分类结果
Table 3. Classification results of SVM
评价指标 原始数据集 扩容数据集 均值变化量 ACC 0.965±0.026 0.967±0.026 0.002 AUC 0.941±0.041 0.999±0.001 0.058 F1 0.848±0.128 0.963±0.028 0.115 表 4 基于KNN的ROC曲线下面积
Table 4. Area under ROC curve based on KNN
特征数量 均值 标准差 1 0.9 991 0.0 001 2 0.9 986 0.0 021 3 0.9 980 0.0 002 4 0.9 963 0.0 032 5 0.9 962 0.0 031 6 0.9 988 0.0 011 7 0.9 938 0.0 037 8 0.9 933 0.0 035 9 0.9 886 0.0 164 10 0.9 898 0.0 170 11 0.9 911 0.0 172 12 0.9 887 0.0 167 表 5 基于SVM的ROC曲线下面积
Table 5. Area under ROC curve based on SVM
特征数量 均值 标准差 1 0.9 959 0.0 040 2 0.9 954 0.0 042 3 0.9 951 0.0 048 4 0.9 953 0.0 045 5 0.9 993 0.0 006 6 0.9 996 0.0 002 7 0.9 995 0.0 001 8 0.9 997 0.0 002 9 0.9 997 0.0 002 10 0.9 997 0.0 001 11 0.9 998 0.0 001 12 0.9 998 0.0 001 -
[1] 周德善, 李志舜, 朱邦元. 鱼雷自导技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2009. [2] 何心怡, 高贺, 陈菁, 等. 鱼雷真假目标识别技术现状与展望[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2016, 24(1): 23-27.HE X Y, GAO H, CHEN J, et al. Current situation and prospect on torpedo's true/false target identification technologies[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2016, 24(1): 23-27. [3] 石敏, 陈立纲, 蒋兴舟, 等. 具有亮点和方位延展特征的线列阵声诱饵研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2005, 17(1): 58-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3486.2005.01.014 [4] 徐枫, 严冰, 王海陆, 等. 水下声自导武器垂直目标亮点高分辨算法仿真与实验研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2009, 17(6): 35-40.XU F, YAN B, WANG H L, et al. Simulation and experimental study of a high-resolution method for torpedo vertical highlights[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2009, 17(6): 35-40. [5] 胡桥, 郝保安, 吕林夏, 等. 基于组合支持向量机的水声目标智能识别研究[J]. 应用声学, 2009, 28(6): 421-430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-310X.2009.06.004HU Q, HAO B A, LÜ L X, et al. Intelligent underwater-acoustic-target recognition based on combination support vector machine[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2009, 28(6): 421-430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-310X.2009.06.004 [6] ZHANG S, LI C, WANG K, et al. Improving recognition accuracy of partial discharge patterns by image oriented feature extraction and selection technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2016, 23(2): 1076-1087. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2015.005226 [7] Strobl C, Boulesteix A L, Kneib T, et al. Conditional variable importance for random forest[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2008, 9(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-1 [8] CHAWLA N V, BOWYER K W, HALL L O, et al. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002, 16: 321-357 doi: 10.1613/jair.953 [9] 王干军, 李锦舒, 吴毅江, 等. 基于随机森林的高压电缆局部放电特征寻优[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(4): 1329-1335.WANG G J, LI J S, WU Y J, et al. Random forest based feature selection for partial discharge recognition of HV cables[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(4): 1329-1335. [10] O’BRIEN, ROBRET, ISHWARAN H. A random forests quantile classifier for class imbalanced data[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 90: 232-249. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.01.036 [11] Bader-El-Den M, TEITEI E, PERRY T. Biased random forest for dealing with the class imbalance problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(7): 2163-2172. [12] Hasan M A M, Nasser M, Ahmad S, et al. Feature selection for intrusion detection using random forest[J]. Journal of Information Security, 2016, 7(3): 129-140. doi: 10.4236/jis.2016.73009 -





 下载:
下载: