Identification of Unmanned Surface Vehicle Maneuverability Parameters Based on Improved WLSSVM
-
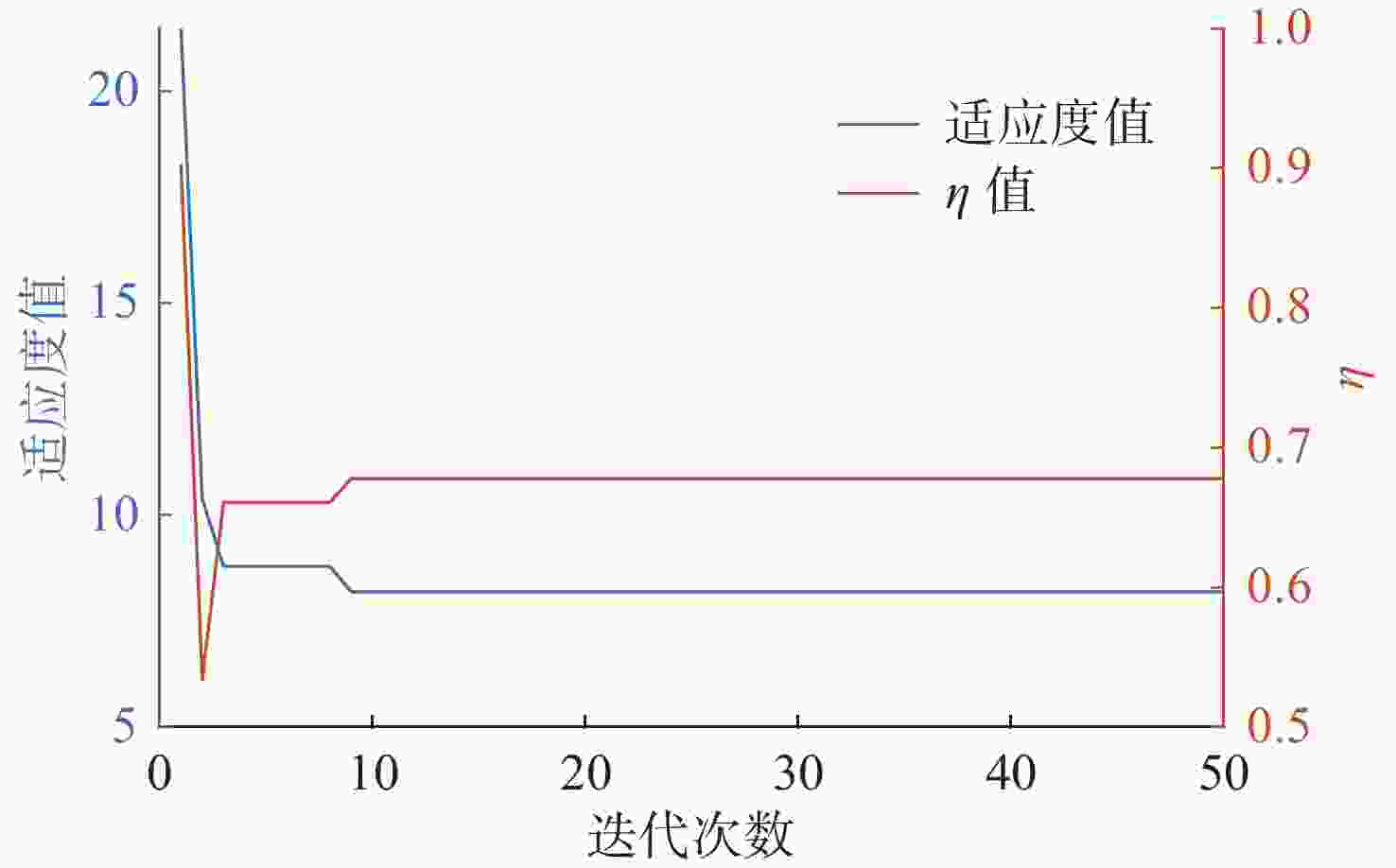
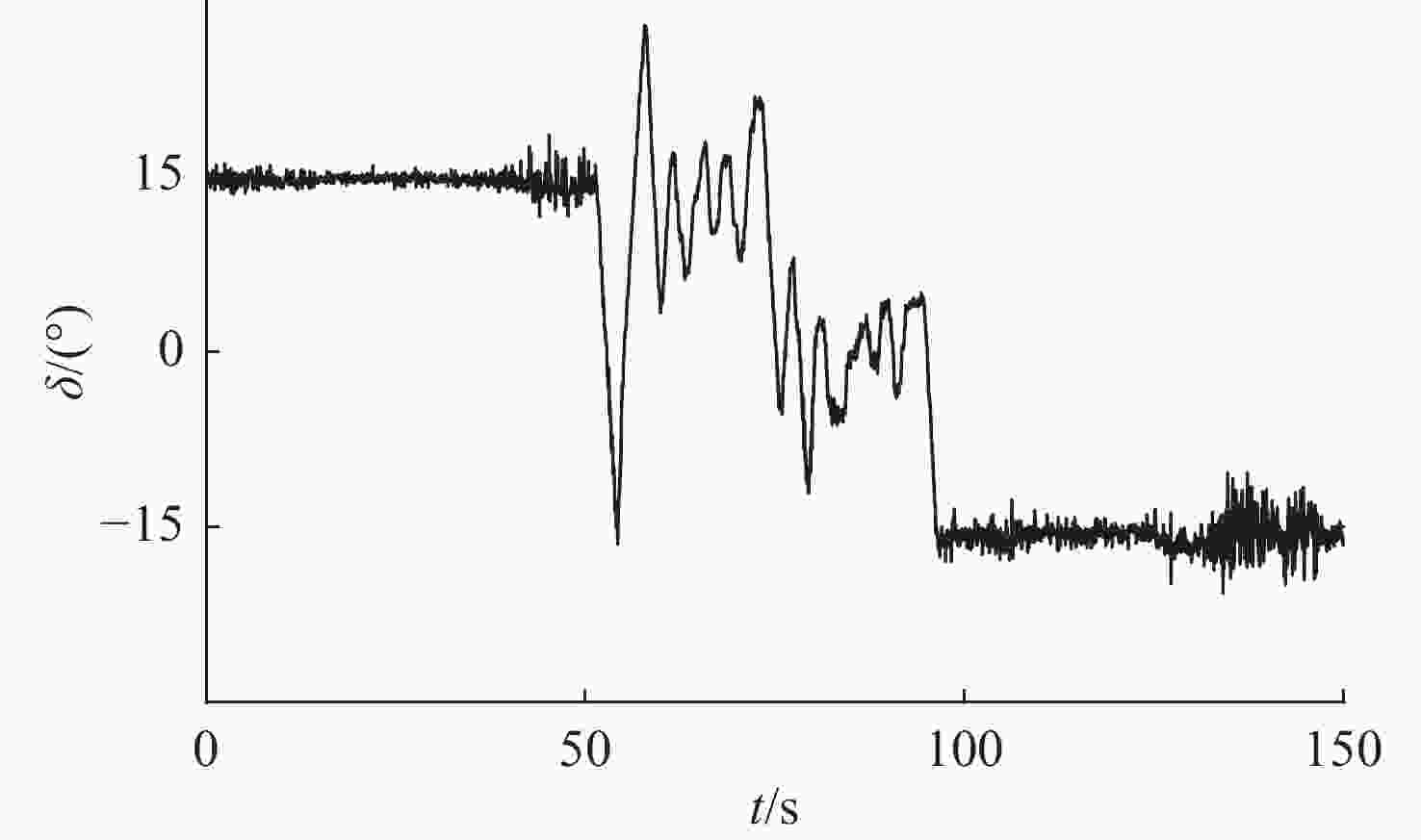
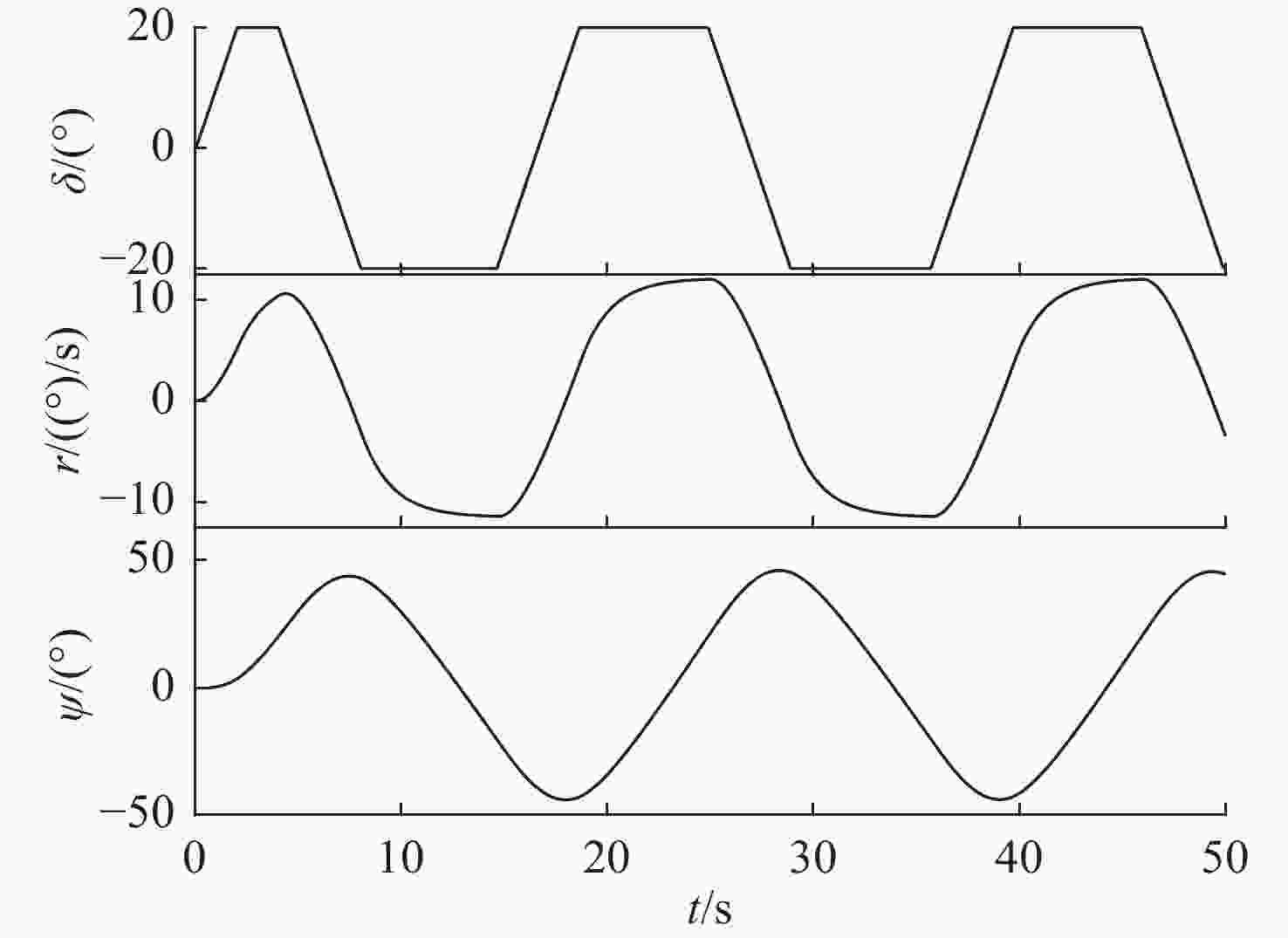
摘要: 为了实现高精度的无人艇操纵运动辨识建模, 针对最小二乘支持向量机(LSSVM)辨识无人艇2阶非线性响应模型时, 部分参数会辨识不准的问题, 设计了余弦处理方法, 对辨识模型进行重构; 为进一步提高辨识精度, 在此基础上根据数据加权思想, 结合引入变异策略的自适应粒子群算法, 提出了一种可对权值寻优的加权最小二乘支持向量机(WLSSVM)算法。基于仿真数据和实船数据的辨识结果表明, 余弦方法重构后的模型很好地解决了参数辨识不准的问题, 权值寻优后的WLSSVM进行参数辨识建模具有更高的预报精度。研究结果能够为无人艇操纵运动的高精度参数辨识建模提供参考。Abstract: A cosine processing method was designed to achieve high-precision identification modeling of unmanned surface vehicle(USV) maneuvering motion and address the issue that some parameters will be inaccurately identified when the second-order nonlinear response model of USVs is identified by least square support vector machine(LSSVM). On this premise, a weighted LSSVM(WLSSVM) algorithm that could optimize the weight was proposed. The algorithm was based on the idea of data weighting and used the adaptive particle swarm optimization technique with a mutation approach. Based on simulation data and actual ship data, the identification results indicate that the model after cosine reconstruction effectively handles the problem of inaccurate parameter identification. At the same time, the WLSSVM with optimized weights has better prediction accuracy for parameter identification modeling. The research findings can serve as a reference for high-precision parameter identification modeling of USV maneuvering motion.
-
表 1 船舶模型参数
Table 1. Ship model parameters
参数名 ${T_1}$ ${T_2}$ ${T_3}$ K $\;\beta $ ${\delta _r}$ 参数值 1.439 7 0.120 2 0.044 0 0.588 3 −0.123 9 0.009 3 表 2 基于仿真数据的参数辨识结果
Table 2. Parameter identification results based on simulation data
参数名 真实值 原始模型+LSSVM 模型重构+LSSVM 原始模型+变异APSO-WLSSVM 模型重构+变异APSO-WLSSVM 辨识结果 相对误差/% 辨识结果 相对误差/% 辨识结果 相对误差/% 辨识结果 相对误差/% ${T_1}$ 1.439 7 1.463 2 1.63 1.463 5 1.65 1.463 2 1.63 1.464 7 1.74 ${T_2}$ 0.120 2 0.147 7 22.88 0.147 9 23.04 0.147 7 22.88 0.147 0 22.30 ${T_3}$ 0.044 0 0.070 7 60.68 0.071 0 61.36 0.070 7 60.68 0.070 9 61.14 K 0.588 3 0.587 9 −0.07 0.588 1 −0.03 0.587 9 −0.07 0.588 3 0 $\beta $ −0.123 9 −0.134 6 8.64 −0.124 9 0.81 −0.134 6 8.64 −0.123 3 −0.48 ${\delta _r}$ 0.009 3 0 −100.00 0.009 3 0 0 −100.00 0.009 3 0 表 3 基于仿真实验数据的辨识建模预报误差
Table 3. Prediction error of identification modeling based on simulation experimental data
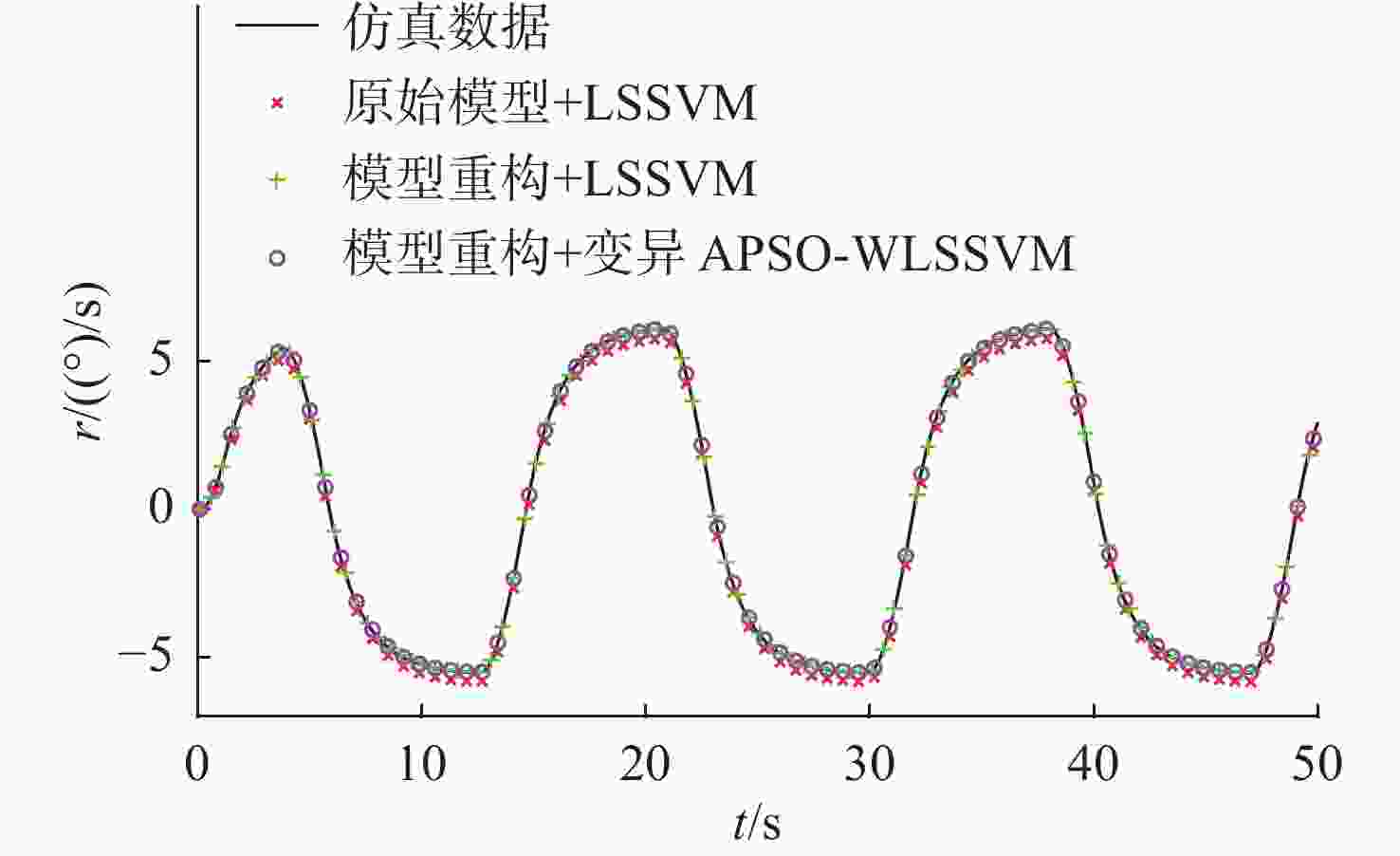
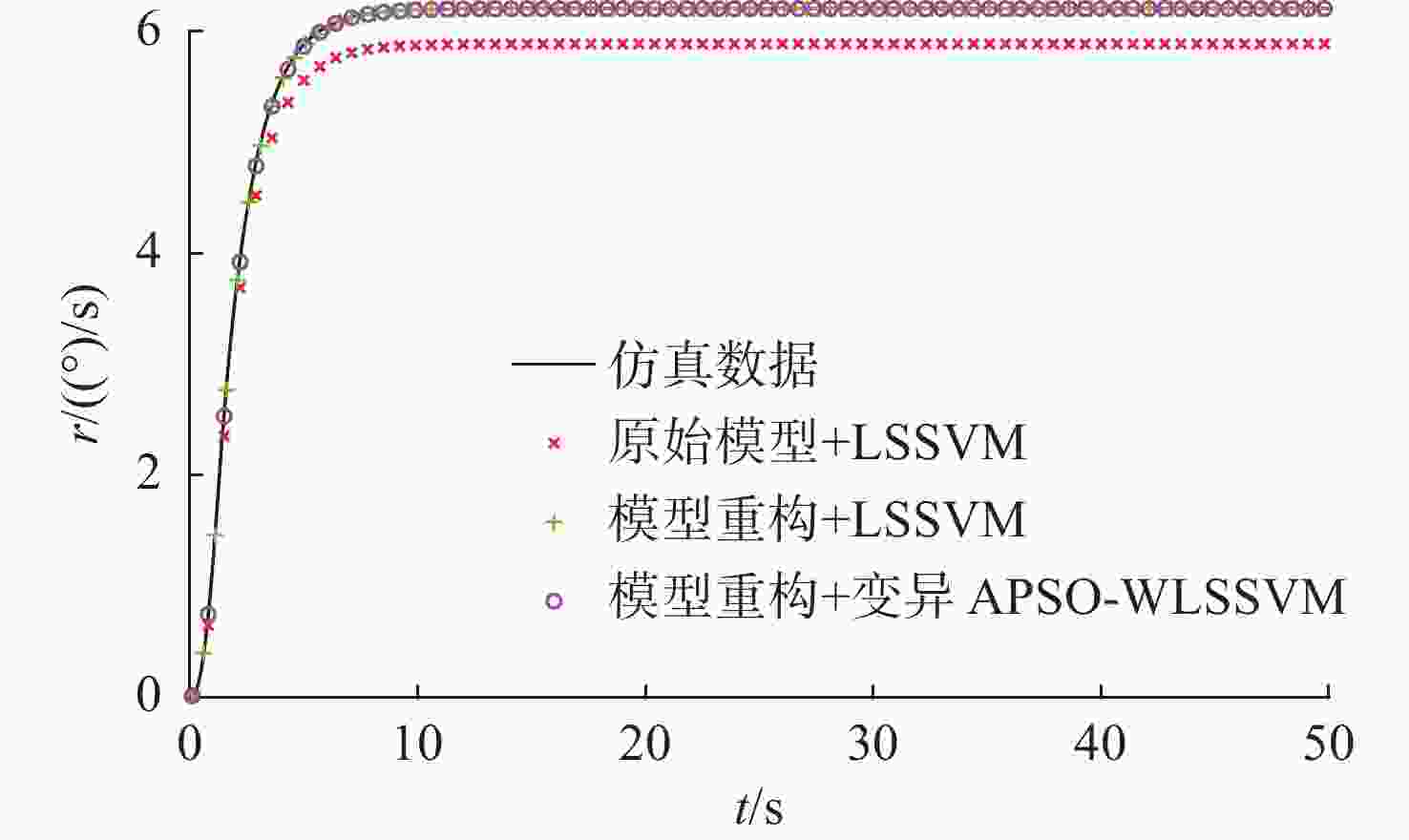
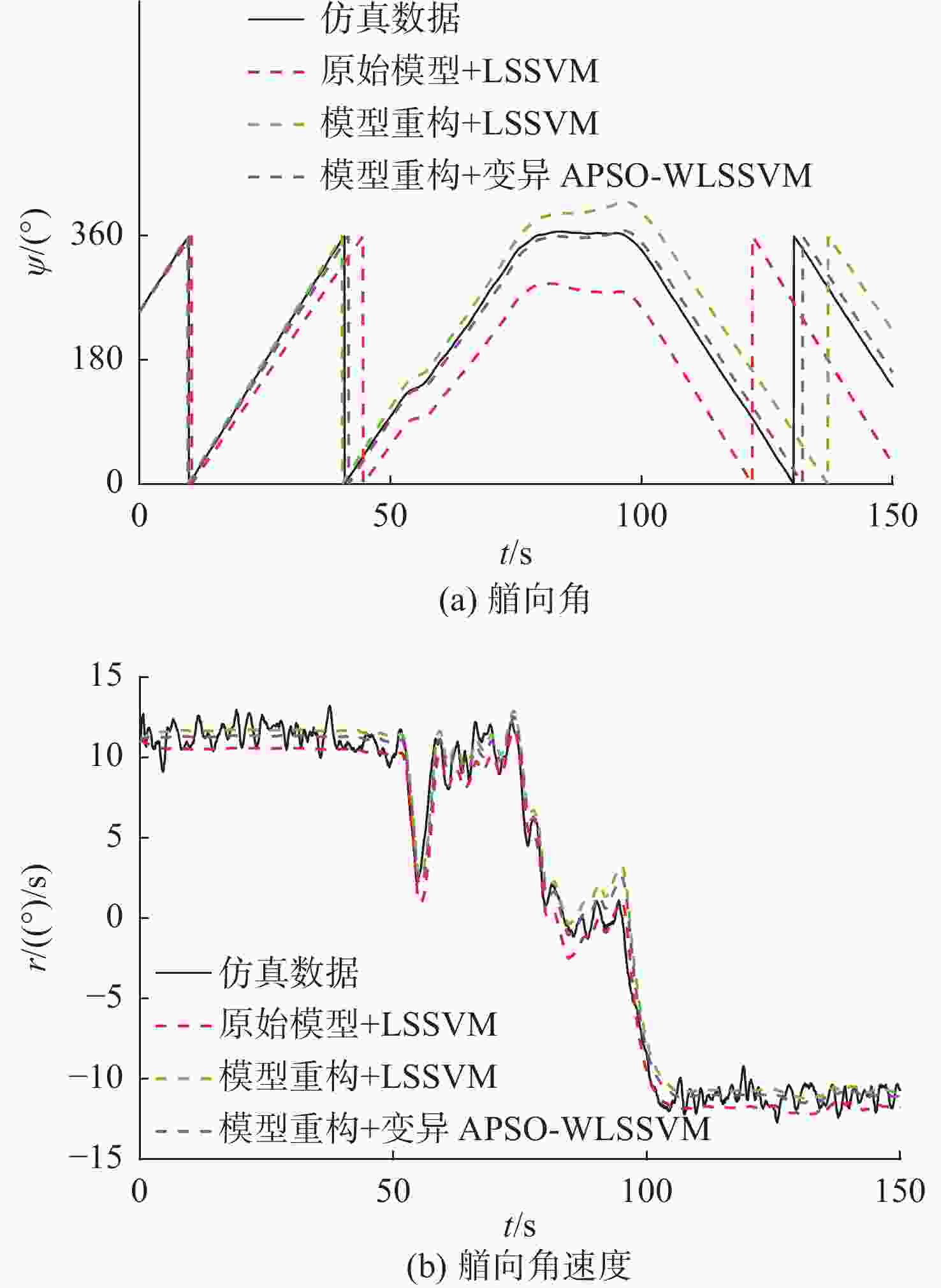
名称 RMSE $ \psi $ r 原始模型+LSSVM 8.704 4 0.317 8 模型重构+LSSVM 0.208 8 0.064 5 模型重构+变异APSO-WLSSVM 0.207 0 0.064 0 表 4 10°/10°Z形操纵运动及10°回转运动预报误差
Table 4. Prediction error of 10°/10° zigzag maneuvering motion and 10° rotary motion
名称 Z形操纵运动RMSE 回转运动RMSE $ \psi $ r $ \psi $ r 原始模型+LSSVM 8.592 3 0.307 7 8.945 4 0.312 9 模型重构+LSSVM 0.101 9 0.039 7 0.184 9 0.009 6 模型重构+变异APSO-WLSSVM 0.101 1 0.039 4 0.137 3 0.009 0 表 5 无人艇部分参数
Table 5. Parameters of the USV
垂线间长/m 型宽/m 吃水/m 空船质量/t 7.500 2.600 0.567 2.970 表 6 基于实船数据的参数辨识结果
Table 6. Parameter identification results based on actual ship data
参数名 原始模型+
LSSVM模型重构+
LSSVM模型重构+
变异APSO-
WLSSVM$ T_{1} $ 4.227 8 4.407 6 4.304 0 $ T_{2} $ 0.069 3 0.069 4 0.069 6 $ T_{3} $ 0.049 2 0.038 0 0.036 6 K 0.988 7 1.018 8 0.994 1 $\beta $ 9.053 5 9.884 3 9.228 0 $ \delta_{r} $ −0.000 1 0.024 3 0.012 0 表 7 基于实船试验数据的辨识建模预报误差
Table 7. Prediction error of identification modeling based on actual ship experimental data
名称 RMSE $ \psi $ r 原始模型+LSSVM 79.472 3 1.105 9 模型重构+LSSVM 52.081 5 1.035 2 模型重构+变异APSO-WLSSVM 13.734 2 0.870 4 -
[1] 郑华荣, 魏艳, 瞿逢重. 水面无人艇研究现状[J]. 中国造船, 2020, 61(z1): 228-240.Zheng Huarong, Wei Yan, Qu Fengzhong. Review on recent developments of unmanned marine surface vessels[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2020, 61(z1): 228-240. [2] 田延飞. 实船试验操纵运动建模与参数辨识研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2018. [3] 赵百岗, 张显库, 李争, 等. 船舶运动辨识建模研究现状与展望[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2021, 43(23): 21-24. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2021.12.004Zhao Baigang, Zhang Xianku, Li Zheng, et al. Research on ship motion identification modelling[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2021, 43(23): 21-24. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2021.12.004 [4] 梅斌. 基于自航试验的船舶操纵运动灰箱辨识建模[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2020. [5] 秦余钢, 马勇, 张亮, 等. 基于改进最小二乘算法的船舶操纵性参数辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 897-903.Qin Yugang, Ma Yong, Zhang Liang, et al. Parameter identification of ship’s maneuvering motion based on improved least square method[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(3): 897-903. [6] 谢朔, 初秀民, 柳晨光, 等. 基于多新息最小二乘法的船舶操纵响应模型参数辨识[J]. 中国航海, 2017, 40(1): 73-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2017.01.016Xie Shuo, Chu Xiumin, Liu Chenguang, et al. Parameter identification of ship maneuvering response model based on multi-innovation least squares algorithm[J]. Navigation of China, 2017, 40(1): 73-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2017.01.016 [7] 孙功武, 谢基榕, 王俊轩. 基于动态遗忘因子递推最小二乘算法的船舶航向模型辨识[J]. 计算机应用, 2018, 38(3): 900-904.Sun Gongwu, Xie Jirong, Wang Junxuan. Ship course identification model based on recursive least squares algorithm with dynamic forgetting factor[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2018, 38(3): 900-904. [8] Zhao B G, Zhang X K. An improved nonlinear innovation-based parameter identification algorithm for ship models[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2021, 74(3): 549-557. doi: 10.1017/S0373463321000102 [9] 包政凯, 朱齐丹, 刘永超. 满秩分解最小二乘法船舶航向模型辨识[J]. 智能系统学报, 2022, 17(1): 137-143.Bao Zhengkai, Zhu Qidan, Liu Yongchao. Ship heading model identification based on full rank decomposition least square method[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2022, 17(1): 137-143. [10] 褚式新, 茅云生, 董早鹏, 等. 基于极大似然法的高速无人艇操纵响应模型参数辨识[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(1): 127-134.Chu Shixin, Mao Yunsheng, Dong Zaopeng, et al. Parameter identification of high-speed USV maneuvering response model based on maximum likelihood algorithm[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(1): 127-134. [11] Chen H L, Li Q, Wang Z Y. Improved maximum likelihood method for ship parameter identification[C]//2018 37th Chinese Control Conference. Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2018: 1614-1621. [12] Xie S, Chu X M, Liu C G, et al. Parameter identification of ship motion model based on multi-innovation methods[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2020, 25(1): 162-184. doi: 10.1007/s00773-019-00639-y [13] 秦操. 基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的船舶运动数学模型辨识[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2021, 43(1): 89-94.Qin Cao. Parameter identification for ship mathematical model based on unscented Kalman filter[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2021, 43(1): 89-94. [14] Zheng J, Yan D W, Yan M, et al. An unscented kalman filter online identification approach for a nonlinear ship motion model using a self-navigation test[J]. Machines, 2022, 10(5): 312. doi: 10.3390/machines10050312 [15] Wang S, Wang L J, Im N, et al. Real-time parameter identification of ship maneuvering response model based on nonlinear Gaussian filter[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 247: 110471. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.110471 [16] Jiang Y, Wang X G, Zou Z J, et al. Identification of coupled response models for ship steering and roll motion using support vector machines[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2021, 110: 102607. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2021.102607 [17] Wang Z H, Zou Z J, Soares C G. Identification of ship manoeuvring motion based on nu-support vector machine[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 183: 270-281. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.04.085 [18] Xu H T, Soares C G. Hydrodynamic coefficient estimation for ship manoeuvring in shallow water using an optimal truncated LS-SVM[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 191: 106488. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106488 [19] Xu H T, Hinostroza M A, Wang Z H, et al. Experimental investigation of shallow water effect on vessel steering model using system identification method[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 199: 106940. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.106940 [20] Zhu M, Hahn A, Wen Y Q, et al. Optimized support vector regression algorithm-based modeling of ship dynamics[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2019, 90: 101842. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2019.05.027 [21] 谢朔, 初秀民, 柳晨光, 等. 基于改进 LSSVM 的船舶操纵运动模型在线参数辨识方法[J]. 中国造船, 2018, 59(2): 178-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2018.02.019Xie Shuo, Chu Xiumin, Liu Chenguang, et al. Online parameter identification method for ship maneuvering models based on improved LSSVM[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2018, 59(2): 178-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2018.02.019 [22] 孙玉山, 徐昊, 曹东东, 等. 果蝇算法在基于LSSVM智能水下机器人操纵运动模型辨识中的应用[J]. 船舶工程, 2017(2): 94-98.Sun Yushan, Xu hao, Cao Dongdong, et al. Application of fruit fly optimization algorithm in model identification of maneuverability motion of underwater vehicle based on LSSVM[J]. Ship Engineering, 2017(2): 94-98. [23] 周欣然, 滕召胜, 蒋星军. 基于无偏置项LSSVM的稳健在线过程建模方法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2010, 23(6): 885-892.Zhou Xinran, Teng Zhaosheng, Jiang Xingjun. Robust online process modeling method based on non-bias LSSVM[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2010, 23(6): 885-892. [24] Luo W L, Soares C G, Zou Z J. Parameter identification of ship maneuvering model based on support vector machines and particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanics & Arctic Engineering, 2016, 138(3): 031101. [25] Zhu M, Hahn A, Wen Y Q, et al. Identification-based simplified model of large container ships using support vector machines and artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2017, 68: 249-261. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2017.09.006 [26] Xu P F, Cheng C, Cheng H X, et al. Identification-based 3 DOF model of unmanned surface vehicle using support vector machines enhanced by cuckoo search algorithm[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 197: 106898. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106898 [27] 周怡, 王俊雄. 自适应粒子群算法在AUV水动力参数辨识中的应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2021, 43(21): 90-95.Zhou Yi, Wang Junxiong. Application of adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm in AUV hydrodynamic parameter identification[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2021, 43(21): 90-95. -




 下载:
下载: