A Modeling Method of Ship Acoustic Wake Echo Signal
-
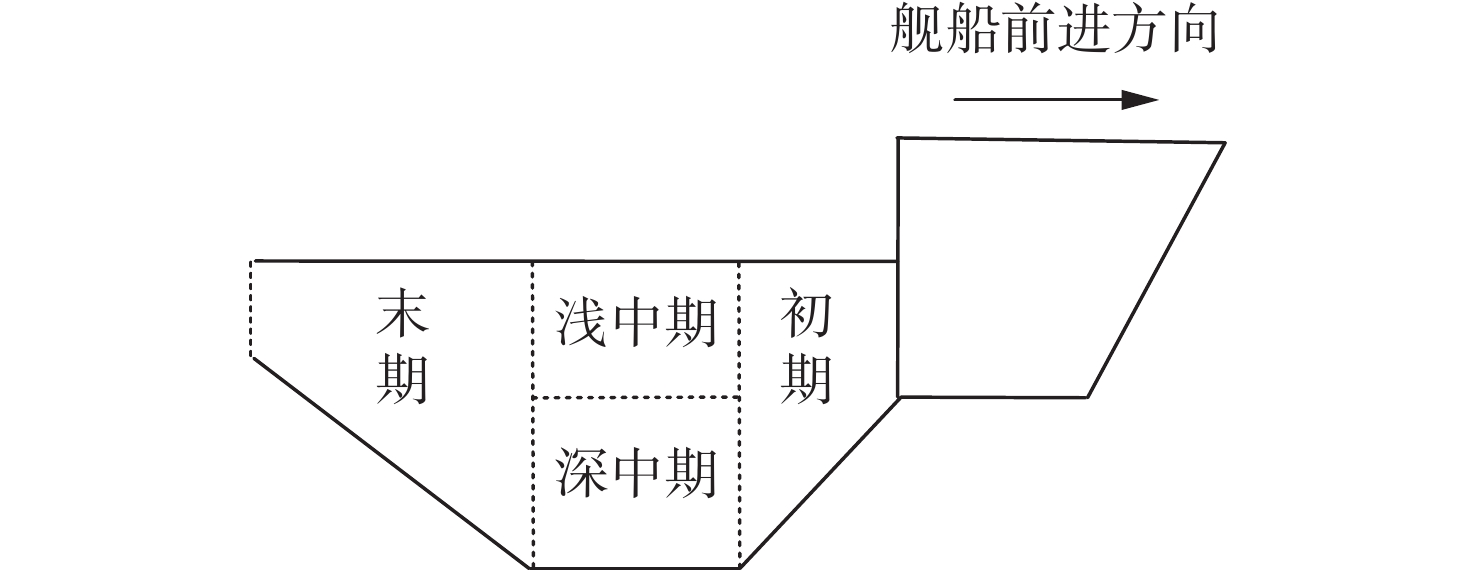
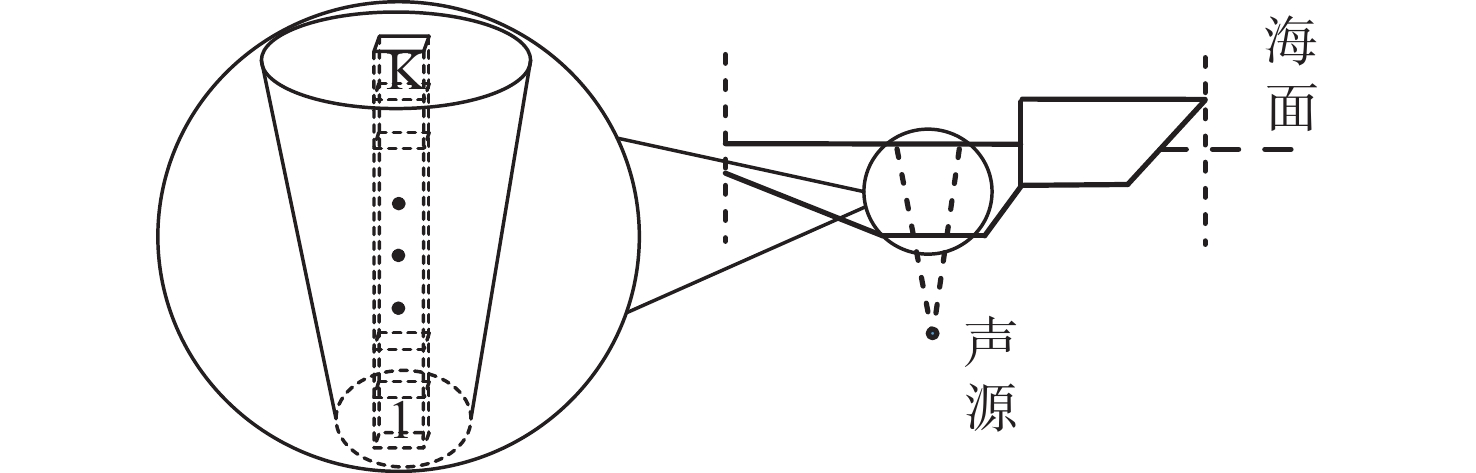
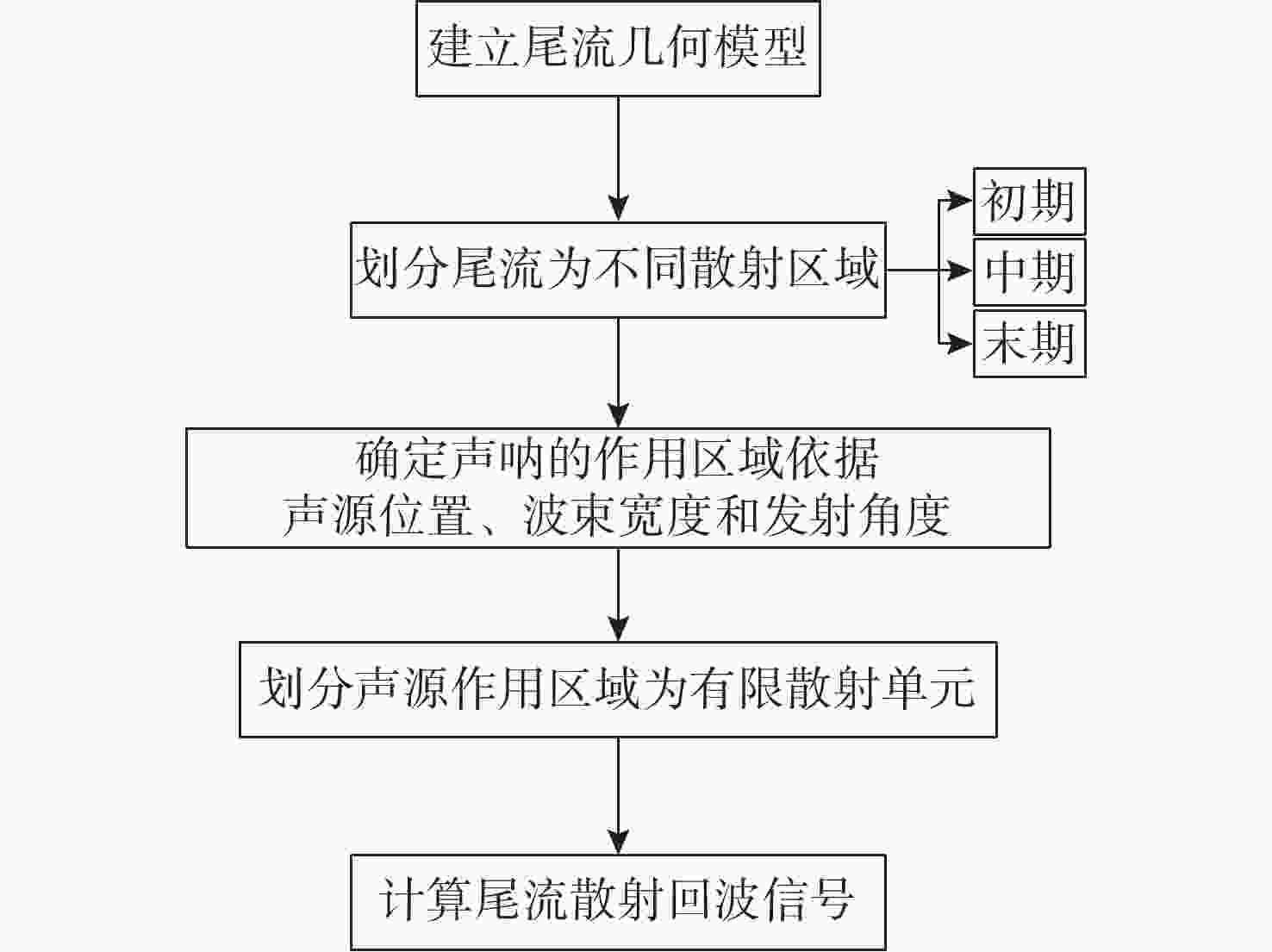
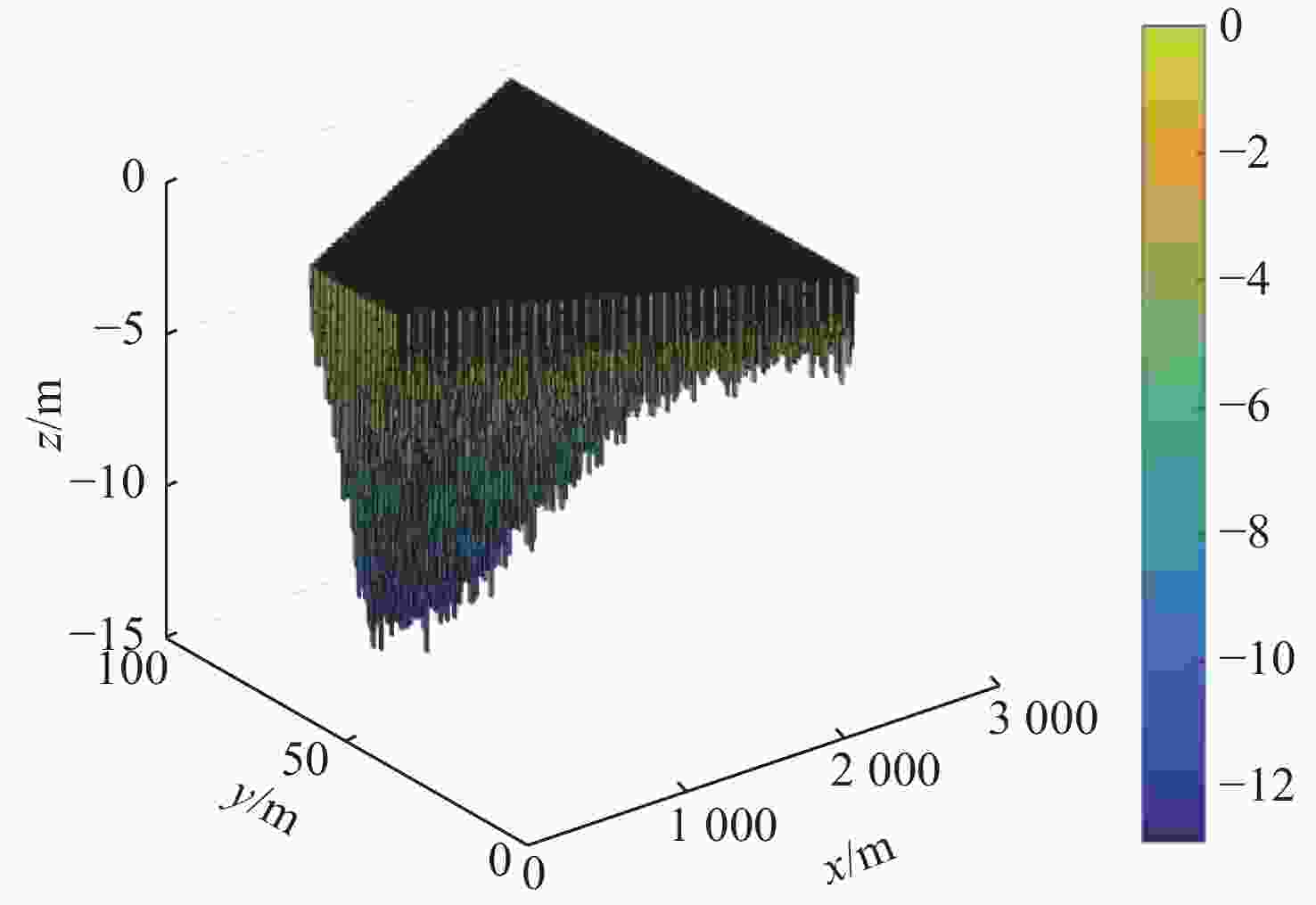
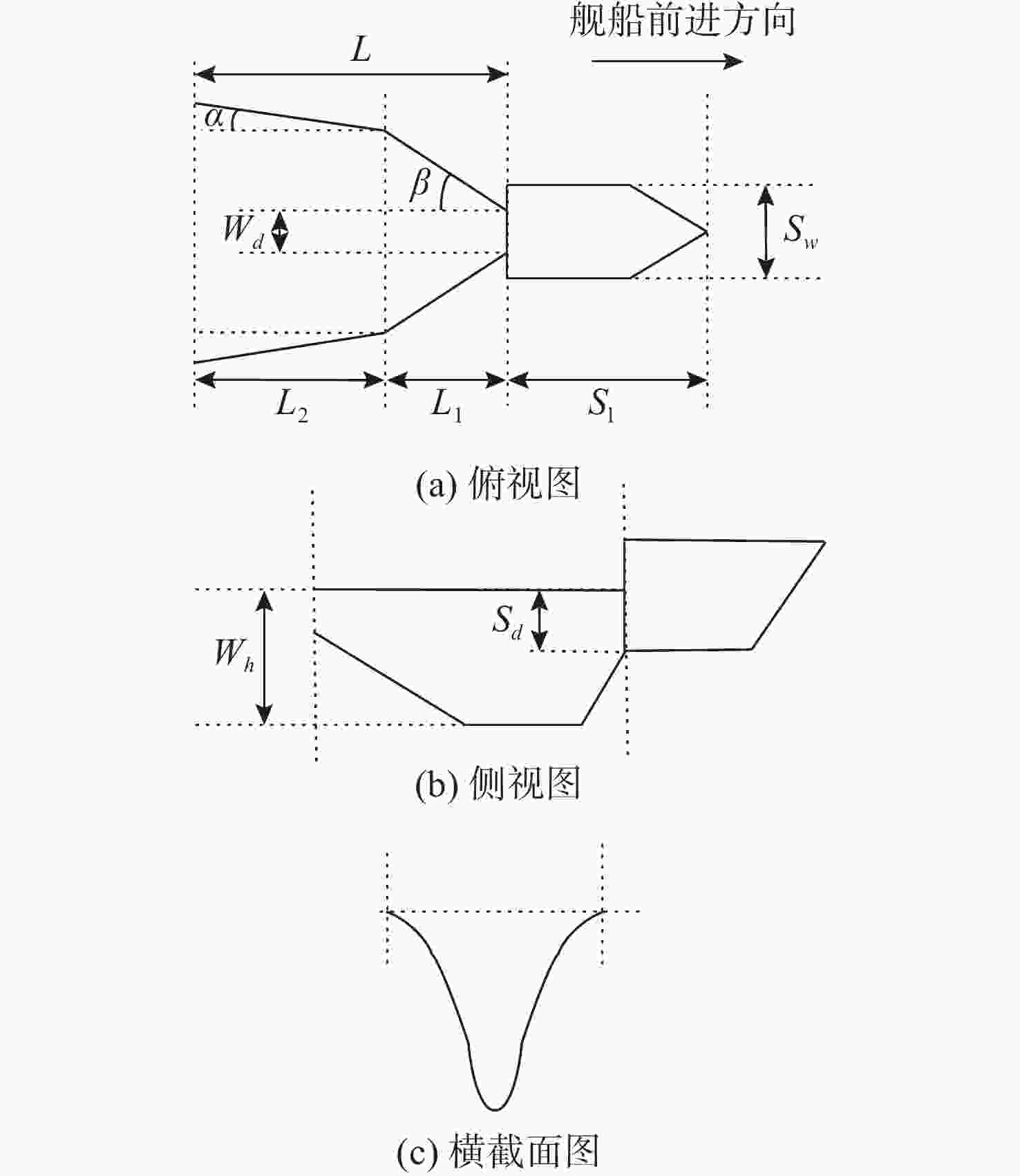
摘要: 通过声尾流回波信号模型构建仿真数据是研究舰船尾流的重要方式。文中针对已有模型忽略单个气泡散射回波的不足, 提出了一种分区域点散射模型。该模型首先依据不同舰船尺寸、航行速度和海况确定尾流几何模型, 进而根据气泡尺寸分布划分尾流为不同散射区域; 然后根据收发平台的波束宽度、位置和发射角度确定尾流自导系统作用范围; 最后划分尾流自导系统作用范围为有限散射单元, 综合考虑传播损失后根据点散射模型计算尾流散射回波信号。仿真和水箱实验结果表明, 文中所提模型可用于舰船尾流仿真, 并为进一步开展尾流检测和识别提供支撑。Abstract: It is an important way to study the ship wake by building simulation data through the acoustic wake echo signal model. At present, the scattering echo of a single bubble is ignored in the existing models. Therefore, a point scattering model for different regions was proposed in this paper. Firstly, the wake geometry model was determined according to the ship size, speed, and sea condition, and then the wake was divided into different scattering regions according to the bubble size distribution(BSD). The range of the wake homing system was determined according to the beam width, position, and launch angle of the transmitting and receiving platform. Finally, the range of the wake homing system was divided into finite scattering elements, and the scattering echo signal was calculated according to the point scattering model after considering the propagation loss. The results of simulation and water tank experiments show that the model can be used in ship wake simulation and provide support for further wake detection and identification.
-
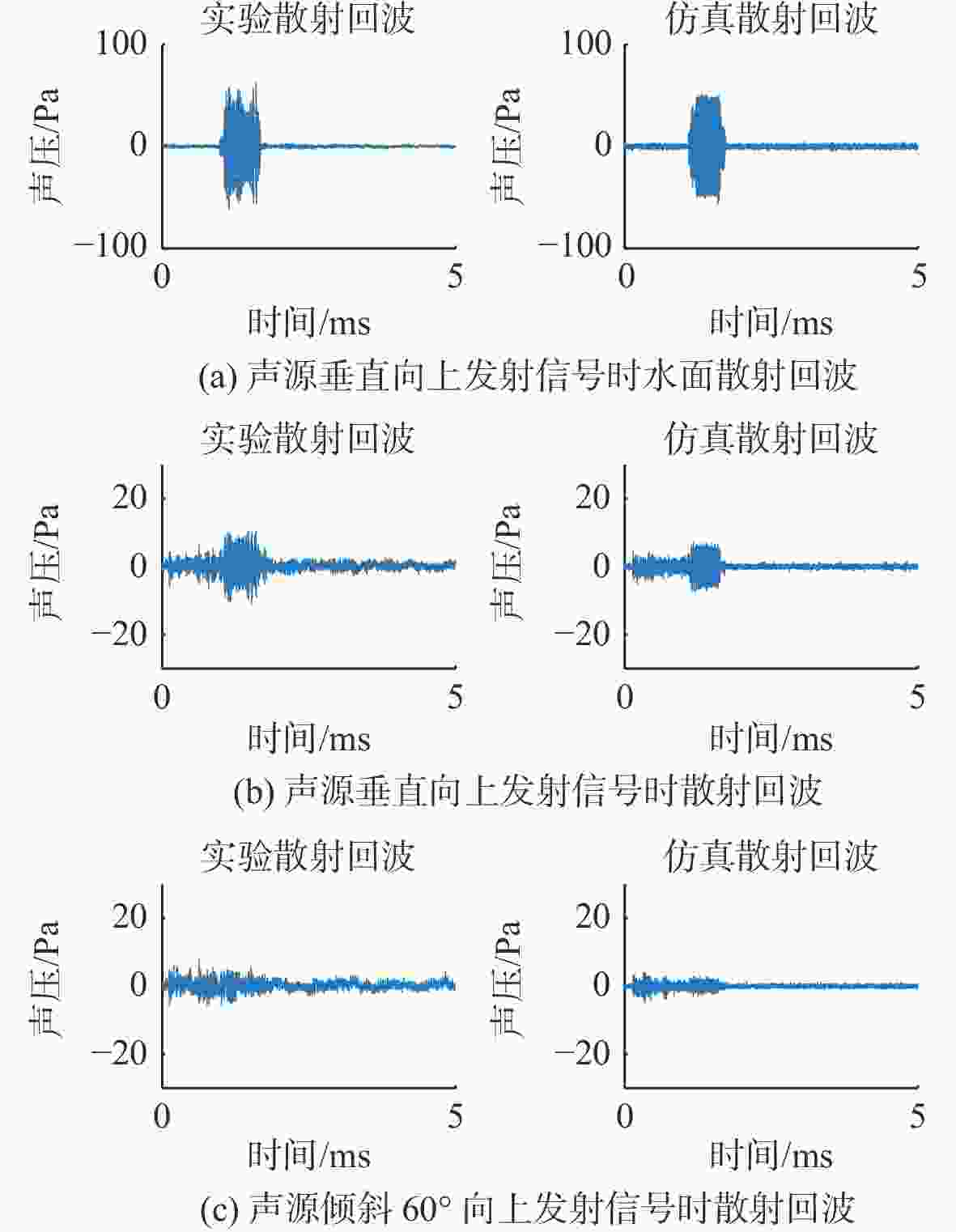
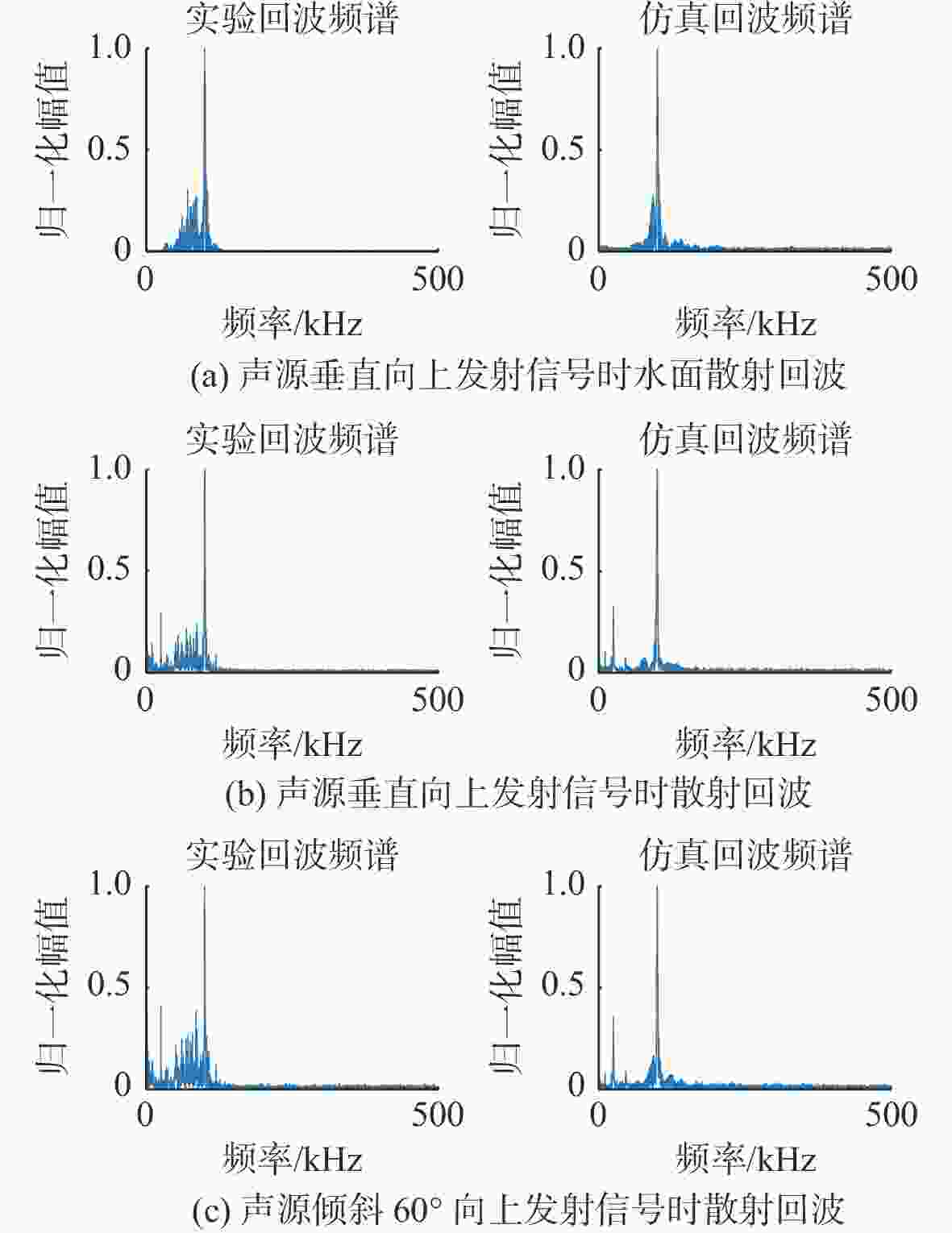
表 1 实验和仿真回波信号的平均幅度和时宽
Table 1. Average amplitude and duration of experimental and simulated echo signals
条件 实验 仿真 平均幅度/Pa 时宽/ms 平均幅度/Pa 时宽/ms A 23.96 0.7 24.5 0.69 B 5.28 1.85 6.25 1.82 C 3.52 1.89 3.45 1.83 -
[1] 赵威. 基于鱼雷自导的舰船尾流回波模型建立方法[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2013, 33(4): 81-83.Zhao Wei. Acoustic model establishment of ship wake echo waveform for self-guided torpedo[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2013, 33(4): 81-83. [2] 梁红, 刘劲波. 尾流自导鱼雷防御系统接收信号模型及参数优化[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2008, 16(4): 47-50.Liang Hong, Liu Jinbo. Receiving signal models and parameters optimization for defence system against wake homing torpedo[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2008, 16(4): 47-50. [3] 李婷, 刘纯武, 黄芝平, 等. 舰船尾流回波信号建模与仿真[J]. 计算机仿真, 2011, 28(6): 26-29.Li Ting, Liu Chunwu, Huang Zhiping, et al. Modeling and simulating of ship wake echo signal[J]. Computer Simulation, 2011, 28(6): 26-29. [4] Mistry N. A study of ship wakes and the enhancement of sonar within them[D]. Hampshir: University of Southampton, 2019. [5] 张庆国, 刘竹青, 黄其培, 等. 舰船尾流气泡声学测试系统研究[J]. 声学技术, 2020, 39(6): 660-668.Zhang Qingguo, Liu Zhuqing, Huang Qipei, et al. Research on acoustic measurement system for ship wake bubbles[J]. Acoustics Technology, 2020, 39(6): 660-668. [6] 杜敬林, 马忠成, 陈建辉, 等. 舰船尾流声散射和几何特征试验[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2010, 31(7): 909-914.Du Jinglin, Ma Zhongcheng, Chen Jianhui, et al. Sound scattering and geometric characteristics of ship wakes[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2010, 31(7): 909-914. [7] 潘逊, 张静远, 张江. 声尾流自导鱼雷导引策略仿真与优化[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2012, 24(3): 98-102.Pan Xun, Zhang Jingyuan, Zhang Jiang. Simulation and optimization of homing strategy for acoustic wake guide torpedo[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2012, 24(3): 98-102. [8] Trevorrow M V, Vagle S, Farmer D M. Acoustical measurements of microbubbles within ship wakes[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1994, 95(4): 1922-1930. doi: 10.1121/1.408706 [9] Leighton T G, White P R, Finfer D C. Bubble acoustics in shallow water: possible applications in Nature[C]//2005 International Conference on Boundary Influences in High Frequency, Shallow Water Acoustics. New York: IEEE, 2005: 433-440. [10] Leifer I, Patro R K. The bubble mechanism for methane transport from the shallow sea bed to the surface: A review and sensitivity study[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2002, 22(16): 2409-2428. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00065-1 [11] 吴丹, 陶超, 刘晓峻. 有限方位扫描的光声断层成像分辨率研究[J]. 物理学报, 2010, 59(8): 5845-5850.Wu Dan, Tao Chao, Liu Xiaojun. Study of the resolution of limited-view photoacoustic tomography[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2010, 59(8): 5845-5850. [12] Francois R E, Garrison G R. Sound absorption based on ocean measurements. Part II: Boric acid contribution and equation for total absorption[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1982, 72(6): 1879-1890. doi: 10.1121/1.388673 [13] Andreeva I B. Scattering of sound by air bladders of fish in deep sound-scattering ocean layers[J]. Sov. Phys. Acoust, 1964, 10: 17-20. [14] Keller J B, Miksis M. Bubble oscillations of large amplitude[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1980, 68(2): 628-633. doi: 10.1121/1.384720 [15] 周德善. 鱼雷自导技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2009. -




 下载:
下载: