Operational Simulation and Efficiency Analysis of Torpedo Electromagnetic Fuse Jammer
-
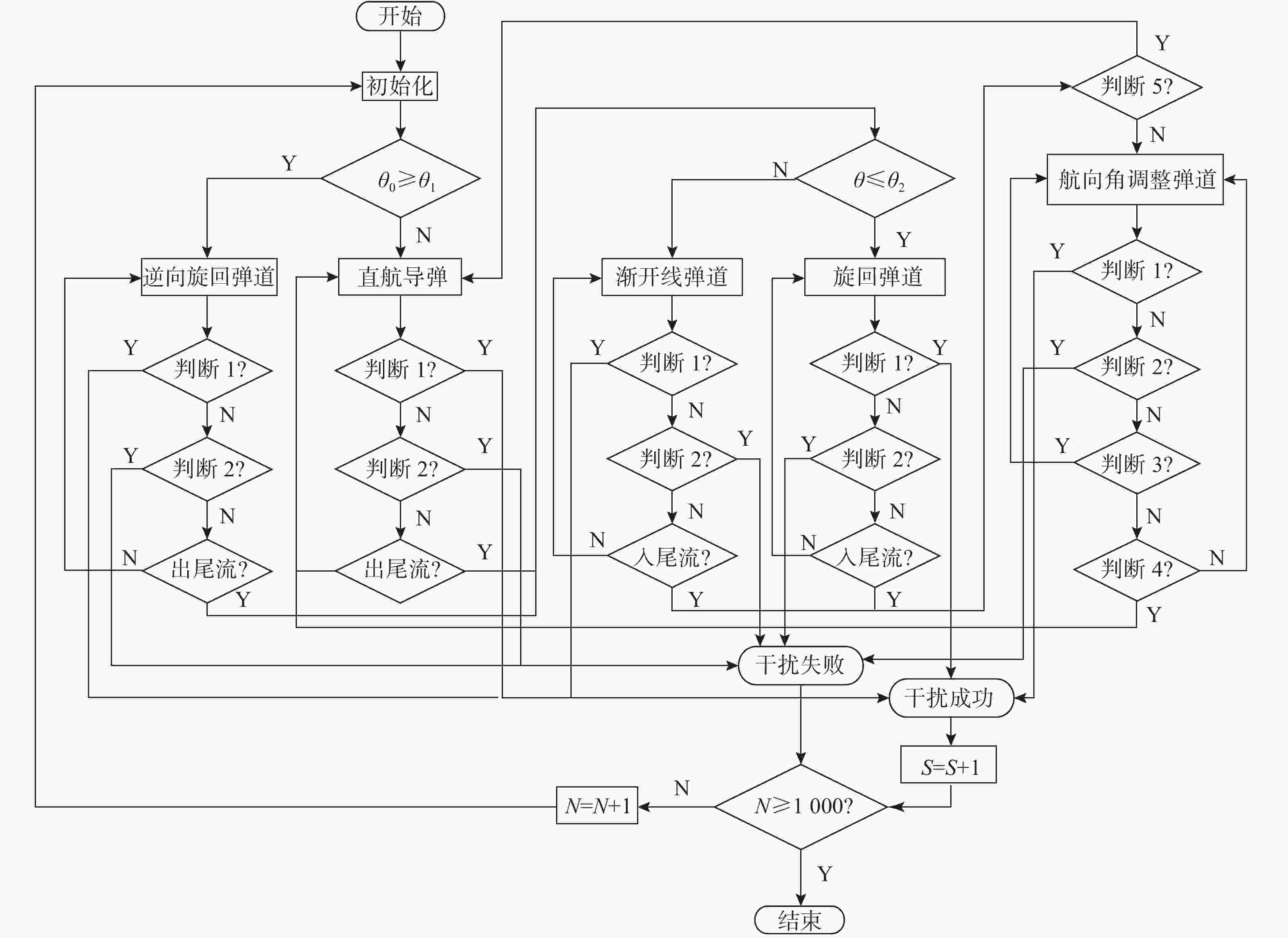
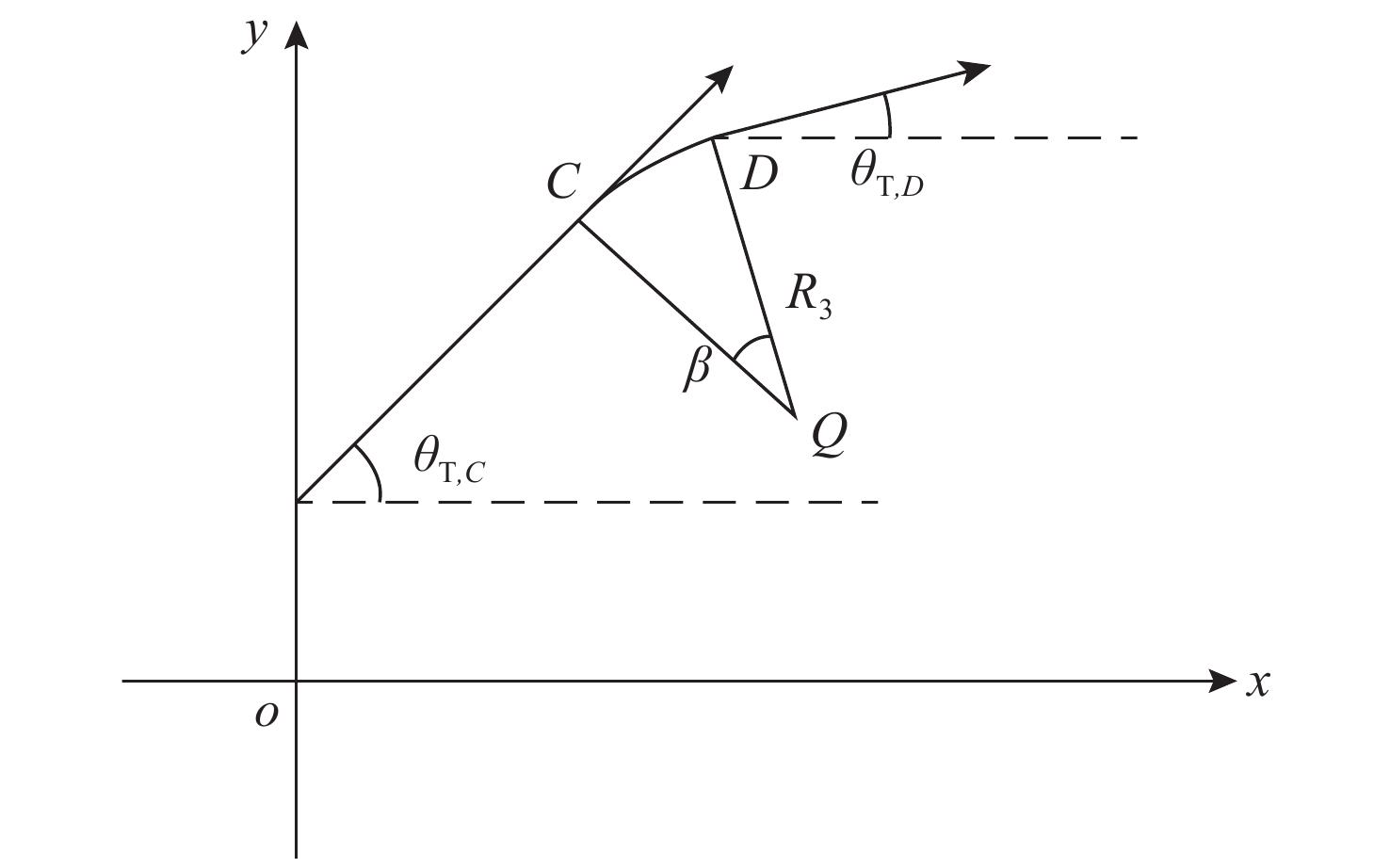
摘要: 鱼雷电磁引信干扰机是一种在水面舰艇尾流区域内对抗尾流自导鱼雷的武器装备, 干扰机作战使用参数的确定决定了其对抗效果的好坏。为确保鱼雷电磁引信干扰机产生足够好的对抗效果, 建立了鱼雷电磁引信干扰机作战使用模型, 并对鱼雷电磁引信干扰机布设间隔、布设数量以及作用半径等参数与使用电磁引信干扰机对抗尾流自导鱼雷的成功概率之间的关系进行仿真。结果表明:使用鱼雷电磁引信干扰机对抗尾流自导鱼雷, 可以有效保护水面舰艇的安全和战斗力, 且干扰机的上述参数对有效提高对抗成功概率具有显著影响, 同时得出在作用半径一定的条件下, 满足干扰效果要求的干扰机布设间隔与布设数量的最佳组合。文中工作可为鱼雷电磁引信干扰机性能指标的确定以及作战使用提供参考。Abstract: Torpedo electromagnetic fuse jammers are a type of weapon equipment used against wake-homing torpedoes in the wake area of surface ships. The operational parameters of the jammer determine its countering effectiveness. Therefore, to ensure that the torpedo electromagnetic fuse jammer can produce sufficient counter-effectiveness, a operational model for the jammer is built, and simulation research is conducted on the relationship between deployment interval, deployment quantity, operating radius, and success probability of using a torpedo electromagnetic fuse jammer against wake-homing torpedoes. The simulation results show that the use of such jammers can effectively protect surface ships and their operational capabilities, and the three parameters have a significant influence on the success probability of using electromagnetic fuse jammers against wake-homing torpedoes. By analyzing the simulation results, it can be concluded that the best combination of the jammer deployment interval and quantity which satisfying the requirements of the jamming effect can be obtained for a certain operating radius. This research provides a valuable reference for the determination of torpedo electromagnetic fuse jammer performance indexes.
-
Key words:
- torpedo /
- electromagnetic fuse jammer /
- efficiency analysis
-
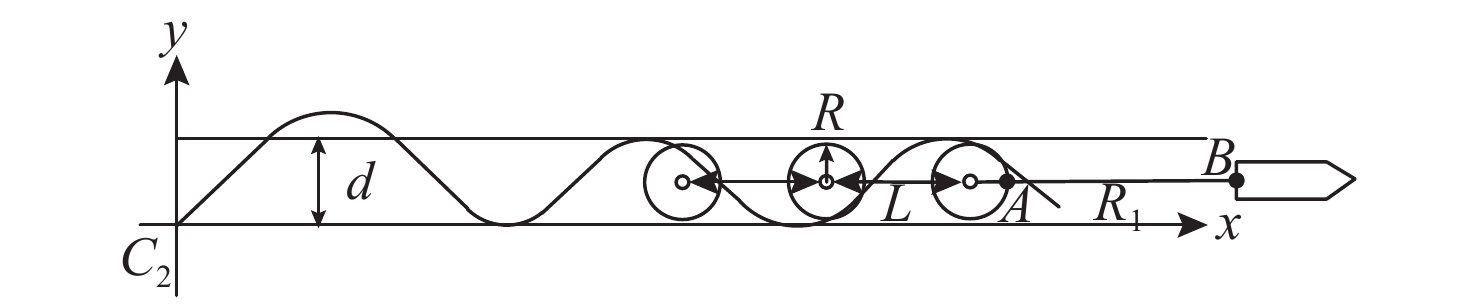
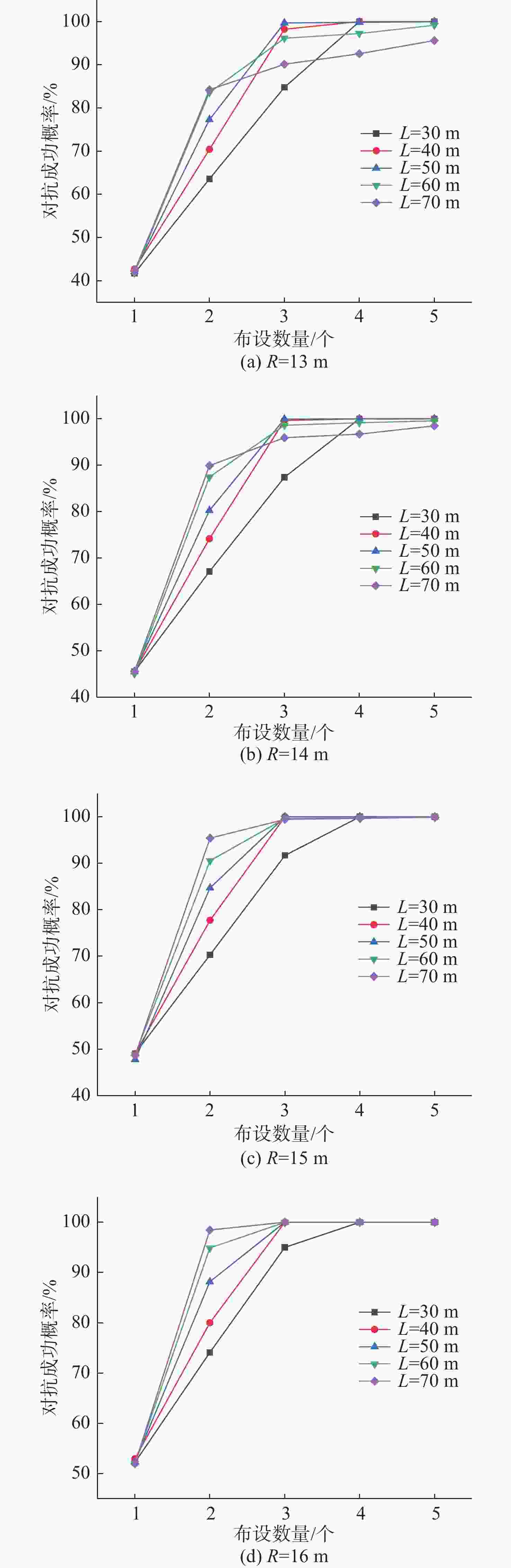
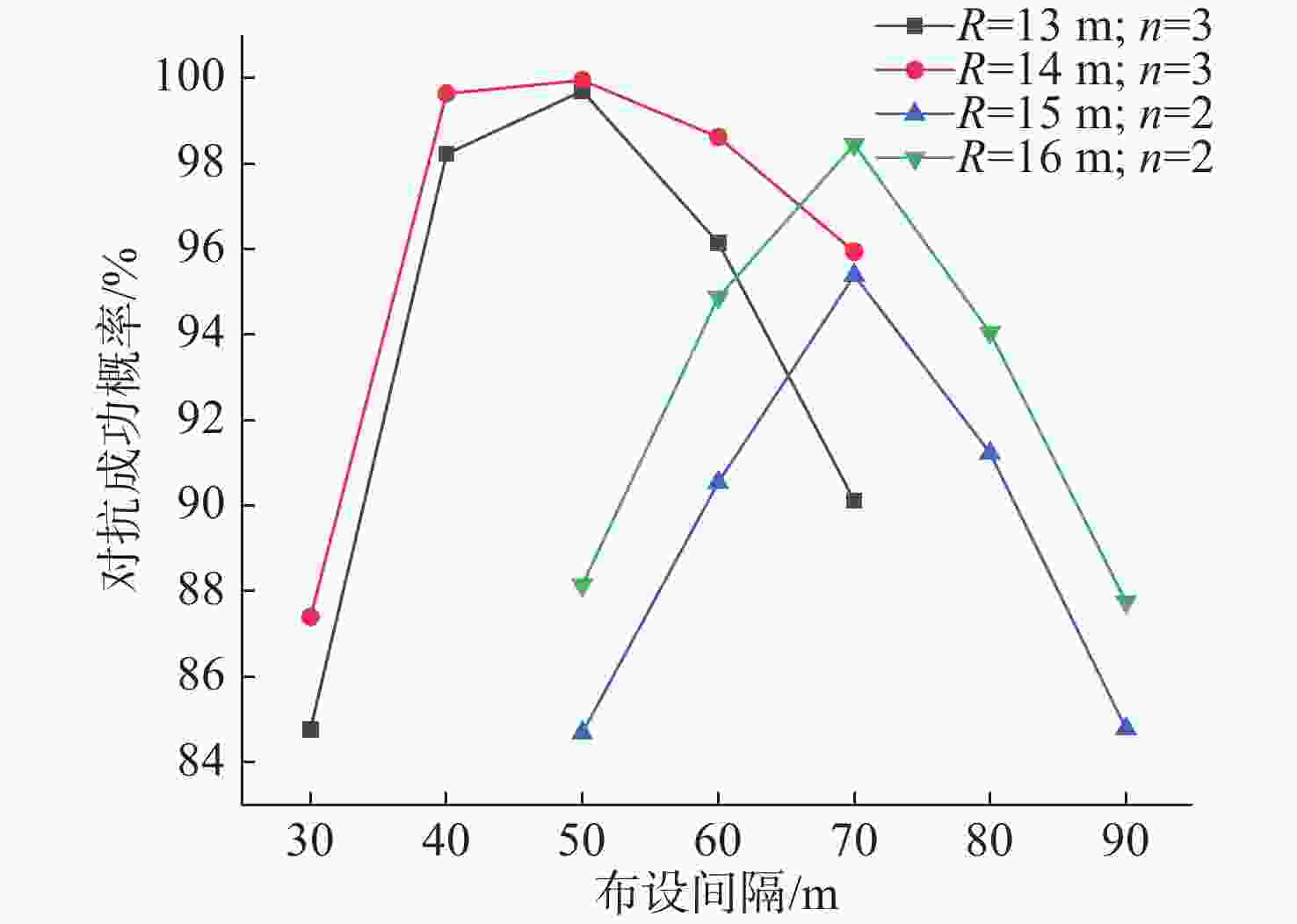
表 1 干扰机的作用半径为13 m时布设间隔与布设数量组合
Table 1. Combination of deployment interval and deployment quantity when R=13 m
干扰机作用半径/m 布设间隔/m 布设数量/个 13 30 4 40 3 50 3 60 3 70 5 表 2 不同作用半径布设间隔与布设数量最佳组合
Table 2. The best combination of deployment interval and deployment quantity at different operating radius
作用半径/m 布设间隔/m 布设数量/个 13 40 3 14 40 3 15 70 2 16 70 2 -
[1] 孙振新, 顾天军. 水面舰艇反鱼雷鱼雷拦截策略研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2020, 28(6): 699-705. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.06.016Sun Zhen-xin, Gu Tian-jun. Research on Anti-Torpedo Torpedo Interception Strategy of Surface Ship[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2020, 28(6): 699-705. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2020.06.016 [2] 侯宝娥, 田恒斗, 李兵, 等. 悬浮式深弹武器系统对鱼雷拦截能力试验方案设计[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(4): 469-472.Hou Bao-e, Tian Heng-dou, Li Bing, et al. Testing Scheme Design on Capability of Hovering Depth Charge Weapon System to Intercept Torpedo[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(4): 469-472. [3] 贾跃, 宋保维, 梁庆卫. 火箭深弹拦截鱼雷方法及作战过程[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2006, 31(3): 41-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2006.03.012Jia Yue, Song Bao-wei, Liang Qing-wei. Intercepting Torpedo Method and Combat Process of Using Rocket Depth Charges[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2006, 31(3): 41-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2006.03.012 [4] 田恒斗, 金良, 迟卫. 尾流自导鱼雷对抗技术现状与研究[J]. 火力指挥与控制, 2010, 35(10): 36-39.Tian Heng-dou, Jin Liang, Chi Wei. The Status and Prospect of the Countermeasure Against Wake Homing Torpedo[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2010, 35(10): 36-39. [5] 赵向涛, 孙续文, 周明. 尾流自导鱼雷弹道逻辑仿真[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2009, 17(2): 40-44.Zhao Xiang-tao, Sun Xu-wen, Zhou Ming. Simulation of Trajectory Logic for Wake Homing Torpedo[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2009, 17(2): 40-44. [6] 董春鹏, 张裕杰, 石小龙. 主动声尾流自导导引过程中信息获取与应用[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2007, 15(3): 15-18.Dong Chun-peng, Zhang Yu-jie, Shi Xiao-long. Acquirement and Application of Information During Guidance of Active Wake Acoustic Homing Torpedo[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2007, 15(3): 15-18. [7] 董春鹏, 石小龙. 主动声尾流自导鱼雷导引弹道分析计算[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2007, 15(2): 19-23.Dong Chun-Peng, Shi Xiao-Long. Guidance Trajectory Analysis and Calculation for Active Acoustic Wake Homing Torpedo[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2007, 15(2): 19-23. [8] 陈颜辉, 孙振新. 水面舰艇纯机动规避尾流自导鱼雷方法[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2010, 18(1): 68-71.Chen Yan-hui, Sun Zhen-xin. Eluding Method of Surface Ship Against Wake Homing Torpedo by Tactic Maneuver[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2010, 18(1): 68-71. [9] 张涛, 任志良, 孙长存, 等. 鱼雷电磁引信接收机对欺骗式干扰抗干扰能力评估[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2011, 19(3): 181-186.Zhang Tao, Ren Zhi-liang, Sun Chang-cun, et al. Evaluation of Anti-interference Capability of Torpedo Electromagnetic Fuze Receiver Against Deceiving Jammings[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2011, 19(3): 181-186. [10] 张爽, 张晓晖, 孙春生. 一种适于计算舰载激光引偏干扰系统安全引偏距离的冲击因子[J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(13): 31-35.Zhang Shuang, Zhang Xiao-hui, Sun Chun-sheng. Impulsive Factor for Safe Distance Calculation of a Ship-based Laser Decoy Jamming System[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(13): 31-35. [11] 孟庆玉, 张静远, 王鹏, 等. 鱼雷作战效能分析[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2020: 203-204. [12] 刘朝辉, 赵峰, 槐万景, 等. 基于仿真的深弹拦截鱼雷作战效能评估分析方法[J]. 火力指挥与控制, 2016, 41(1): 41-44.Liu Zhao-hui, Zhao Feng, Huai Wan-jing, et al. Method to Evaluate Operational Effectiveness of Hovering Depth Charge Intercepting Torpedo Based on Simulation[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2016, 41(1): 41-44. [13] 张洪刚, 王鹏, 张静远. 机动规避条件下尾流自导鱼雷射击瞄点选取方法[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2015, 23(2): 145-149.Zhang Hong-gang, Wang Peng, Zhang Jing-yuan. An Aiming Point Selection Method for Wake Homing Torpedo against Elusive Maneuver[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2015, 23(2): 145-149. [14] 焦瑜呈. 海水中电磁波特性的分析与研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2018, 38(8): 176-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2018.08.040Jiao Yu-cheng. Analysis and Research of the Electromagnetic Properties of Seawater[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2018, 38(8): 176-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2018.08.040 -




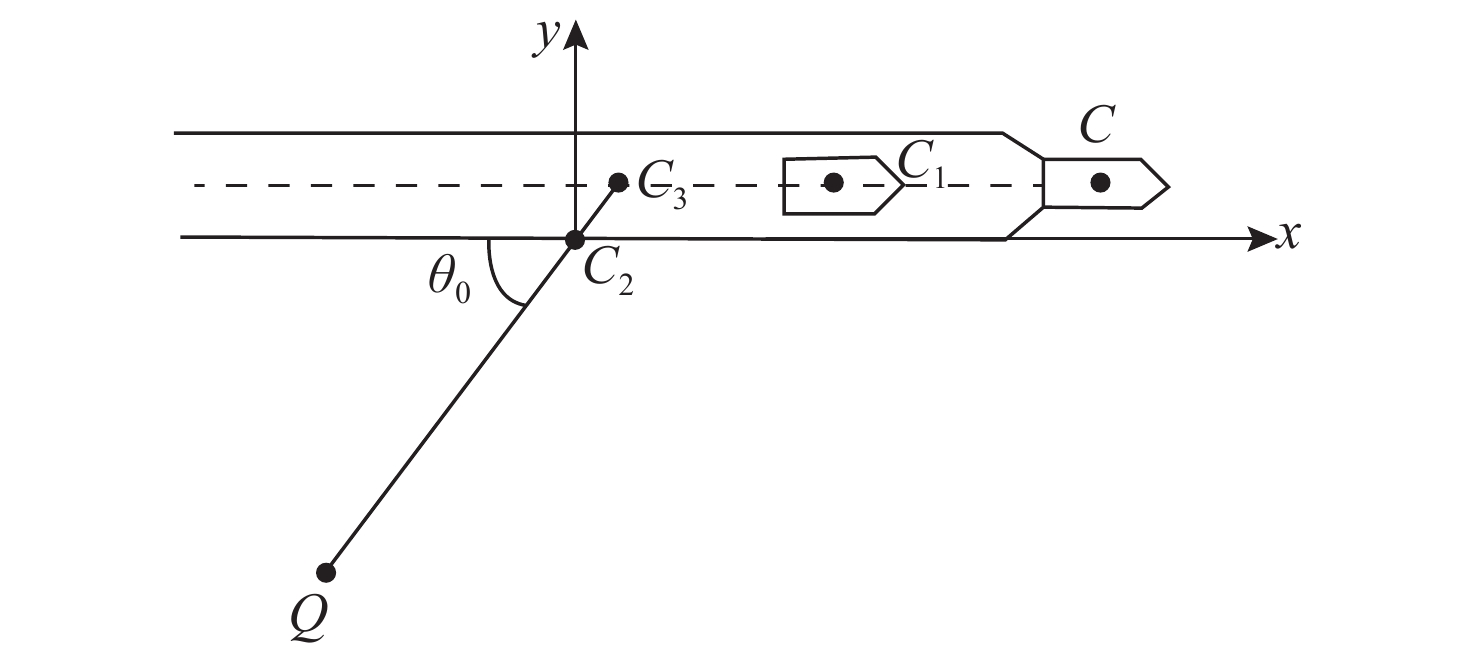
 下载:
下载: