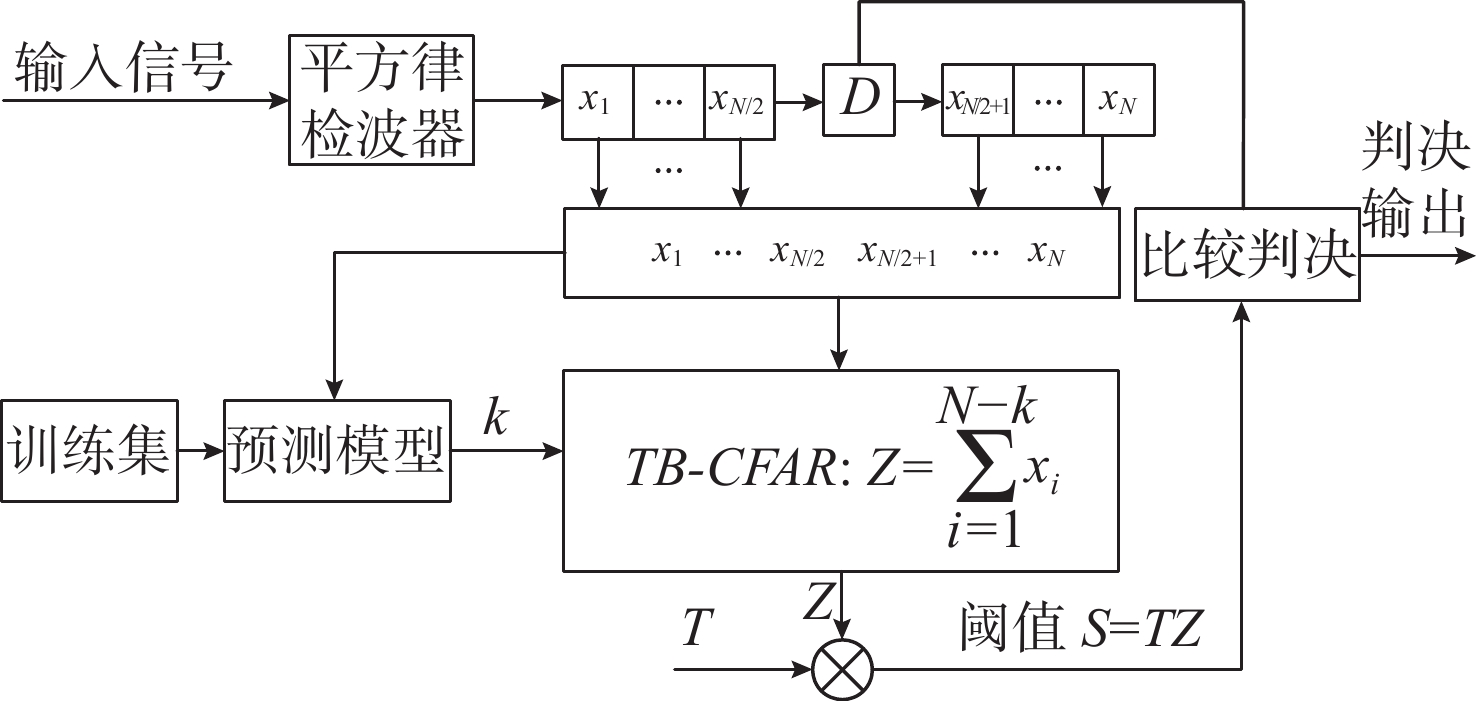
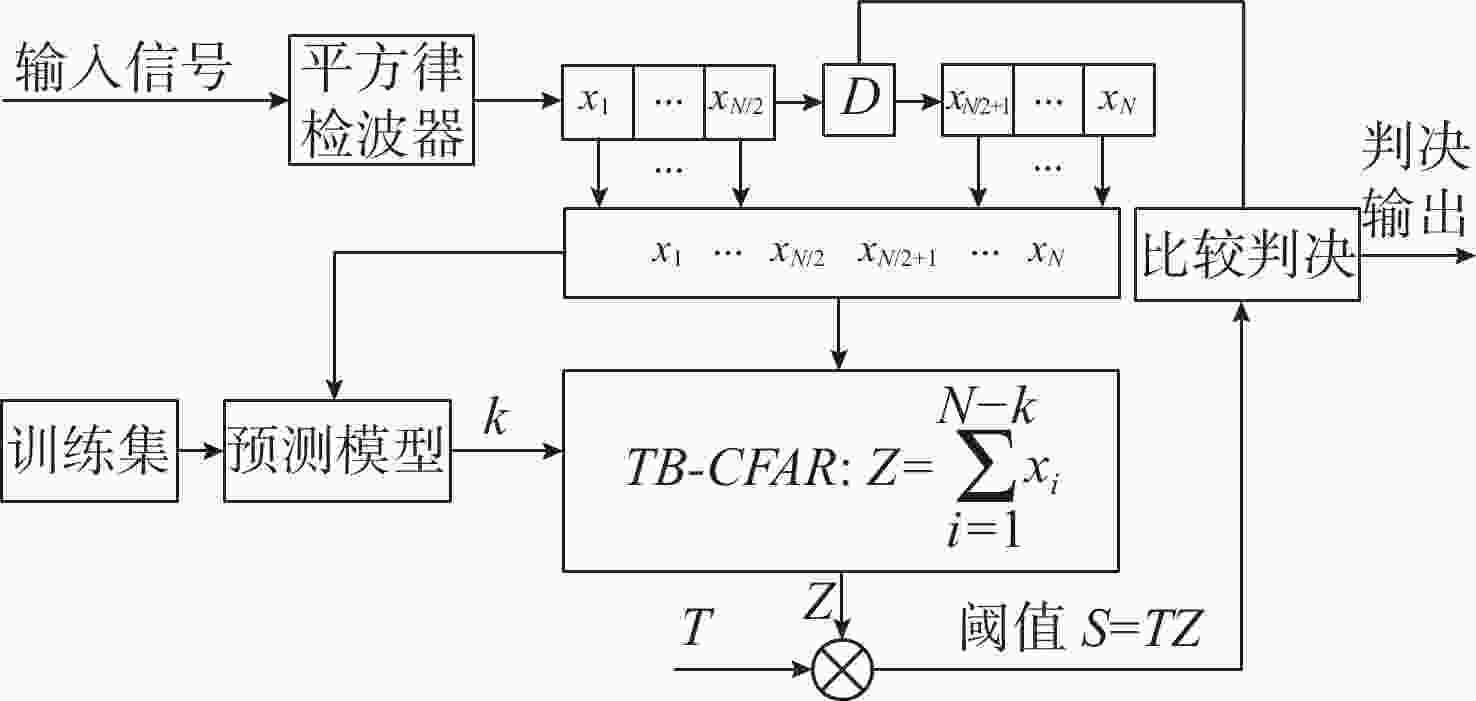
Design of a Multi-target Interference Resistant Adaptive Detector under Homogeneous Reverberation Backgrounds
-
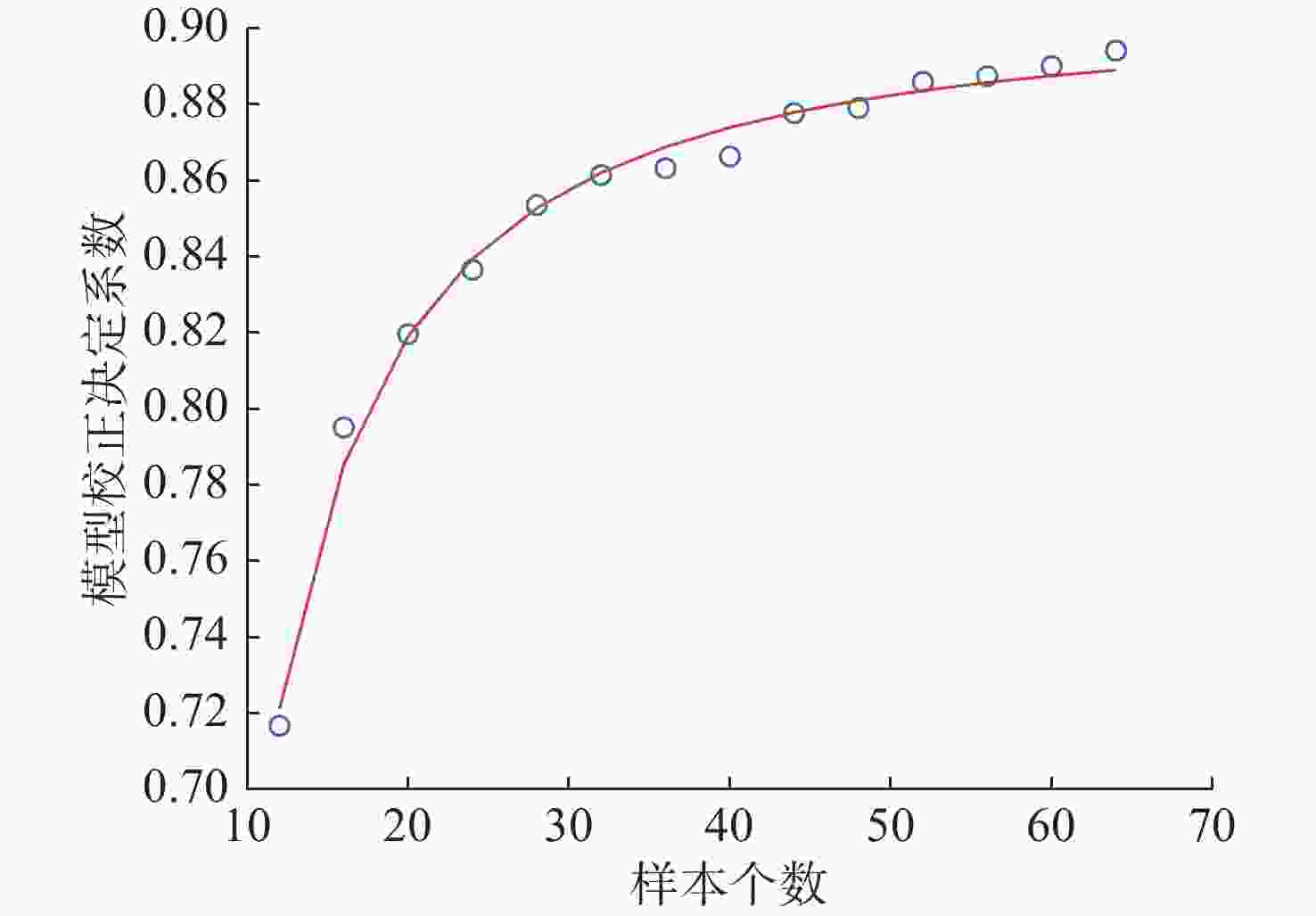
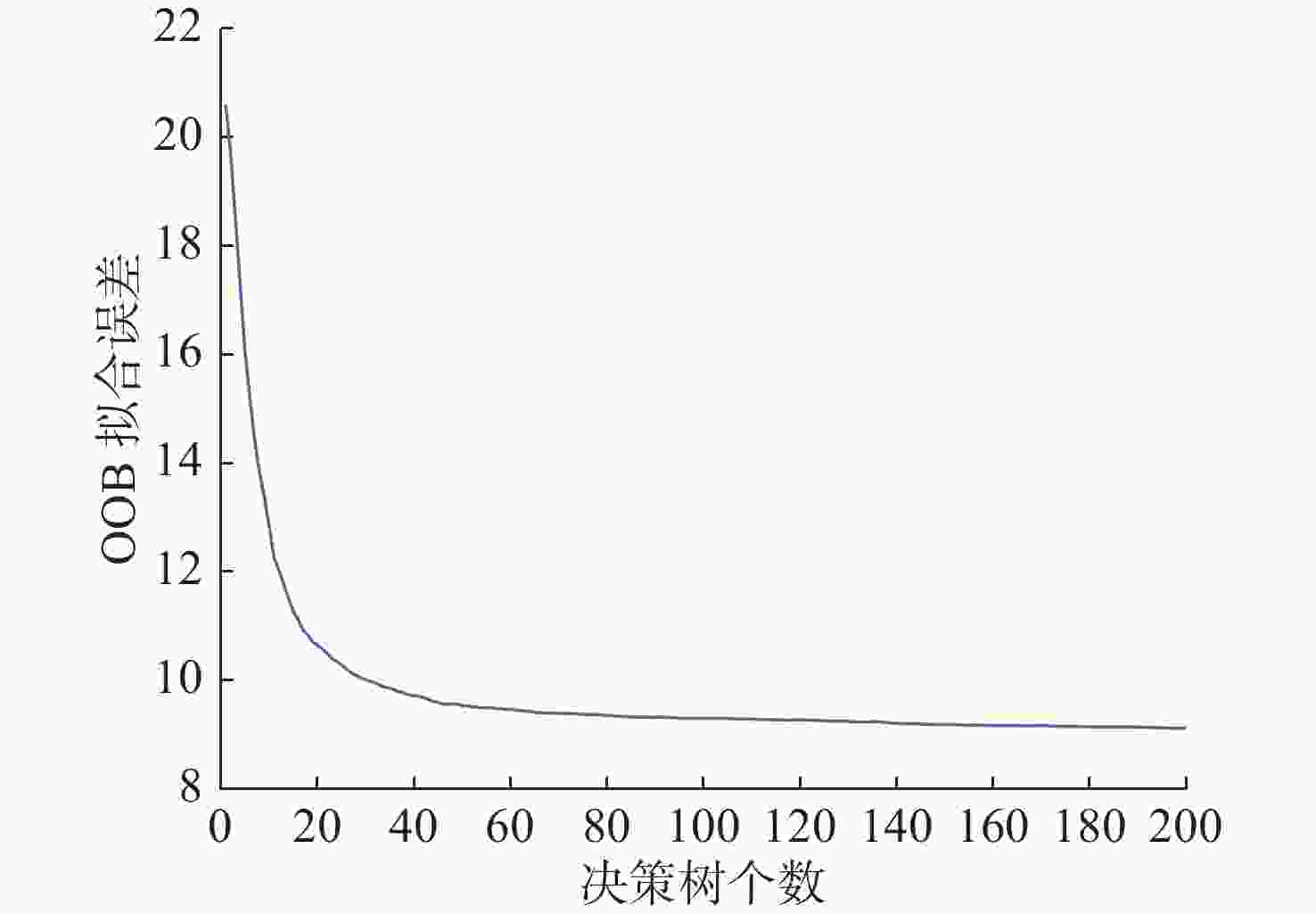
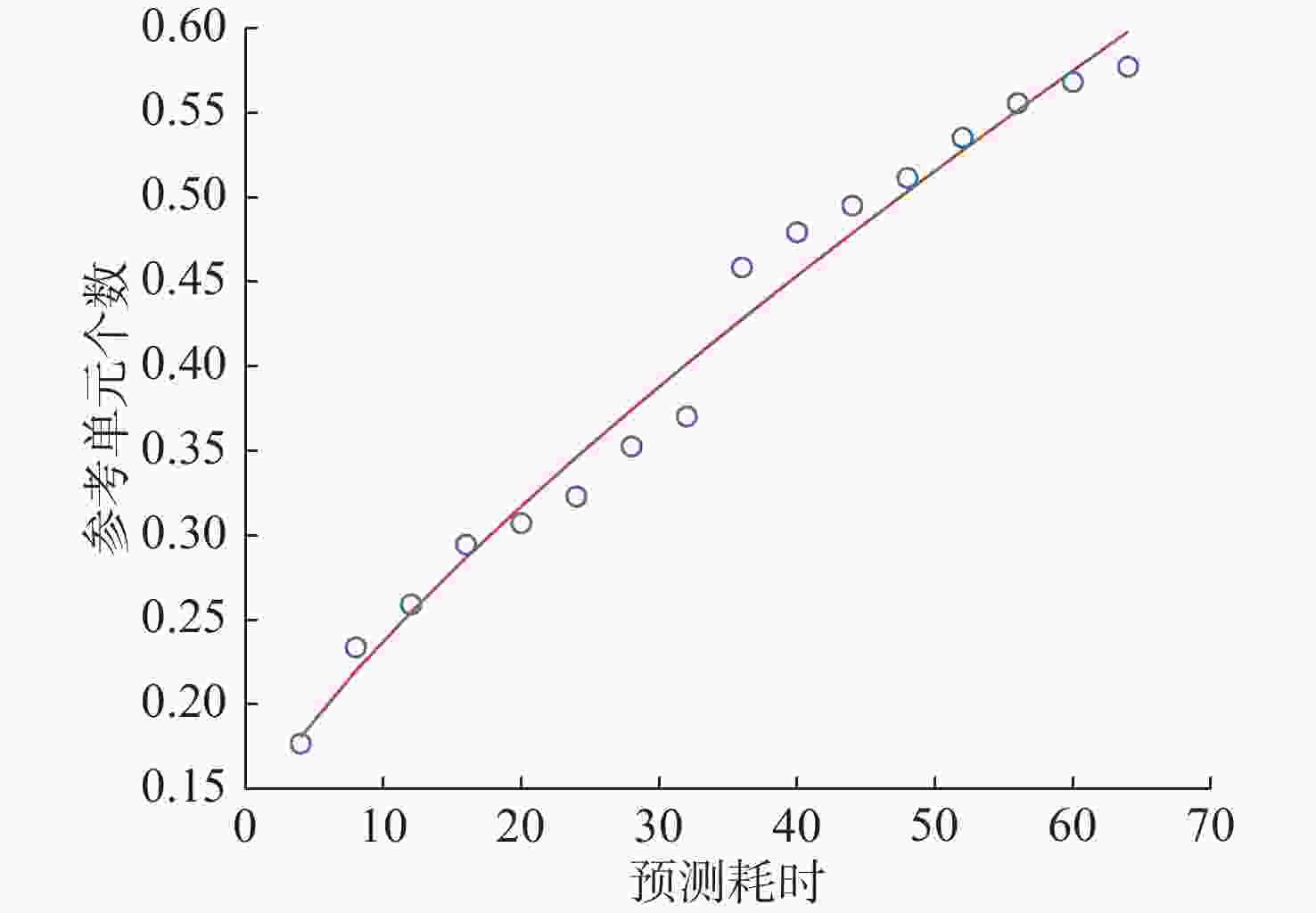
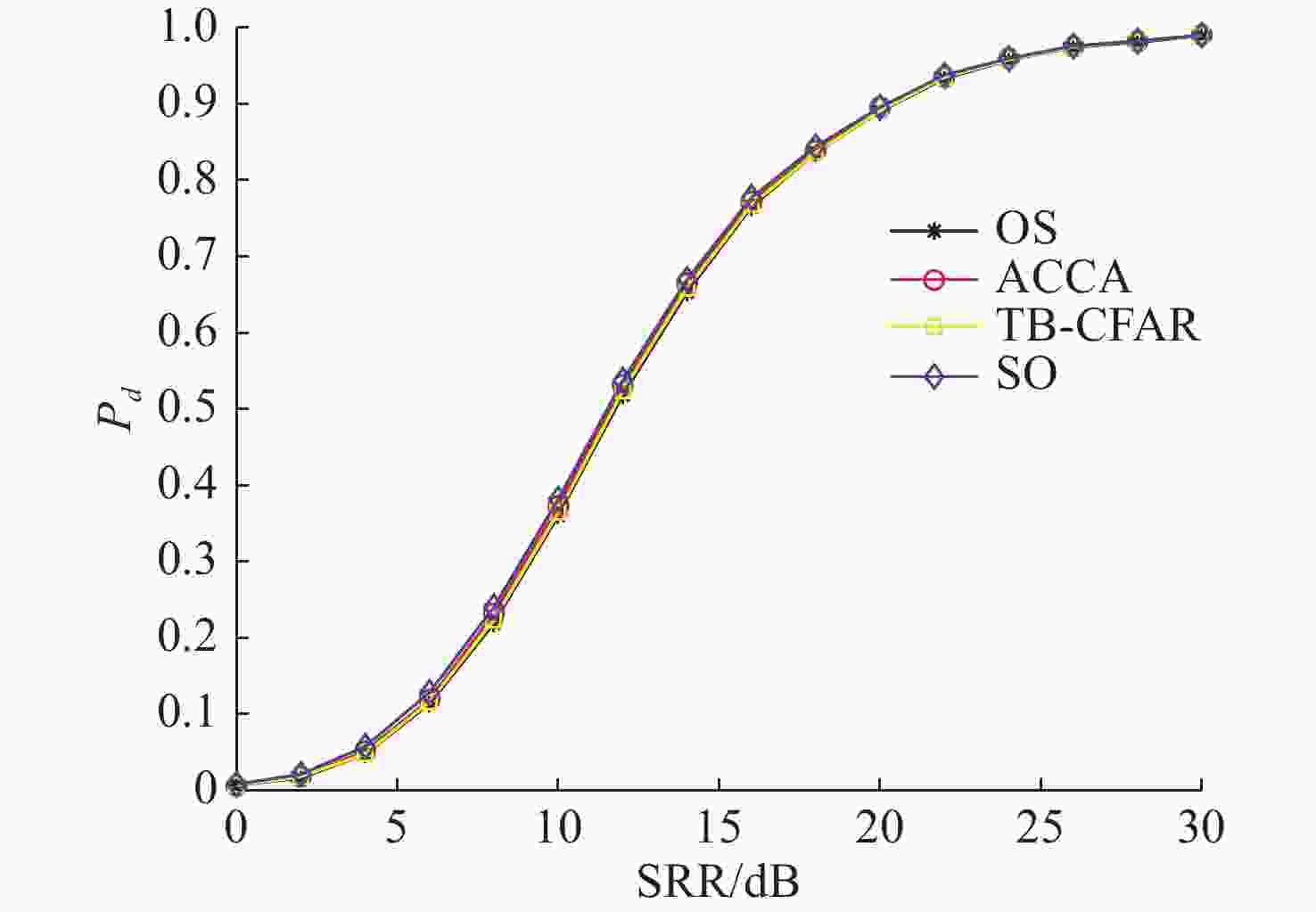
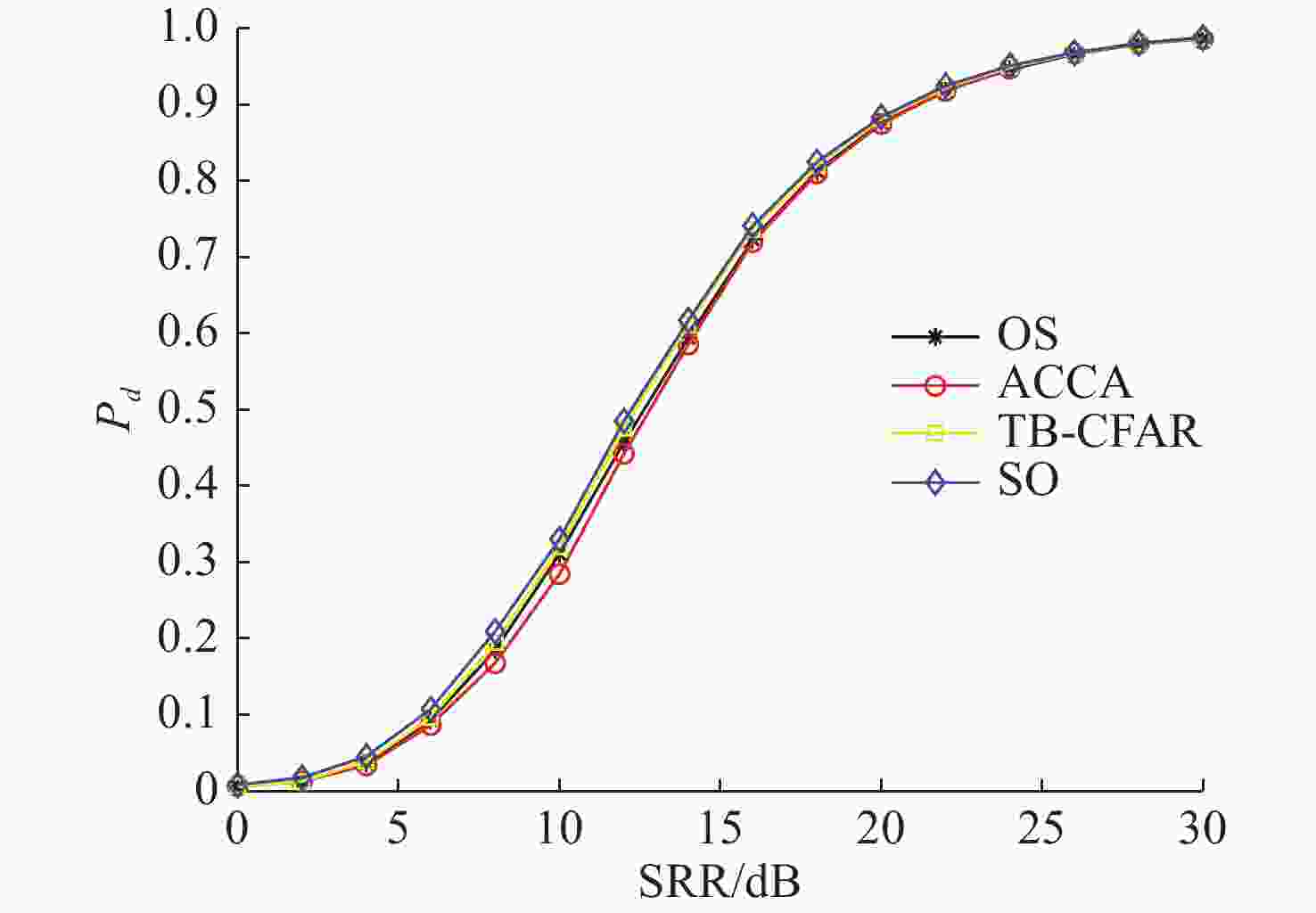
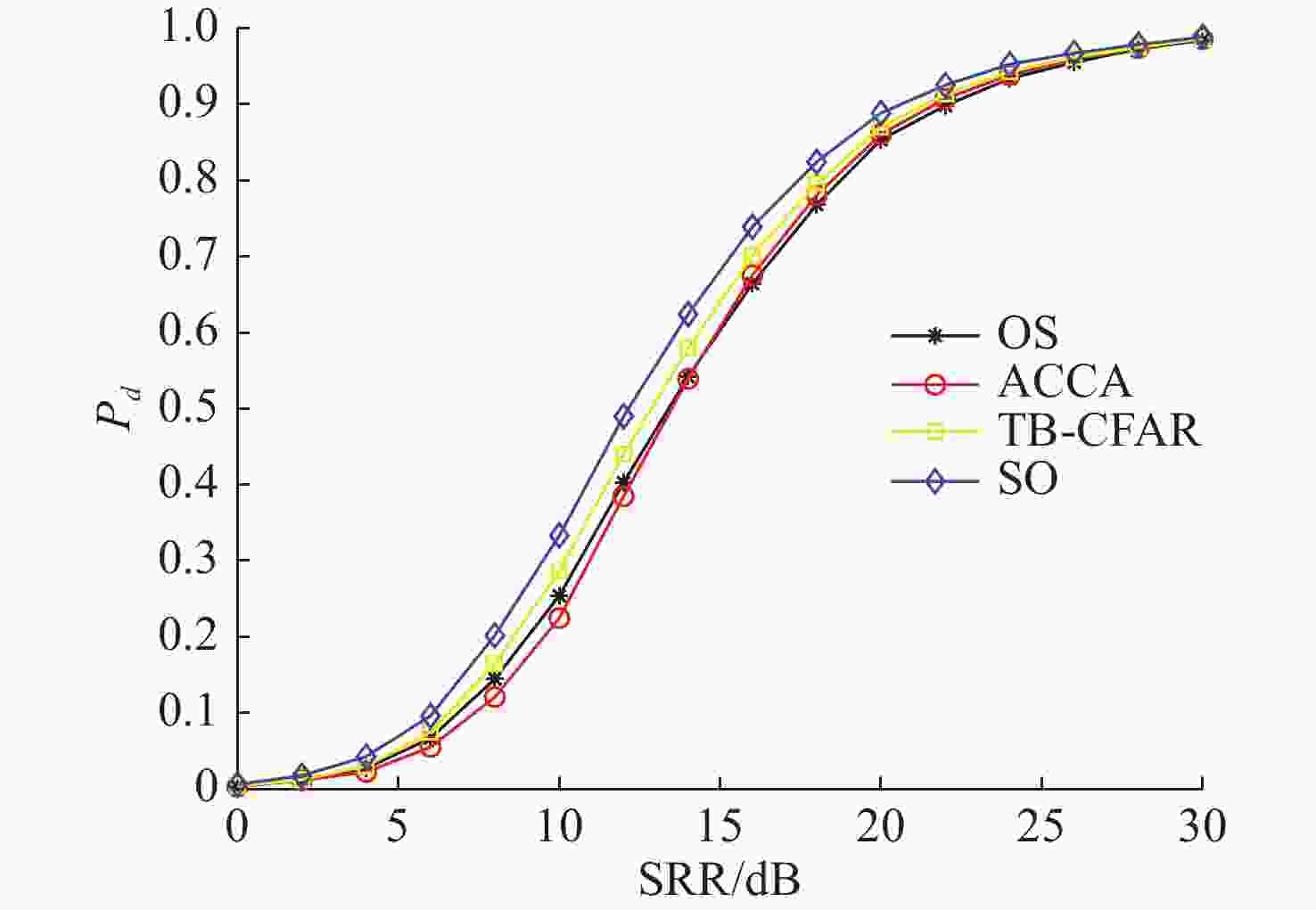
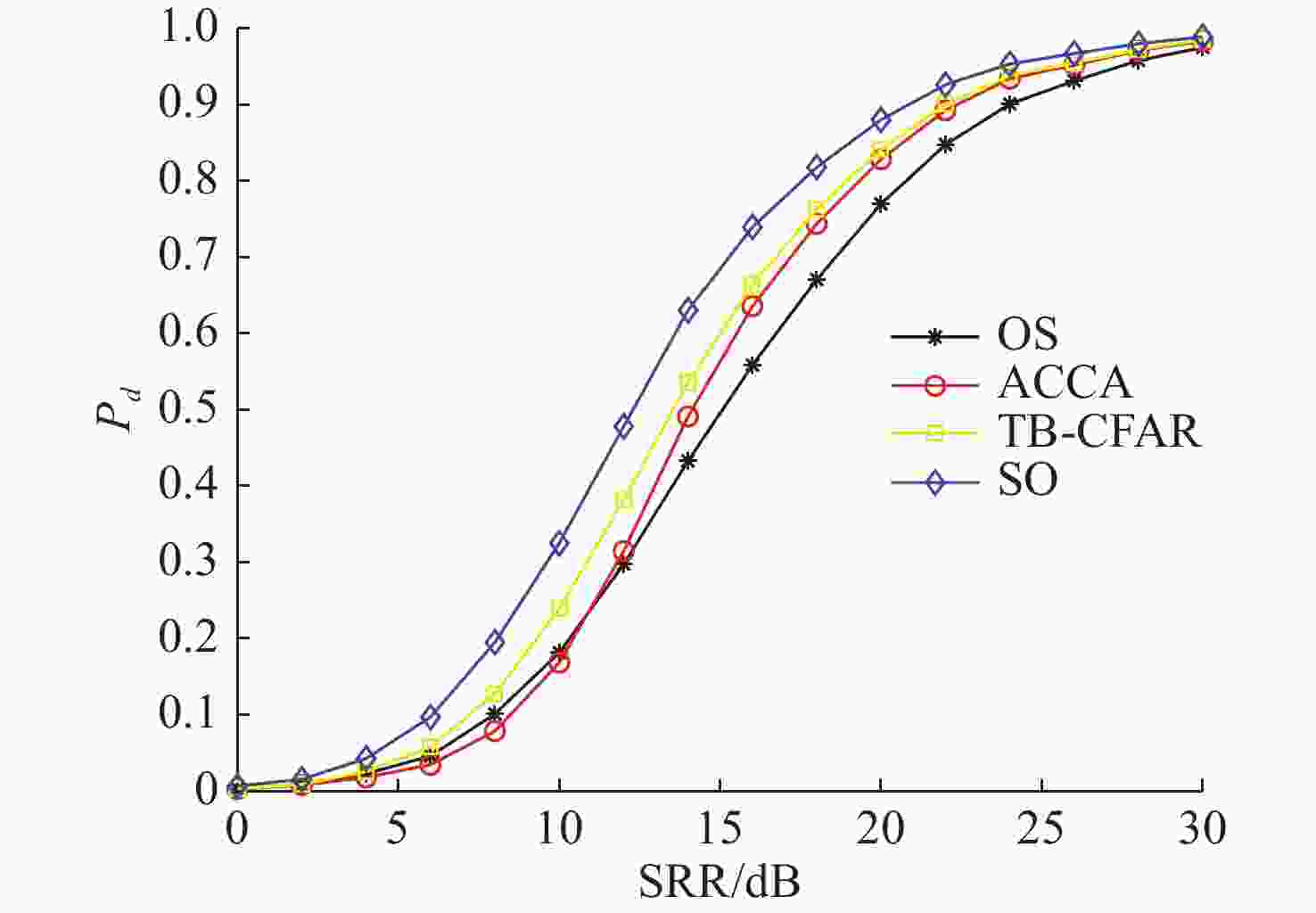
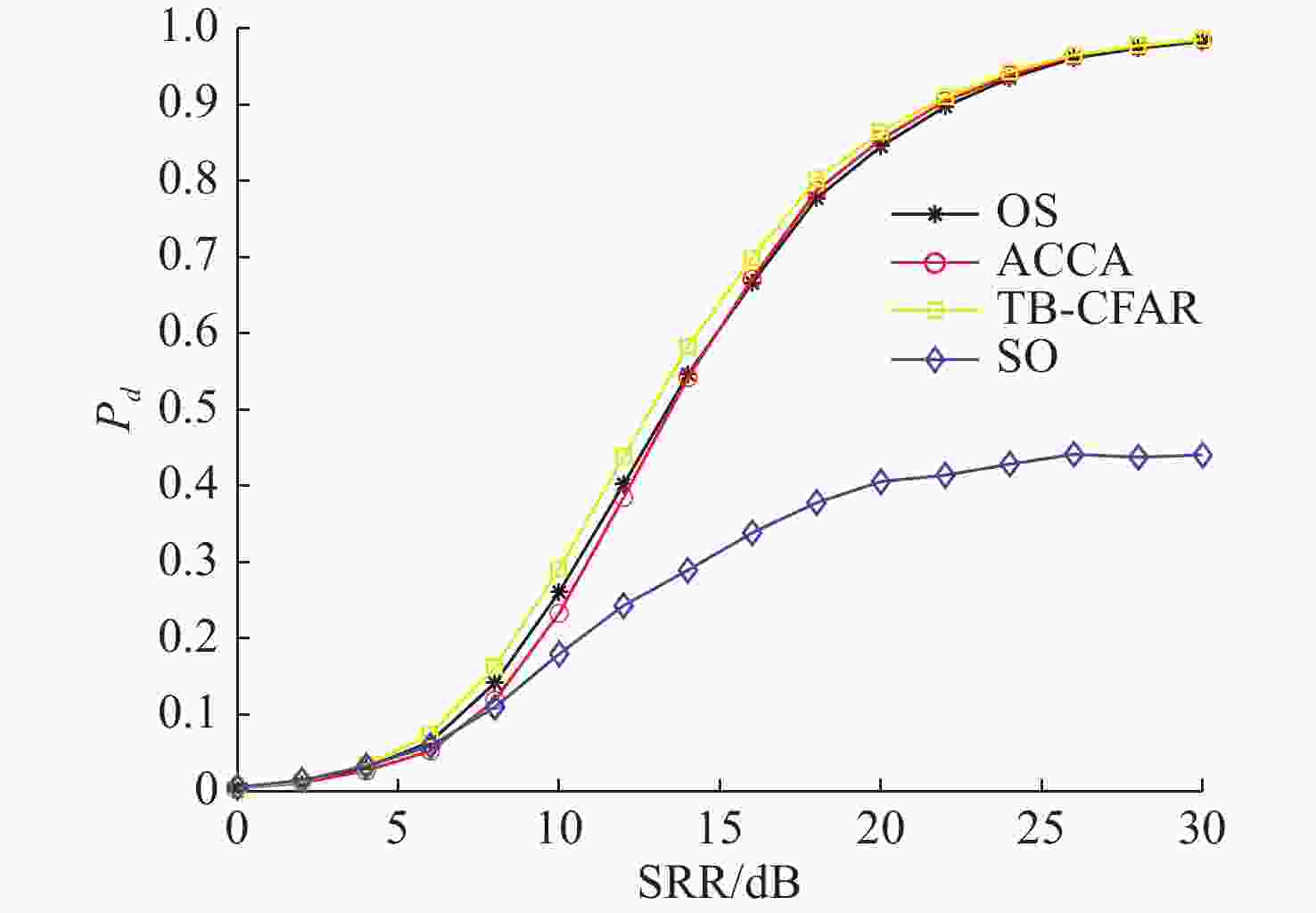
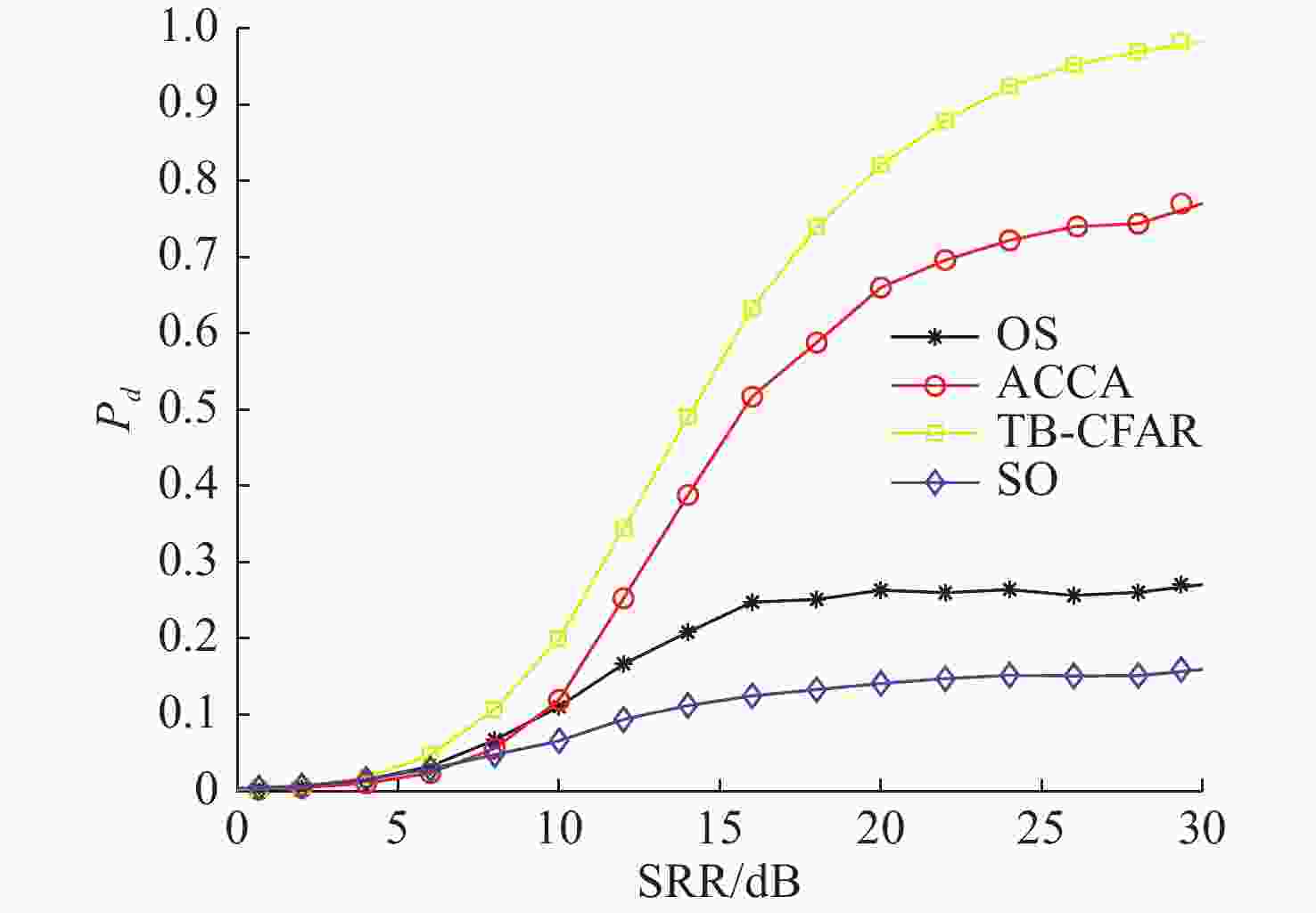
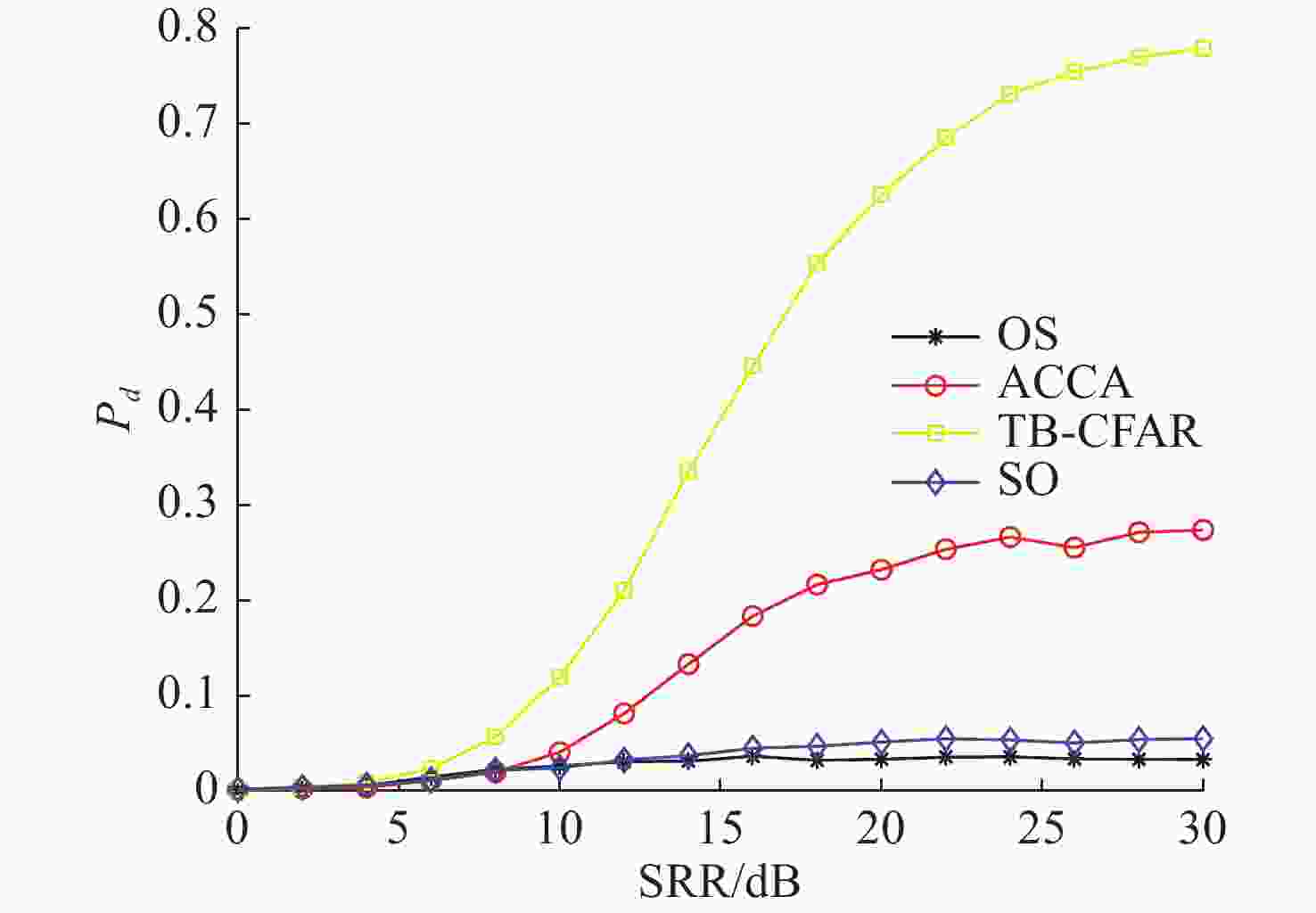
摘要: 为提高恒虚警方法的抗多目标干扰能力, 文中提出了一种能够对抗多目标干扰的新型自适应检测器。该检测器将参考单元作为背景环境的特征值, 利用TreeBagger算法构建估计器。在训练阶段, 利用参考单元和TreeBagger算法构建干扰目标个数估计器; 在检测阶段, 参考单元作为估计器的输入, 当前背景的干扰目标个数作为估计器的输出。进一步将估计结果作为该检测器的门限序值, 剔除干扰目标, 完成检测。利用蒙特卡洛仿真方法分析检测器在均匀混响背景和多目标干扰背景下的性能, 结果显示, 相较于现有方法, 所提方法的检测器具有更好的抗多目标干扰性能。Abstract: In this study, a new adaptive detector that can resist multi-target interference was proposed to improve the resistance to multi-target interference when using the constant false alarm rate(CFAR) method. This detector uses reference units as the feature value of the background environment and the TreeBagger algorithm for the construction of the estimator. In the training process, the reference units and TreeBagger algorithm were first used to construct the estimator, which was used to estimate the number of interference targets. In the detection process, the reference units were then used as the inputs of the estimator and the number of interference targets in the current background as the output of the estimator. Furthermore, the estimation results were used as the sequence threshold for the detector. Consequently, the detector was able to eliminate the interference targets and complete detection. The performance of the detector under homogeneous reverberation and multi-target interference backgrounds was then analyzed using the Monte Carlo simulation method, and a comparison of the results with those of existing methods was conducted, which showed that the proposed detector had a better performance at resisting multi-target interference.
-
Key words:
- constant false alarm rate /
- interference resistance /
- multi-target /
- adaptive detector
-
表 1 训练样本
Table 1. Train samples
干扰目标个数 SRR 训练样本数 样本标识 k 0 100 k 1 100 $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ 35 100 -
[1] 殷超然, 闫林杰, 郝程鹏, 等. 均匀混响背景下抗多目标干扰恒虚警检测器设计[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(4): 434-441.Yin Chao-ran, Yan Lin-jie, Hao Cheng-peng, et al. Design of a Multi-Target Interference Resistant Constant False Alarm Rate Detector for Homogeneous Reverberation Background[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(4): 434-441. [2] Finn H M. Adaptive Detection Mode with Threshold Control as a Function of Spatially Sampled-Clutter-Level Estimates[J]. RCA Review, 1968, 29: 414-464. [3] Trunk G V. Range Resolution of Targets Using Automatic Detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1978(5): 750-755. [4] Rohling H. Radar CFAR Thresholding in Clutter and Multiple Target Situations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1983, 19(4): 608-621. [5] Rickard J T, Dillard G M. Adaptive Detection Algorithms for Multiple-Target Situations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace & Electronic Systems, 1977, 13(4): 338-343. [6] Zaimbashi A, Norouzi Y. Automatic Dual Censoring Cell-averaging CFAR Detector in Non-homogenous Environments[J]. Signal Processing, 2008, 88(11): 2611-2621. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2008.04.016 [7] 曲超, 郝程鹏, 杨树元. 基于自动删除算法的恒虚警检测器[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2008, 23(5): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2008.05.003Qu Chao, Hao Cheng-peng, Yang Shu-yuan. CFAR Detector Based on Automatic Censoring Algorithm[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition & Processing, 2008, 23(5): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2008.05.003 [8] Barkat M, Farrouki A. Automatic Censoring CFAR Detector Based on Ordered Data Variability for Nonhomogeneous Environments[J]. IEEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2005, 152(1): 43-51. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045006 [9] Himonas S D, Barkat M. Automatic Censored CFAR Detection for Nonhomogeneous Environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic systems, 1992, 28(1): 286-304. doi: 10.1109/7.135454 [10] 王皓, 衣同胜. 基于神经网络CA/OS-CFAR检测方法[J]. 兵工自动化, 2018(2): 15-18.Wang Hao, Yi Tong-sheng. CA/OS-CFAR Detection Method Based on Neural Network[J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2018(2): 15-18. [11] Wang L, Wang D, Hao C. Intelligent CFAR Detector Based on Support Vector Machine[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 26965-26972. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2774262 [12] 李娜. 雷达有源干扰分类与识别方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2017. [13] 刘明骞, 高晓腾, 张俊林. 多类型的雷达有源干扰感知新方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2019, 53(10): 103-108,121. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201910014Liu Ming-qian, Gao Xiao-teng, Zhang Jun-lin. A Novel Sensing Method for Multi-Types of Radar Active Jamming[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2019, 53(10): 103-108,121. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201910014 [14] 魏煜宁, 张劲东, 李勇, 等. 雷达干扰信号识别决策树的自动化设计方法[J]. 电光与控制, 2020, 27(4): 82-86.Wei Yu-ning, Zhang Jin-dong, Li Yong, et al. A Method for Automatic Design of Decision Tree in Radar Jamming Signal Recognition[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2020, 27(4): 82-86. [15] Xu J L, Sun D W. Identification of Freezer Burn on Frozen Salmon Surface Using Hyperspectral Imaging and Computer Vision Combined with Machine Learning Algorithm[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2017, 74: 151-164. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2016.10.014 [16] Breiman L. Random Forests, Machine Learning 45[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2001, 2: 199-228. [17] 李航. 统计学习方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2012. [18] 贾怀勤. 应用统计[M]. 5版. 北京: 对外经济贸易大学出版社, 2010. [19] 孙梦茹, 郝程鹏, 刘明刚. 具有提升抗干扰能力的距离扩展目标模糊CFAR检测方法[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(9): 1580-1589. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.09.016Sun Meng-ru, Hao Cheng-peng, Liu Ming-gang. A Fuzzy CFAR Detection Method for Range-extended Targets with Enhanced Anti-jamming Capability[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(9): 1580-1589. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.09.016 -




 下载:
下载: