Unsupervised Controllable Enhancement of Underwater Images Based on Multi-Attribute Representation Disentanglement
-
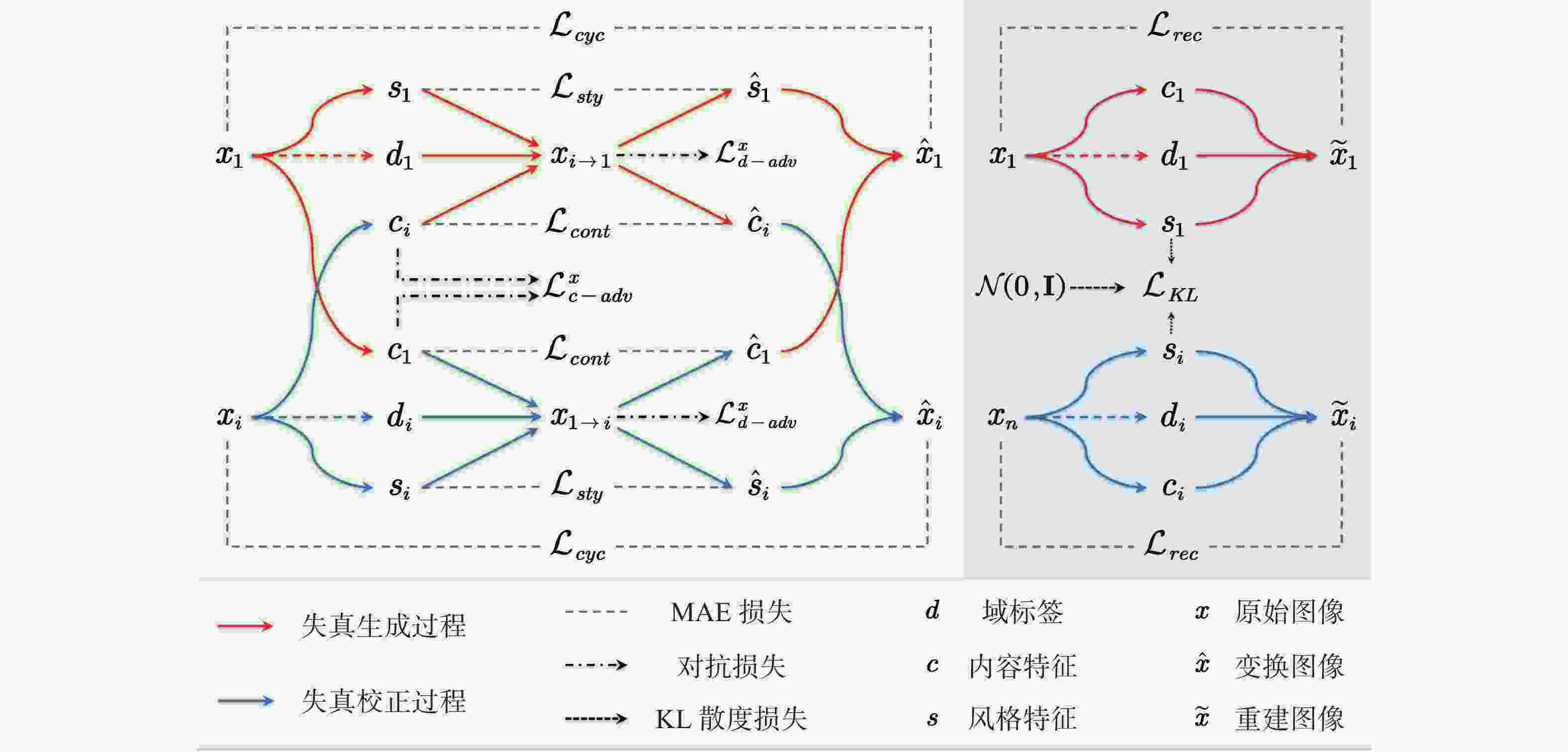
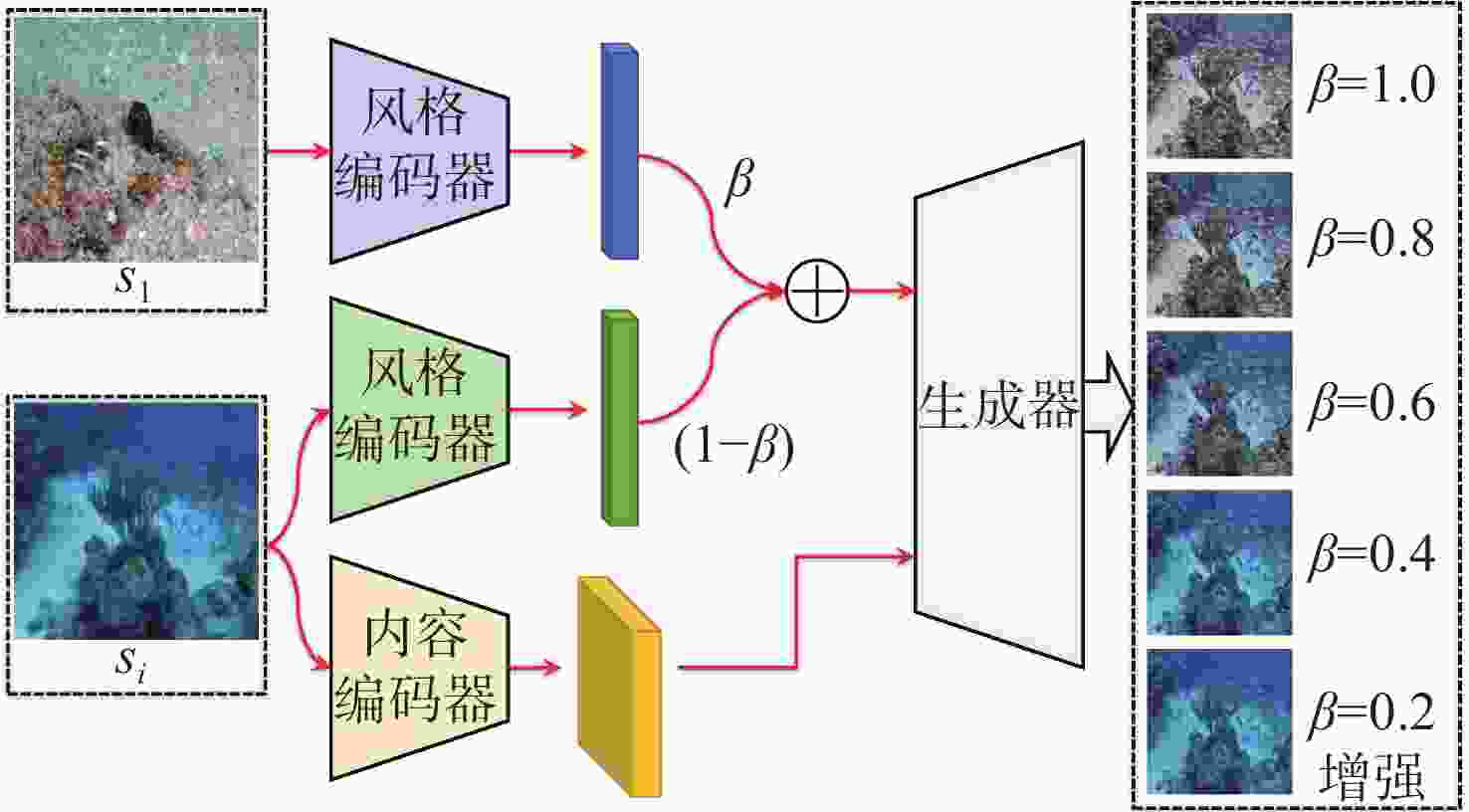
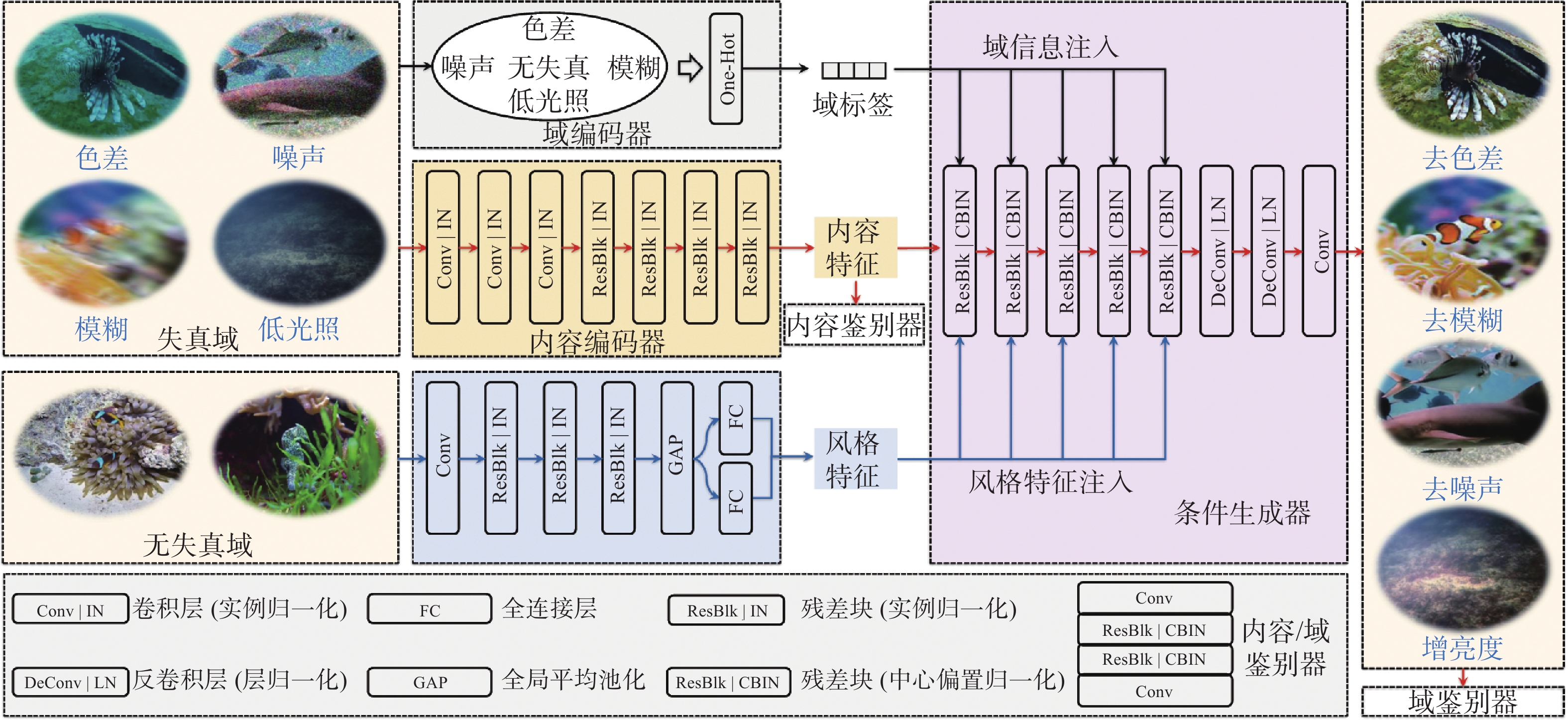
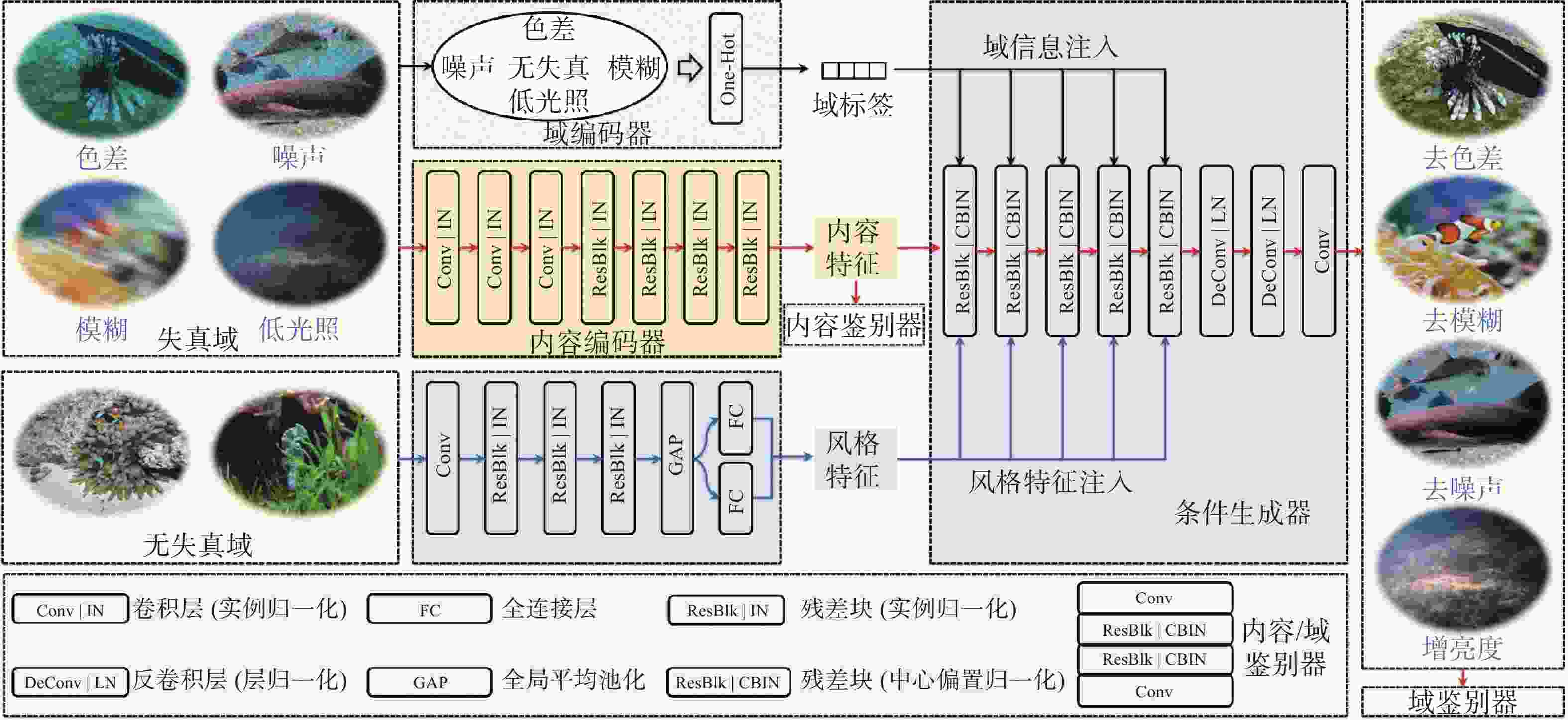
摘要: 水下图像无监督增强技术多面向特定失真因素, 对于水下多类失真图像适应性略显不足; 图像的内容属性(结构)会随风格属性(外观)迁移变化, 导致增强效果不受控, 影响后续环境感知处理的稳定性和准确性。针对这一问题, 文中提出一种基于多域表征解耦的水下图像无监督可控增强方法。首先设计了多域统一的表征解耦循环一致对抗变换框架, 提高了算法对多失真因素的适应性; 其次构建了双编码-条件解码网络结构; 最后设计了多域属性表征解耦的系列损失, 提高了质量、内容、风格等属性表征的独立表达性和可控性。实验结果表明, 所提算法不仅可以消除水下图像的色差、模糊、噪声和低光照等多类失真, 还可通过线性插值的方式量化图像风格码对水下图像进行可控增强。Abstract: The unsupervised enhancement technique for underwater images exhibits a limited adaptability towards various distortions inherent in multi-class distortion underwater images. The structural content of the images tends to change alongside the style attributes during the enhancement process, resulting in uncontrolled enhancement effects that impede the stability and accuracy of subsequent environmental perception and processing. To address this issue, a method based on multi-domain representation disentanglement for controllable unsupervised enhancement of underwater images is proposed in the paper. Initially, a framework of multi-domain unified representation disentanglement cycle-consistent adversarial translations is devised, thereby enhancing the algorithm's adaptability to multiple distortion factors. Subsequently, a dual-encoding conditional decoding network structure is constructed. Finally, a series of losses for multi-domain attribute representation disentanglement is designed to enhance the independence and controllability of quality, content, style, and other attribute representations. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm not only eliminates various distortions such as color aberration, blur, noise, and low illumination in underwater images but also enables controllable enhancement through linear interpolation of image style codes for underwater images.
-
表 1 不同方法对真实水下图像增强效果的定量比较
Table 1. Quantitative comparison of MARD on authentic underwater images
方法 UICM UIConM UIQM UCIQE FDUM 原图 3.6224 0.2625 2.5340 3.9142 0.4109 IBLA 6.4838 0.1812 2.1623 5.5139 0.6325 RGHS 5.2957 0.2907 3.1511 3.5498 0.5450 UNTV 5.3940 0.2660 2.3329 5.1342 0.7444 HLRP 7.3082 0.2423 2.5512 5.9461 0.6860 CycleGAN 3.4447 0.2934 3.0545 3.5104 0.4416 UGAN 4.5803 0.3012 3.1357 4.1050 0.5558 Water-Net 4.6380 0.3053 3.1117 4.1674 0.4678 UWCNN 6.2946 0.1407 2.1627 5.4348 0.5818 FUnIE-GAN 5.2013 0.2989 3.2322 5.0836 0.5693 UWCNN-SD 5.3061 0.2812 3.1682 4.6163 0.6730 MARD 6.4966 0.3080 3.4824 5.6065 0.7912 表 2 不同方法测试不同分辨率图像所需运行时间比较
Table 2. Comparison of runtime required to test images of various resolutions by different methods
分辨率(ppi) UNTV(s) ULAP(s) Water-Net(s) Ucolor(s) MARD(s) 256×256 3.542 0.364 1.036 7.793 0.059 640×480 10.291 1.708 2.545 29.192 0.254 800×600 16.267 2.704 3.459 42.760 0.469 1280×720 27.048 4.664 4.630 183.850 0.791 1920×1080 59.642 10.538 10.793 261.418 1.728 表 3 不同损失下MARD的定量比较
Table 3. Quantitative comparison using different losses
方法 UICM UIConM UIQM UCIQE FDUM M1 ($ {L_{\rm{adv}}} $) 5.3 885 0.2 480 3.0 152 4.3 691 0.5 439 M2 (M1 &$ {L_{{\text{cyc}}}} $) 6.1 866 0.2 782 3.2 383 5.0 122 0.6 502 M3 (M2 &$ {L_{\rm{cont}}} $) 6.1 811 0.2 948 3.1 439 4.5 623 0.6 504 M4 (M3 &$ {L_{\rm{sty}}} $$ {L_{\rm{sty}}} $) 6.3 042 0.2 944 3.3 290 4.6 493 0.6 958 M5 (M4 &$ {L_{\rm{rec}}} $) 6.3 427 0.2 931 3.4 253 4.4 586 0.7 674 M6 (M5 &$ {L_{\rm{KL}}} $) 6.4 966 0.3 080 3.4 824 5.6 065 0.7 912 -
[1] Song W, Wang Y, Huang D M, et al. Enhancement of underwater images with statistical model of background light and optimization of transmission map[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2020, 66(1): 153-169. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2019.2960942 [2] Xie J, Hou G J, Wang G D, et al. A variational framework for underwater image dehazing and deblurring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 32(6): 3514-3526. [3] McGlamery B L. A computer model for underwater camera systems[J]. Proceedings of the Society of Photo-0ptical Instrumentation Engineers, 1980, 208: 221-231. [4] Zhuang P X, Wu J M, Porikli F, et al. Underwater image enhancement with hyper-laplacian reflectance priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 5442-5455. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3196546 [5] Zhou J C, Pang L, Zhang D H, et al. Underwater image enhancement method via multi-interval subhistogram perspective equalization[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2023, 48(2): 474-488. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2022.3223733 [6] Zhuang P X, Li C Y, Wu J M. Bayesian retinex underwater image enhancement[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 101: 104171. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104171 [7] Zhuang P X, Ding X H. Underwater image enhancement using an edge-preserving filtering retinex algorithm[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79: 17257-17277. doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-08404-4 [8] Fu X Y, Zhuang P X, Huang Y, et al. A retinex-based enhancing approach for single underwater image[C]//2014 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). Paris, France: IEEE, 2014: 4572-4576. [9] Li C Y, Guo C L, Ren W Q, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 4376-4389. [10] Qi Q, Li K Q, Zheng H Y, et al. SGUIE-Net: Semantic attention guided underwater image enhancement with multi-scale perception[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 6816-6830. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3216208 [11] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//28th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), advances in neural information processing systems, Montreal, Canada: NIPS, 2014, 27: 2672-2680. [12] 胡雨航, 赵磊, 李恒等. 多特征选择与双向残差融合的无监督水下图像增强[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2023, 37(9): 190-202.Hu Yuhang, Zhao Lei, Li Heng, et al. Unsupervised underwater image enhancement with multi-feature selection and bidirectional residual fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics Measurement & Instrumentation, 2023, 37(9): 190-202. [13] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017: 2242-2251 [14] 刘彦呈, 董张伟, 朱鹏莅等. 基于特征解耦的无监督水下图像增强[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3389-3398. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211517Liu Yancheng, Dong Zhangwei, Zhu Pengli, Liu Siyuan. Unsupervised underwater image enhancement based on feature disentanglement[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3389-3398. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211517 [15] Yu X M, Ying Z Q, Li T M, et al. Multi-mapping image-to-image translation with central biasing normalization[J/OL]. arXiv preprint(2018-04-17)https://www.arxiv.org/abs/1806.10050v5. [16] Zhu P L, Liu Y C, Xu M Y, et al. Unsupervised multiple representation disentanglement framework for improved underwater visual perception[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2023. [17] Marques T P, Albu A B. L2UWE: A Framework for the Efficient Enhancement of Low-Light Underwater Images Using Local Contrast and Multi-Scale Fusion[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, USA: IEEE, , 2020: 2286-2295. [18] Peng Y T, Cosman P C. Underwater image restoration based on image blurriness and light absorption[J]. IEEE transactions on image processing, 2017, 26(4): 1579-1594. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2663846 [19] Huang D, Wang Y, Song W, et al. Shallow-water image enhancement using relative global histogram stretching based on adaptive parameter acquisition[C]//2018 MultiMedia Modeling: 24th International Conference. Bangkok, Thailand: MMIC, 2018: 453-465. [20] Song W, Wang Y, Huang D M, et al. A rapid scene depth estimation model based on underwater light attenuation prior for underwater image restoration[J]. Advances in Multimedia Information Processing-PCM, 2018, 11164: 678-688. [21] Fabbri C, Islam M J, Sattar J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, Australia: IEEE, 2018: 7159-7165. [22] Li C, Anwar S, Porikli F. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107038. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107038 [23] Islam M J, Xia Y Y, Sattar J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227-3234. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974710 [24] Wu S C, Luo T, Jiang G Y, et al. A two-stage underwater enhancement network based on structure decomposition and characteristics of underwater imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2021, 46(4): 1213-1227. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2021.3064093 [25] Li C Y, Anwar S, Hou J H, et al. Underwater image enhancement via medium transmission-guided multi-color space embedding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 4985-5000. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3076367 [26] Yang M, Sowmya A. An underwater color image quality evaluation metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 6062-6071. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2491020 [27] Panetta K, Gao C, Agaian S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2015, 41(3): 541-551. [28] Yang N, Zhong Q H, Li K, et al. A reference-free underwater image quality assessment metric in frequency domain[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 94: 116218. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2021.116218 -




 下载:
下载: