GPA based domain adaptive feature refinement method for underwater target detection
-
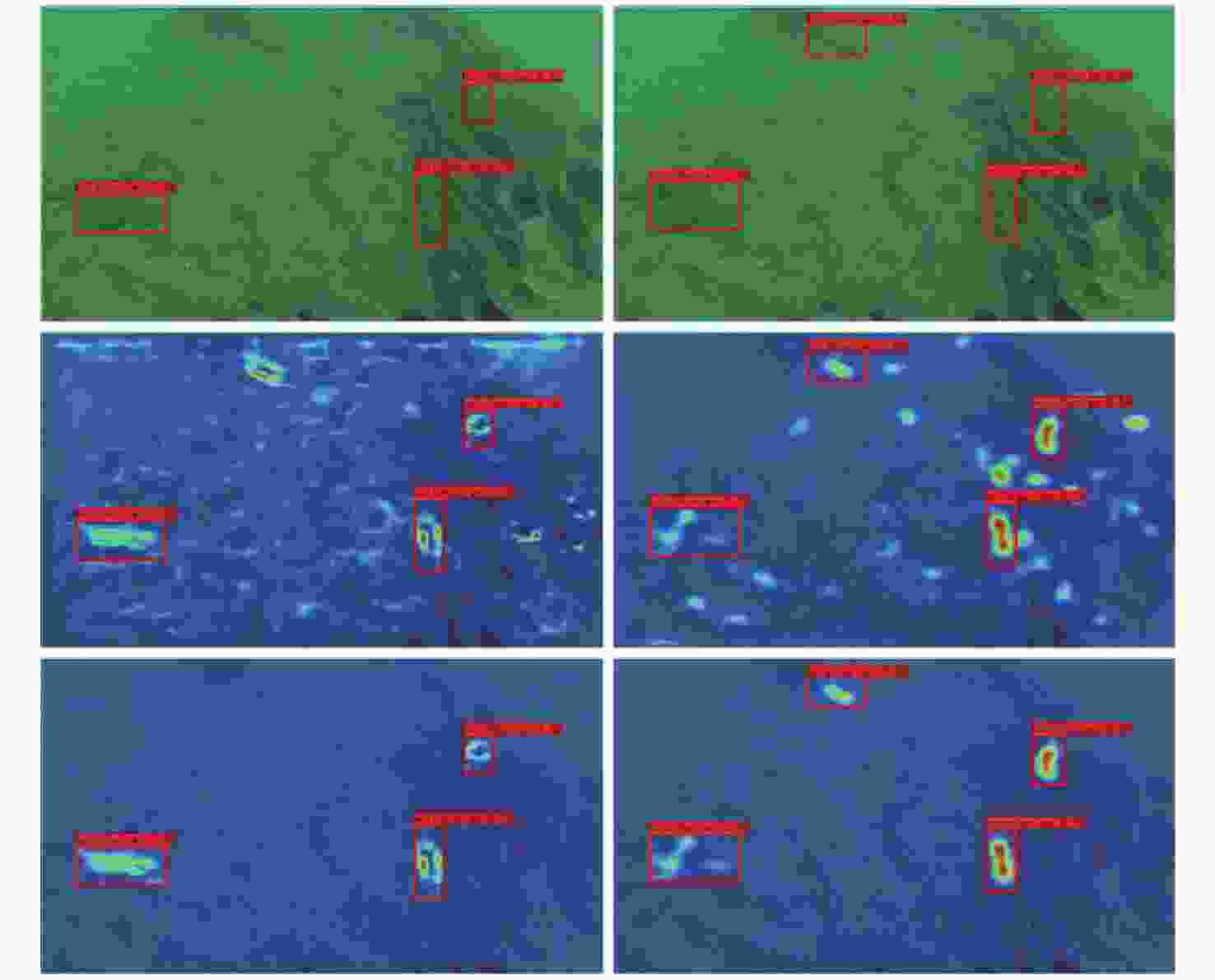
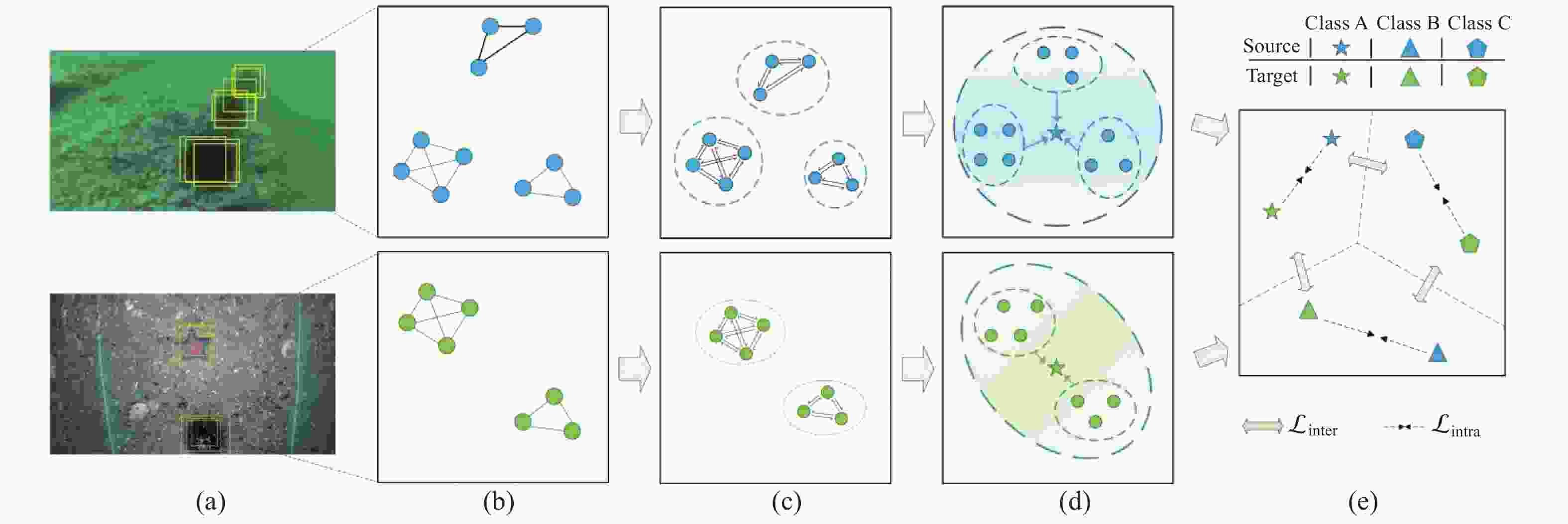
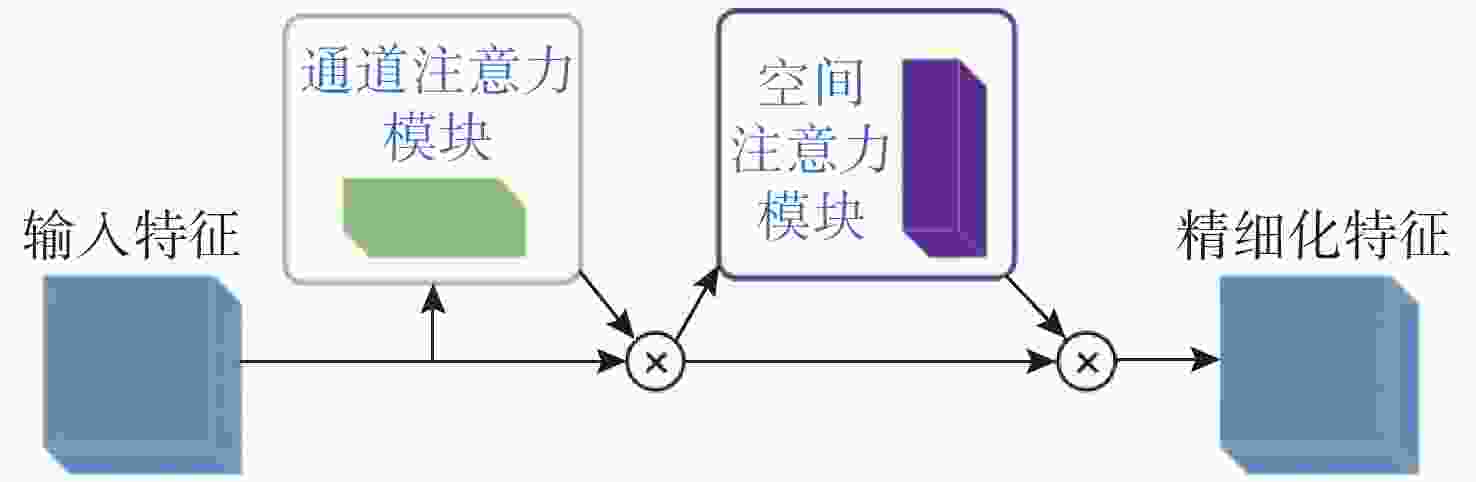
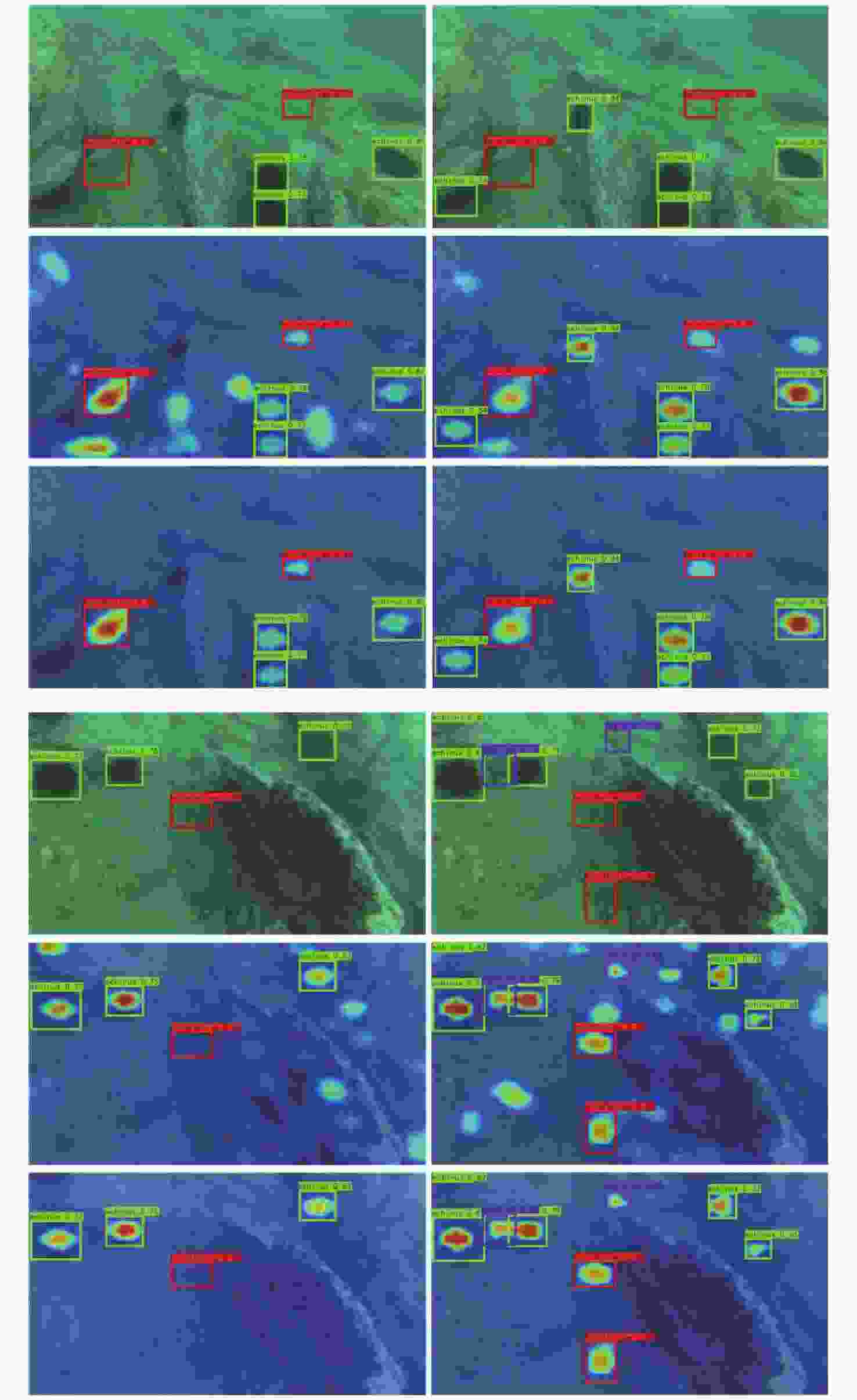
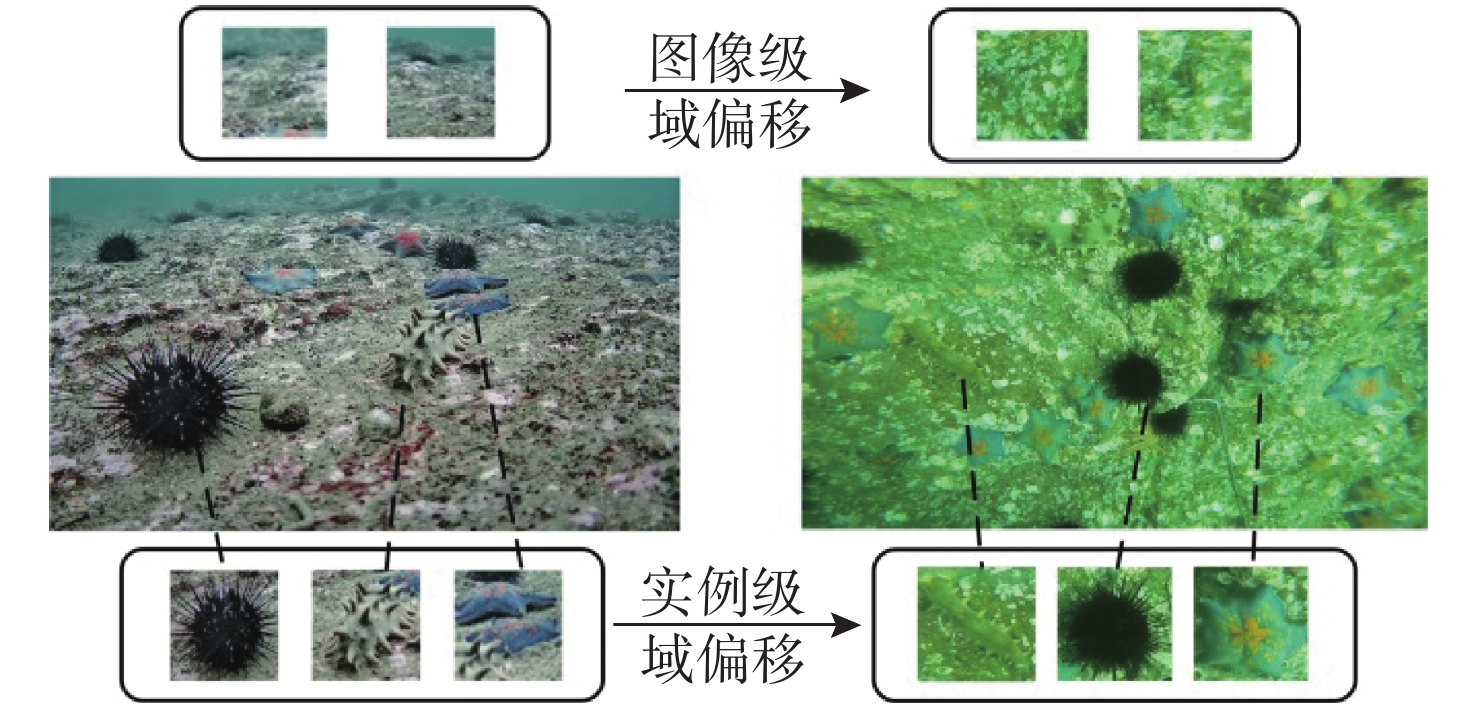
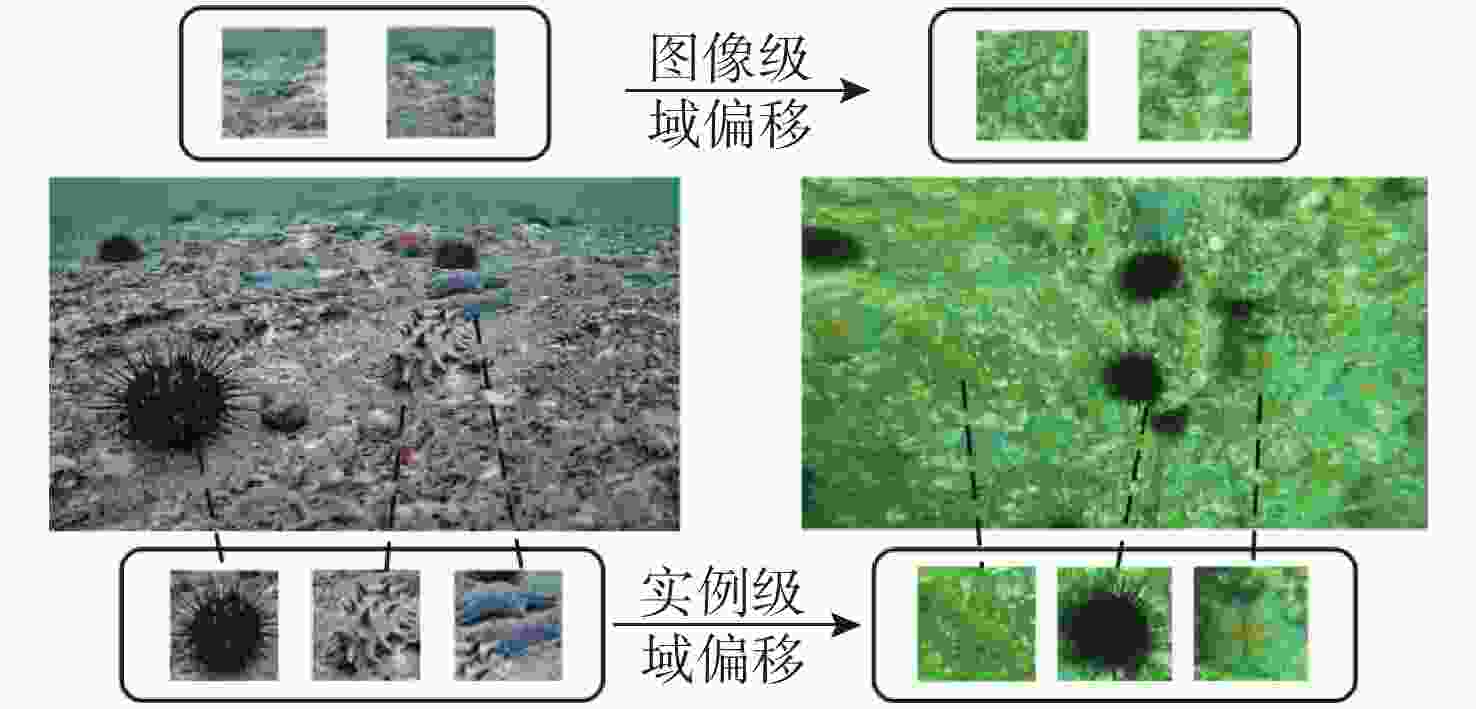
摘要: 水下环境因受到光照、泥沙等影响, 在水下进行目标检测时通常更容易出现域偏移而导致检测精度下降。针对此现象, 文中提出了基于图诱导对齐的域自适应水下目标检测方法, 图诱导原型对齐(GPA)是通过区域建议之间基于图的信息传播得到图像中的实例级特征, 再导出每个类别的原型表示用于类别级域的对齐。通过上述操作可以很好地聚合水下目标不同的模态信息, 以此实现源域和目标域的对齐从而减少域偏移带来的影响。此外, 为了使神经网络专注于不同水域分布下的实例级特征, 还在其中添加了卷积块注意(CBAM)模块。实验结果证明, 水下环境中GPA能有效对齐源域和目标域中的实例特征, CBAM可以使网络更加注意图像中的实例特征, 提高检测精度。Abstract: Underwater environments are often more susceptible to domain shift and reduced detection accuracy during underwater object detection due to the influence of lighting, sediment, and other factors. In response to this phenomenon, this article proposes a domain adaptive underwater target detection method based on graph induced alignment. Graph induced prototype alignment (GPA) obtains instance level features in the image through graph based information propagation between region proposals, and then derives prototype representations for each category for category level domain alignment. The above operations can effectively aggregate different modal information of underwater targets, thereby achieving alignment between the source and target domains and reducing the impact of domain offset. In addition, in order to focus the neural network on instance level features under different water distribution, a Convolutional Block Attention module (CBAM) was also added to it. The experimental results have shown that GPA can effectively align instance features in the source and target domains in underwater environments, while CBAM can make the network pay more attention to instance features in images and improve detection accuracy.
-
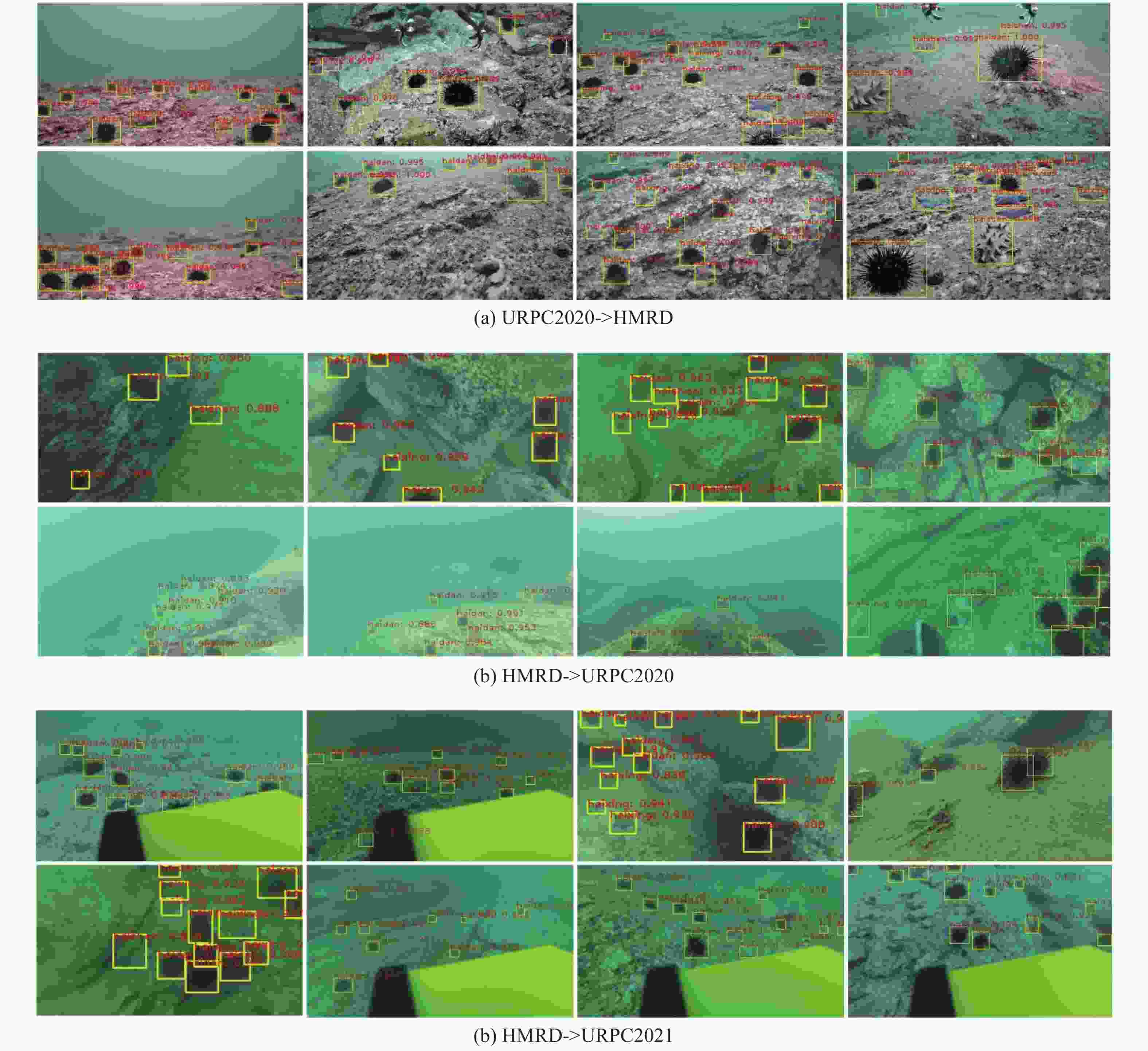
表 1 水下数据集URPC2020->HMRD实验结果(%)
Table 1. Underwater dataset URPC2020->HMRD experimental results(%)
方法 海参 海胆 海星 平均精度 基线 41.7 62.3 47.4 50.3 GPA方法 48.1 67.9 54.7 56.9 DA方法 49.2 68.1 58.6 58.6 本方法 52.0 69.7 60.1 60.6 表 2 公共数据集VOC12->VOC07实验结果(%)
Table 2. Public dataset VOC12->VOC07 experimental results(%)
方法 自行车 鸟 轿车 牛 狗 人 沙发 火车 平均精度 基线 73.7 69.3 72.1 77.2 80.0 76.2 60.1 88.3 74.6 GPA方法 76.0 68.1 74.2 75.3 84.2 77.8 61.8 85.9 75.4 DA方法 77.0 75.0 82.1 79.3 83.3 76.0 71.4 77.6 77.7 本方法 74.5 68.6 74.6 77.1 83.4 77.6 63.5 88.5 76.0 表 3 公共数据集sim10K->cityscapes实验结果(%)
Table 3. Public dataset sim10K->Cityscapes experimental results(%)
方法 精度 基线 34.9 GPA方法 46.1 DA方法 45.8 本方法 48.3 -
[1] 邱志明, 马焱, 孟祥尧, 等. 水下无人装备前沿发展趋势与关键技术分析[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(1): 1-9.Qiu Zhiming, Ma Yan, Meng Xiangyao, et al. Analysis on the development trend and key technologies of unmanned underwater equipment[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(1): 1-9. [2] 郝紫霄, 王琦. 基于声呐图像的水下目标检测研究综述[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(2): 339-348.Hao Zixiao, Wang Qi. Underwater target detection based on sonar image[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(2): 339-348. [3] 孙杰, 王红萍, 张丹, 等. 不同颜色照明下的水下成像差异研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2023, 31(4): 648-653.Sun Jie, Wang Hongping, Zhang Dan, et al. Difference between underwater imaging with illumination sources with different colors[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2023, 31(4): 648-653. [4] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ECCV, 2016: 21-37. [5] He K M, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[J/OL] ArXiv Preprint(2015-12-10). https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385. [6] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger[J/OL]ArXiv Preprint(2016-12-25). https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.08242. [7] Khodabandeh M, Vahdat A, Ranjbar M, et al. A robust learning approach to domain adaptive object detection[C]//IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), IEEE, 2019: 480-490. [8] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, IEEE, 2016: 779-788. [9] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, IEEE, 2014: 580-587. [10] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [11] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, IEEE, 2017: 936-944. [12] Gkioxari G , He K , Piotr Dollár, et al. Mask R-CNN[P]. 2017[2024-01-19]. [13] 罗逸豪, 刘奇佩, 张吟等. 基于深度学习的水下图像目标检测综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(10): 3468-3482. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221402Luo Yihao, Liu Qipei, Zhang Yin, et al. A review of underwater image object detection based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2023, 45(10): 3468-3482. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221402 [14] 姚文清, 李盛, 王元阳. 基于深度学习的目标检测算法综述[J]科技资讯, 2023, 21(16): 185-188.Yao Wenqing, Li Sheng, Wang Yuanyang. Overview of deep learning based object detection algorithms [J] Science and Technology Information, 2023, 21 (16): 185-188 [15] Sun B, Saenko K. Deep coral: Correlation alignment for deep domain adaptation[C]//Computer Vision–ECCV 2016 Workshops: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ECCV, 2016: 443-450. [16] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[P]. 2015[2024-01-19]. [17] Xu M, Wang H, Ni B, et al. Cross-domain detection via graph-induced prototype alignment[C]2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, IEEE, 2020, 12352-12361. [18] Vidit V, Engilberge M, Salzmann M. CLIP the Gap: A single domain generalization approach for object detection[C]//2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, IEEE, 2023: 3219-3229. [19] Vibashan V S, Oza P, Patel V M. Instance relation graph guided source-free domain adaptive object detection[C]//2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, IEEE, 2023: 3520-3530. [20] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[M]//Computer vision-ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 3-19. [21] Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel at-tention for deep convolutional neural net-works[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, IEEE, 2020: 11531-11539. [22] Liu J, Ni B, Li C, et al. Dynamic points agglomeration for hierarchical point sets learning[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), IEEE, 2019: 7545-7554. [23] Gretton A, Borgwardt K M, Rasch M J, et al. A kernel two-sample test[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Re-search, 2012, 13(1): 723-773. [24] Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Zhang N, et al. Deep domain confusion: Maximizing for domain invariance[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint(2014-12-10), https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3474v1. [25] Sankaranarayanan S, Balaji Y, Castillo C D, et al. Generate to adapt: Aligning domains using generative adversarial net-works[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, IEEE, 2018: 8503-8512. [26] Xu M, Zhang J, Ni B, et al. Adversarial domain adaptation with domain mixup[C]//2020 AAAI conference on Technical Track: Machine Learning, New York, USA, AAAI, 2020: 6502-6509. [27] Xie S, Zheng Z, Chen L, et al. Learning semantic representa-tions for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]//International conference on machine learning, Stockholm, Sweden, ICML, 2018: 5423-5432. [28] Chen C, Xie W, Huang W, et al. Progressive feature alignment for unsupervised domain adaptation[J/OL]ArXiv Preprint(2019-5-19) http://export.arxiv.org/abs/1811.08585. [29] Pan Y, Yao T, Li Y, et al. Transferrable prototypical networks for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2019: 2239-2247. [30] Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation net-works[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conferenceoncomputer vision and pattern recognition. 2018: 7132-7141. [31] Zhang H, Zu K, Lu J, et al. EPSANet: An efficient pyramid squeeze attention blockon convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 16793-16802. [32] Qin Z, Zhang P, Wu F, et al. Fcanet: Frequency channel attention networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2021: 783-792. [33] Li X, Hu X, Yang J. Spatial group-wise enhance: Improving semantic feature learning in convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer VisionandPattern Recognition. IEEE, 2018: 1873-1882. [34] Liu Z, Wang L, Wu W, et al. TAM: Temporal adaptive module for video recognition[J]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020, 14: 11337-11346. [35] Lin X, Guo Y A, Wang J. Global correlation network: End-to-end joint multi-object detection and track-ing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Com-puter Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020: 7060-7069. [36] Saito K, Ushiku Y, Harada T, et al. Strong-weak distribution alignment for adaptive object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 6956-6965. -




 下载:
下载: