Nonlinear Programming Based Fault-tolerant Control for X-rudder Underwater Vehicles with Rudder Failures
-
摘要: X舵因具有优越的操纵性和安全性, 近年来被越来越多的应用于自主式水下航行器上。为了充分发挥X舵的容错能力, 提出一种面向舵故障的水下航行器容错运动控制算法, 并将其部署在一种X舵水下航行器原型上。容错运动控制算法由动力学控制和控制分配两部分组成。其中, 动力学控制中多闭环增量反馈控制算法的引入可以使输出的虚拟舵角指令平缓且平滑; 控制分配算法通过求解以分配误差和控制输出最小化为优化目标, 以舵故障、舵角饱和以及其他物理限制为约束条件的非线性规划问题, 实现了虚拟舵角向X舵执行机构控制输入的转换, 且赋予了X舵水下航行器容错运动能力。现场试验结果表明: 所提出的容错运动控制算法产生的舵角指令是平滑的, 且X舵水下航行器在舵故障后仍保持一定的航行控制能力, 这对设计应用于X舵水下航行器的容错操舵系统具有一定的指导意义。Abstract: X rudder has been increasingly applied to autonomous underwater vehicles in recent years due to its better maneuverability and safety. To fully utilize the fault-tolerant capability of the X rudder, this paper proposes a fault-tolerant motion control algorithm for underwater vehicles oriented towards rudder failures and deploys it on a prototype of an X rudder underwater vehicle. The fault-tolerant motion control algorithm consists of two parts: dynamics control and control allocation. In the dynamics control, the introduction of a multi-loop incremental feedback control algorithm in the output virtual rudder instruction can make it smooth and gentle. The control allocation algorithm converts the virtual rudder command to the control input of the X rudder actuator by solving a nonlinear programming problem with the optimization goal of minimizing the allocation error and control output, and considering the constraints of rudder failure, rudder angle saturation, and other physical limitations. This also enables the X rudder underwater vehicle to have fault-tolerant motion capabilities. Field trial results show that the rudder instructions generated by the fault-tolerant motion control algorithm proposed in this paper are smooth, and the X rudder underwater vehicle still maintains a certain control capability after the rudder failure. This has certain guiding significance for the design of a fault-tolerant steering system applied to X rudder underwater vehicles.
-
Key words:
- x-rudder /
- AUV /
- control allocation /
- fault-tolerant control /
- nonlinear programming
-
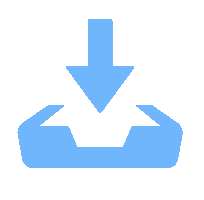
表 1 X舵AUV主要参数
Table 1. Main Parameters of X-rudder AUV
参数名 参数值 艇长/m 2.964 水下全排水体积/m3 0.229 5 总质量/kg 231.9 最大推力/N 75.6 表 2 卡舵故障设置
Table 2. Rudder jamming settings
试验序号 故障舵序号 卡舵角度/(°) 1 舵1 0 2 舵2 −5 3 舵3 −10 -
[1] 黄琰, 李岩, 俞建成, 等. AUV智能化现状与发展趋势[J]. 机器人, 2020, 42(2): 215-231.Huang Yan, Li Yan, Yu Jiancheng, et al. State-of-the-art and development trends of AUV intelligence[J]. Robot, 2020, 42(2): 215-231. [2] 陈纪军, 潘子英, 彭超, 等. 十字形和X形艉舵航行体的水动力特性对比[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2020, 15(2): 8-16.Chen Jijun, Pan Ziying, Peng Chao, et al. Comparison of hydrodynamic characteristics of SUBOFF with cruciform and X-form rudder arrangement[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2020, 15(2): 8-16. [3] Overpelt, Anderson N B. Free running manoeuvring model tests on a modern generic SSK class submarine(BB2)[C]//Royal Institution of Naval Architects. Sydney, Australia: [s. n.], 2015: 1-12. [4] Nakamura M, Hyakudome T. Motion control performance of AUV "YUMEIRUKA" with broken X rudder[J]. Journal of the Japan Society of Naval Architects and Ocean Engineers, 2019(29): 103-115. [5] Wang W, Xia Y, Chen Y, et al. Motion control methods for X-rudder underwater vehicles: Model based sliding Mode and non-model based iterative sliding mode[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 216: 108054. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108054 [6] Xia Y, Xu K, Wang W, et al. Optimal robust trajectory tracking control of a X-rudder AUV with velocity sensor failures and uncertainties[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 198: 106949. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.106949 [7] 商建朋, 李文魁, 黄跃鹏. 潜艇X舵控制分配器设计和仿真[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2020, 15(2): 137-142.Shang Jianpeng, Li Wenkui, Huang Yuepeng, et al. Design and simulation of X-rudder control allocator for submarine[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2020, 15(2): 137-142. [8] Wang W, Wen T, He X, et al. Robust trajectory tracking and control allocation of X-rudder AUV with actuator uncertainty[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2023, 136: 105535. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2023.105535 [9] 褚振忠, 朱大奇. 基于自适应区域跟踪的自主式水下机器人容错控制[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 57-63.Chu Zhenzong, Zhu Daqi. Fault-tolerant control of autonomous underwater vehicle based on adaptive region tracking[J]. Journal of Shandong University(Engineering Science), 2017, 47(5): 57-63. [10] Liu X, Zhang M, Wang Y, et al. Design and experimental validation of an adaptive sliding mode observer-based fault-tolerant control for underwater vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 27(6): 2655-2662. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2018.2870829 [11] Li X G, Chao H, Wang J M, et al. An iterative learning extended-state observer-based fuzzy fault-tolerant control approach for AUVs[J]. Marine Technology Society journal, 2021(4): 55. [12] 王小平. X舵AUV控制分配优化与容错控制方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2020. [13] 曾俊宝, 李硕, 李一平, 等. 便携式自主水下机器人控制系统研究与应用[J]. 机器人, 2016, 38(1): 91-97.Zeng Junbao, Li Suo, Li Yiping, et al. Research and application of the control system for a portable autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Robot, 2016, 38(1): 91-97. [14] 高彬彬. 基于ROS的AUV嵌入式控制系统研究与设计[D]. 杭州: 杭州电子科技大学, 2020. [15] 邱海洋, 曾庆军, 智鹏飞. 基于MOOS的自主式水下机器人导航系统[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(6): 721-726.Qiu Haiyang, Zeng Qingjun, Zhi Pengfei. Navigation system of autonomous underwater vehicle based on MOOS[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 42(6): 721-726. [16] Hien N V, Truong V T, Bui N T. A model-driven realization of AUV controllers based on the MDA/MBSE approach[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020, 848776: 1-14. [17] 郑煜. 大尺度无人潜艇的应急控制技术研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019. [18] 李慧, 赵琳, 毛英. 海况干扰下潜艇六自由度运动分析[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2017, 38(1): 94-100. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201511027Li Hui, Zhao Lin, Mao Ying. Analysis of six-degree-of-freedom motion in submarines under sea disturbance[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2017, 38(1): 94-100. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201511027 [19] Bazaraa M S. Nonlinear programming: theory and algorithms[M]. New York, U. S: Wiley Publishing, 2006. [20] Granas A, Dugundji J. Fixed point theory[M]. Berlin, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. [21] 李岳明, 王小平, 张英浩, 等. 水中航行器控制分配技术应用现状[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2020, 42(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2020.01.001Li Yueming, Wang Xiaoping, Zhang Yinghao, et al. Application status of underwater vehicle control allocation technology[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2020, 42(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2020.01.001 -





 下载:
下载: