Electrochemical Characteristics of Typical Ship Materials in Low-Temperature Seawater
-
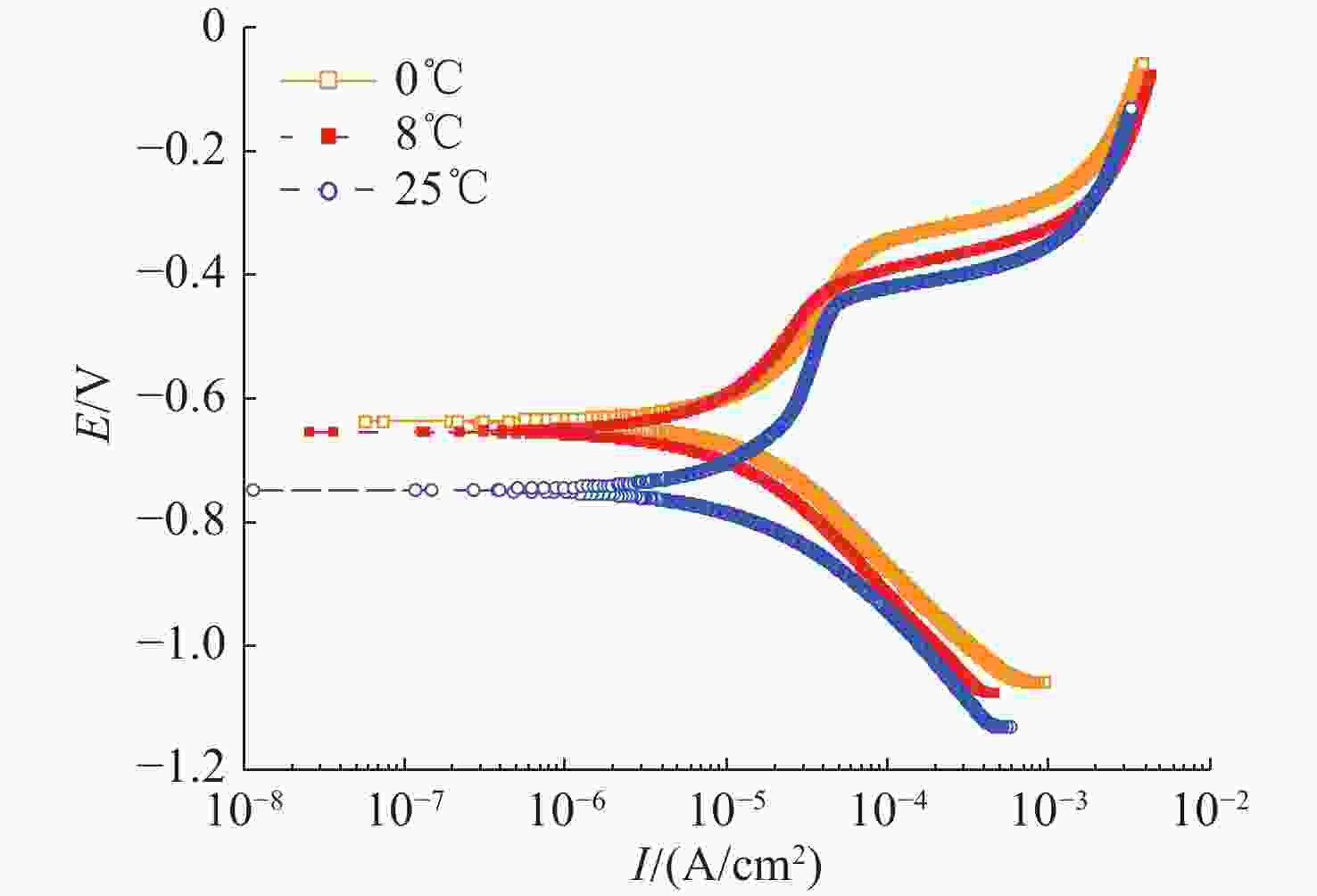
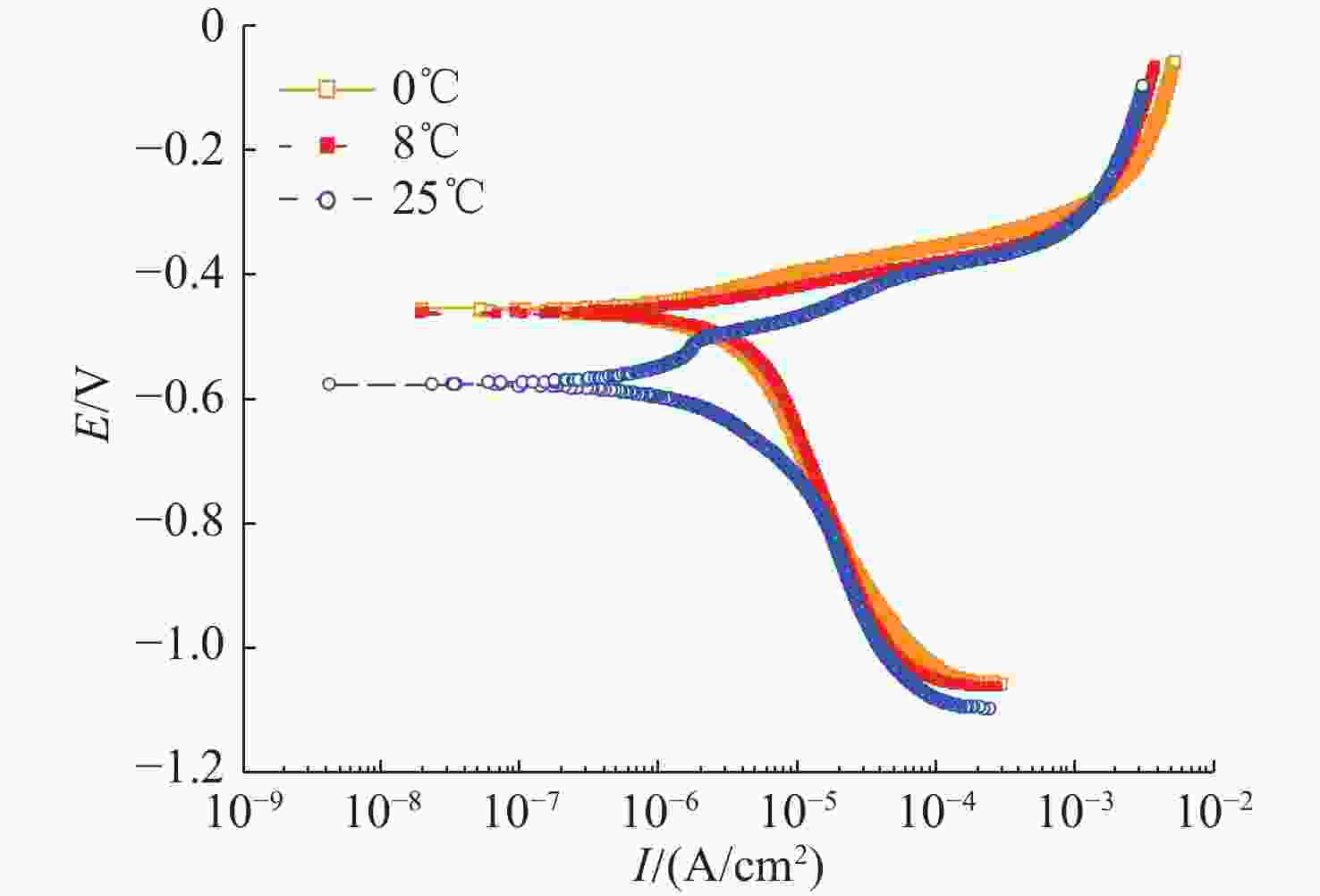
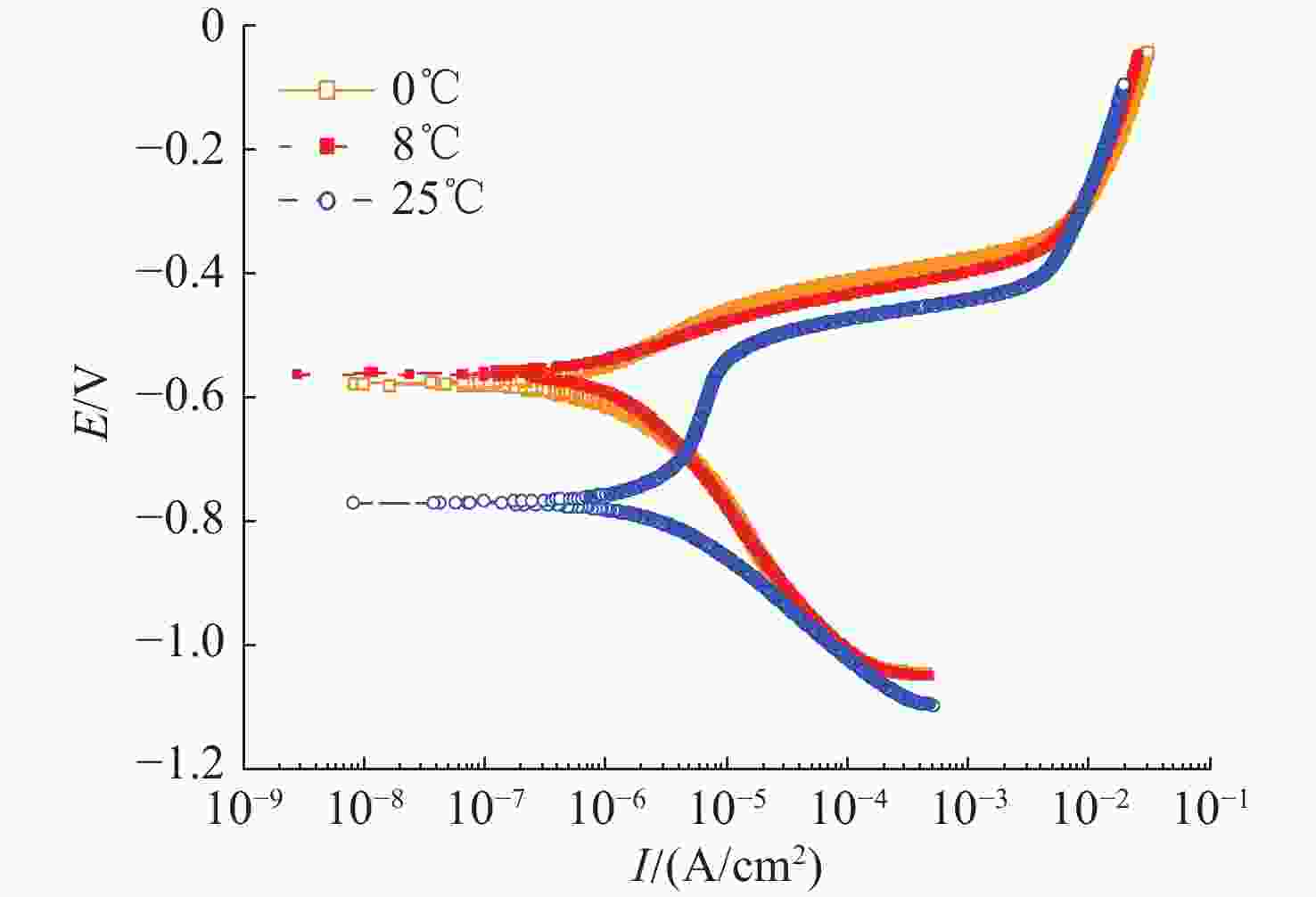
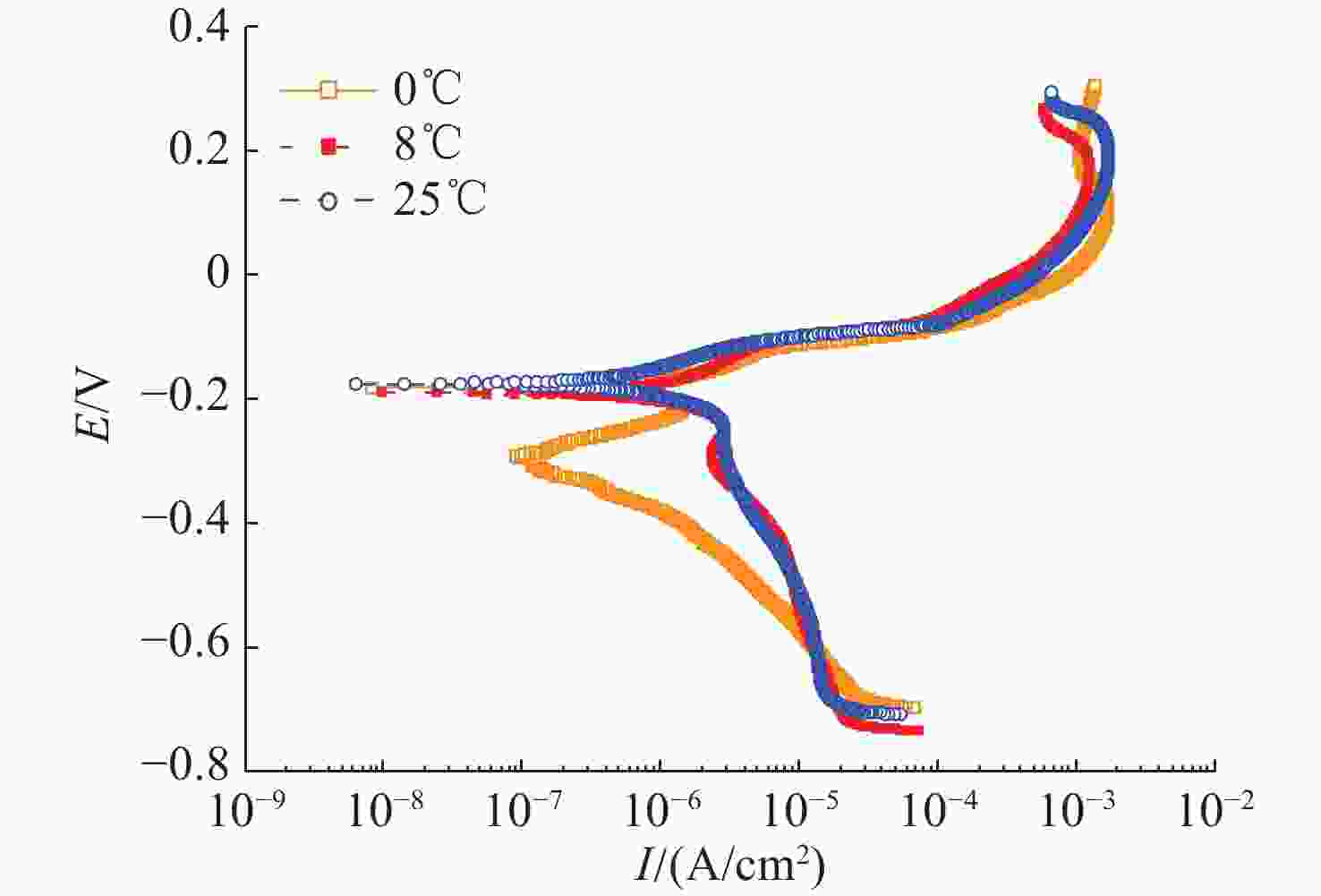
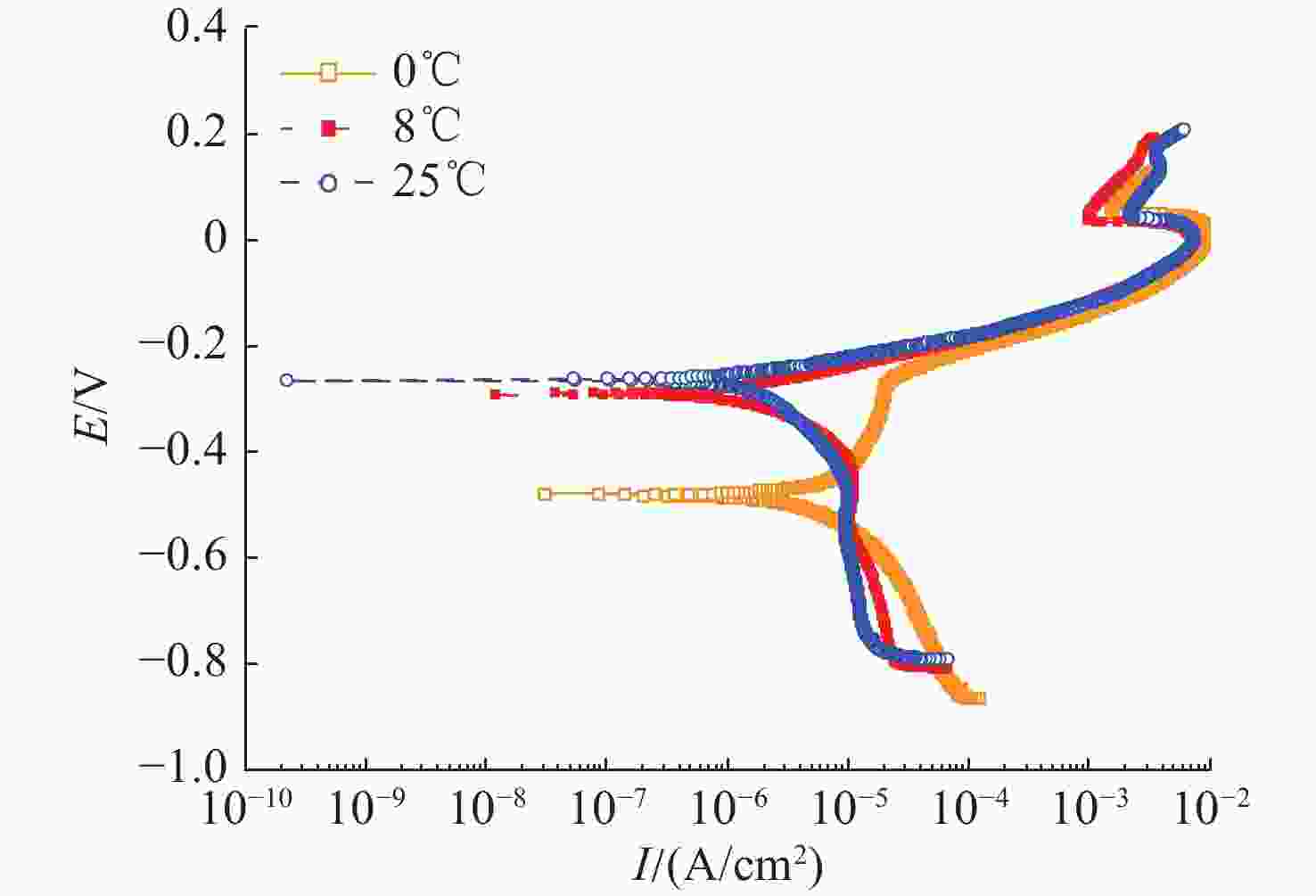
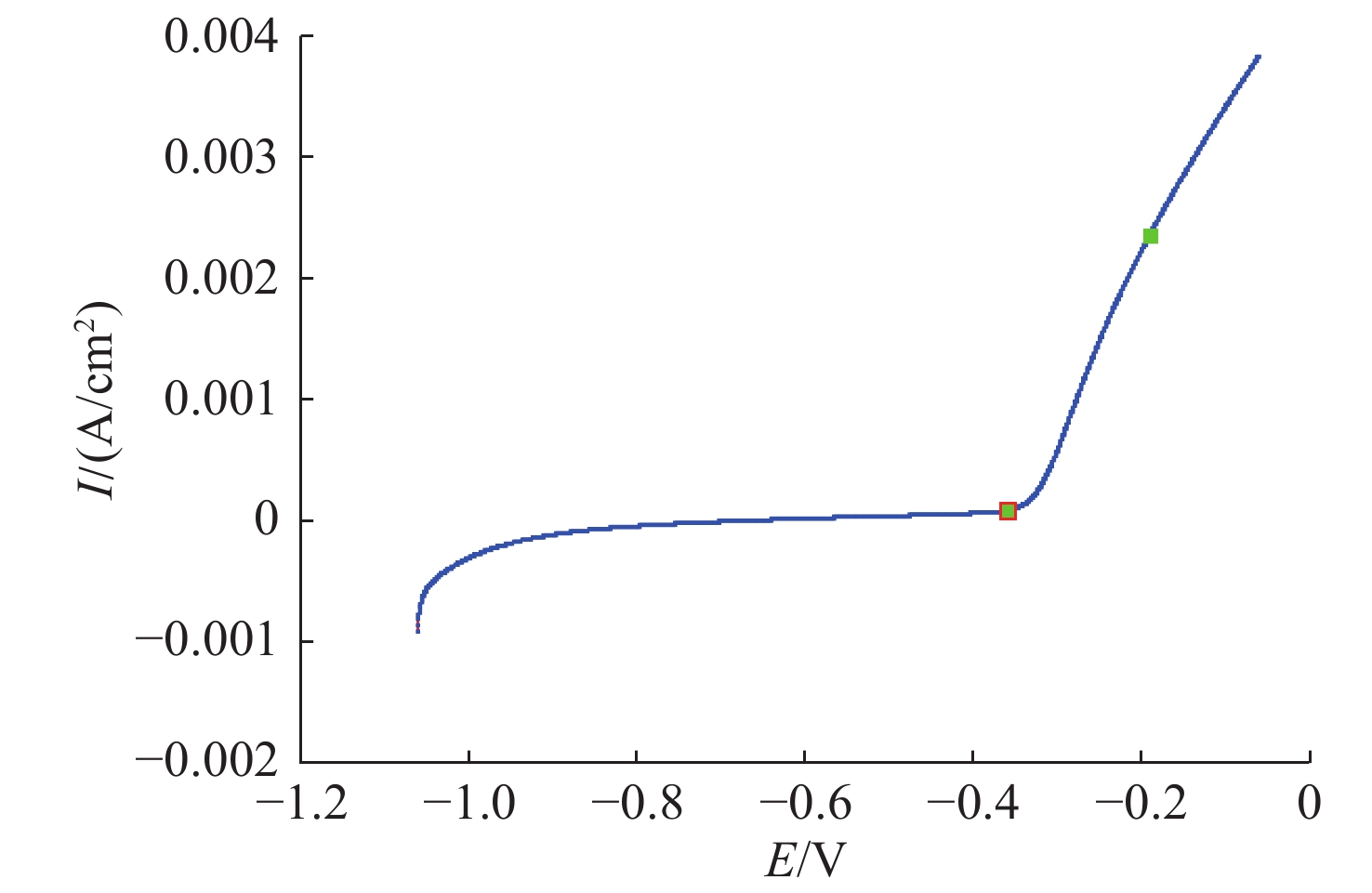
摘要: 船舶金属材料在海洋环境中的电化学特性是船舶电场特性产生过程中的重要影响因素, 长期以来, 国内多聚焦于常温海水环境下的金属材料电化学性能研究, 对低温海水环境下的金属材料电化学特性研究较少。文中针对3种典型的船舶主体材料, 开展了不同温度及盐度影响试验, 对比分析其在低温海水环境下的极化电位、极化曲线及极化电阻, 总体结果表明金属材料的开路电位随海水温度的降低而增大, 自腐蚀电位随着海水温度的降低而正移, 随着海水温度的降低溶解活化程度变低。文中工作可为进一步研究电场特征控制和分析评估提供基础理论参考。Abstract: The electrochemical characteristic of ship metal materials in marine environments is an important factor affecting the generation of ship electric field characteristics. For a long time, researchers have mainly focused on the electrochemical characteristics of metal materials in normal-temperature seawater but paid less attention to the electrochemical characteristics of metal materials in low-temperature seawater. For three typical ship materials, experiments were designed based on the influence of different temperatures and salinity changes, and the polarization potential, polarization curve, and polarization resistance were compared in the low-temperature seawater. The results show that with the decrease in seawater temperature, the open circuit potential of metal materials and self-corrosion potential increase, but the degree of dissolution activation decreases. The proposed method may provide a reference for the study of electric field characteristic control and analysis and evaluation.
-
Key words:
- low temperature seawater /
- ship materials /
- salinity /
- polarization curve
-
表 1 环境因素影响试验设计
Table 1. Environmental factor affecting test design
序号 试验件材料 温度/℃ 盐度/% 1 高强钢1# 0 0.35 2 2.00 3 3.50 4 8 0.35 5 2.00 6 3.50 7 25 0.35 8 2.00 9 3.50 10 高强钢2# 0 0.35 11 2.00 12 3.50 13 8 0.35 14 2.00 15 3.50 16 25 0.35 17 2.00 18 3.50 19 铜合金 0 0.35 20 2.00 21 3.50 22 8 0.35 23 2.00 24 3.50 25 25 0.35 26 2.00 27 3.50 表 2 不同环境下高强钢1#开路电位
Table 2. Open circuit potential of high-strength steel 1# under different environments
序号 盐度/% 温度/℃ 开路电位/V 1 0.35 0 −0.557 621 6 2 8 −0.577 322 2 3 25 −0.632 556 3 4 2.00 0 −0.540 334 3 5 8 −0.562 500 1 6 25 −0.587 693 3 7 3.50 0 −0.550 457 5 8 8 −0.563 194 1 9 25 −0.628 237 7 表 3 不同环境下高强钢2#开路电位
Table 3. Open circuit potential of high-strength steel 2# under different environments
序号 盐度/% 温度/℃ 开路电位/V 1 0.35 0 −0.555 202 7 2 8 −0.564 018 2 3 25 −0.597 781 4 4 2.00 0 −0.525 225 0 5 8 −0.533 390 5 6 25 −0.559 813 5 7 3.50 0 −0.543 708 0 8 8 −0.550 279 3 9 25 −0.597 205 3 表 4 不同环境下铜合金开路电位
Table 4. Open circuit potential of copper alloy under different environments
序号 盐度/% 温度/℃ 开路电位/V 1 0.35 0 −0.195 224 0 2 8 −0.234 144 3 3 25 −0.208 928 6 4 2.00 0 −0.273 376 7 5 8 −0.265 310 0 6 25 −0.281 084 6 7 3.50 0 −0.363 952 3 8 8 −0.309 637 3 9 25 −0.293 071 4 表 5 不同环境下高强钢1#极化电阻
Table 5. Polarization resistance of high-strength steel 1# under different environments
序号 盐度/% 温度/℃ 极化电阻/(Ω/cm2) 1 0.35 0 65.100 2 8 61.425 3 25 79.074 4 2.00 0 17.975 5 8 22.314 6 25 22.824 7 3.50 0 15.611 8 8 14.575 9 25 14.518 表 6 不同环境下高强钢2#极化电阻
Table 6. Polarization resistance of high-strength steel 2# under different environments
序号 盐度/% 温度/℃ 极化电阻/(Ω/cm2) 1 0.35 0 54.665 2 8 74.629 3 25 84.965 4 2.00 0 20.903 5 8 19.827 6 25 19.032 7 3.50 0 12.722 8 8 14.556 9 25 18.837 表 7 不同环境下铜合金极化电阻
Table 7. Polarization resistance of copper alloy under different environments
序号 盐度/% 温度/℃ 极化电阻/(Ω/cm2) 1 0.35 0 101.170 2 8 154.480 3 25 124.640 4 2.00 0 30.878 5 8 21.915 6 25 28.046 7 3.50 0 19.860 8 8 16.229 9 25 16.390 表 8 不同环境下金属电位差
Table 8. Metal potential difference under different environments
序号 金属材质 盐度/% 温度/℃ 电位差/V 1 高强钢1# 铜合金 0.35 0 0.362 40 2 8 0.343 18 3 25 0.423 63 4 2.00 0 0.266 96 5 8 0.297 19 6 25 0.306 61 7 3.50 0 0.186 51 8 8 0.253 56 9 25 0.335 17 10 高强钢2# 铜合金 0.35 0 0.359 98 11 8 0.329 87 12 25 0.388 85 13 2.00 0 0.251 85 14 8 0.268 08 15 25 0.278 73 16 3.50 0 0.179 76 17 8 0.24064 18 25 0.30413 -
[1] 孙公毅, 裴建新, 陈家林, 等. 水下极低频电磁信号探测中的海流感应电磁噪声压制[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(12): 72-80.Sun Gongyi, Pei Jianxin, Chen Jianlin, et al. Current induced electromagnetic noise suppression in underwater extremely low frequency electromagnetic signal detection[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(12): 72-80. [2] 孙强, 姜润翔, 喻鹏, 等. 船体状态对电流补偿式电场隐身控制参量的影响[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2020, 28(12): 657-662.Sun Qiang, Jiang Runxiang, Yu Peng et al. Effects of hull states on the control parameter of the current compensation electric field stealth[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2020, 28(12): 657-662. [3] 孙宝全, 颜冰, 姜润翔, 等. 船舶静电场在船舶跟踪定位中的应用[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2018, 26(1): 57-62.Sun Baoquan, Yan Bing, Jiang Runxiang et al. Application of ship static electric field of ship tracking and positioning[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2018, 26(1): 57-62. [4] 李越, 张伽伟, 程锦房. 基于信号特征的舰船轴频电场检测改进算法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(4): 398-405.Li Yue, Zhang Jiawei, Cheng Jinfang. Improved detection algorithm of ship’s shaft-frequency electric field based on signal features[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(4): 398-405. [5] 卞强, 张民, 柳懿, 等. 一种基于ANSYS 的舰船静电场分析方法[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2010, 22(6): 65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3486.2010.06.014Bian Qiang, Zhang Min, Liu Yi, et al. An analytic method of ship static electric field[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2010, 22(6): 65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3486.2010.06.014 [6] 李俊, 包中华, 龚沈光, 等. 优化ICCP 系统的船舶静电场隐身研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2011, 23(1): 67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3486.2011.01.014Li Jun, Bao Zhonghua, Gong Shenguang, et al. Optimization of ICCP systems to minimise static electric signatures for stealth vessels[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2011, 23(1): 67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3486.2011.01.014 [7] 张华, 王向军, 单潮龙, 等. 基于目标静电场的水中兵器制导方法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 23(3): 470-474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.03.009Zhang Hua, Wang Xiangjun, Shan Chaolong, et al. Research of guidance method based on the electrostatic field of target for underwater weapon[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 23(3): 470-474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.03.009 [8] 刘春阳, 王建山, 赵玉龙. 海洋环境对潜艇阴极保护和水下腐蚀静电场的影响[J]. 船电技术, 2022, 42(6): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4862.2022.06.018Liu Chunyang, Wang Jianshan, Zhao Yulong. Effects of marine environment on cathodic protection and underwater corrosion electrostatic field of submarine[J]. Marine Electric and Electronic Engineering, 2022, 42(6): 56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4862.2022.06.018 [9] 余定峰, 耿攀, 徐正喜, 等. 基于有限元的水下航行器腐蚀静电场特性分析[J]. 船电技术, 2016, 36(6): 23-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4862.2016.06.006Yu Dingfeng, Geng Pan, Xu Zhengxi, et al. Analysis on corrosion related static electric field of underwater vehicle by finite element method[J]. Marine Electric and Electronic Engineering, 2016, 36(6): 23-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4862.2016.06.006 [10] 王泗环, 郁大照, 王腾. 不同环境因素对H62铜合金极化曲线的影响分析[J]. 海军航空工程学院学报, 2019, 34(3): 309-316.Wang Sihuan, Yu Dazhao, Wang Teng. Influence analysis of different environmental factors on polarization curve of h62 copper alloy[J]. Journal of Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University, 2019, 34(3): 309-316. [11] 王凤平, 康万利, 敬和民. 腐蚀电化学原理、方法及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. [12] 洪刚, 程旭东, 张海兵, 等. Al-Sn-Ga-Bi-Pb-Cd合金电极低温海水电化学性能研究[J]. 电镀与精饰, 2008, 40(4): 33-37.Hong Gang, Cheng Xudong, Zhang Haibing et al. Elecrochemical behavior of Al-Sn-Ga-Bi-Pb-Cd alloy in cold seawater[J]. Plating and Finishing, 2008, 40(4): 33-37. -





 下载:
下载: