Review of Non-Acoustic Detection Technologies of Submarines
-
摘要: 传统声学探潜技术由于作战环境的复杂化已逐渐受限, 与此同时, 非声探潜技术的重要性日益展现。文章分别介绍了磁异探潜技术、激光探潜技术、尾流探潜技术、电场探潜技术以及红外探潜等其他非声探潜技术, 详细描述了各种非声探潜技术的优势及其局限性, 并对非声探潜技术的发展趋势进行了展望, 旨在为研究非声探潜技术提供有益参考。Abstract: Due to the complexity of the combat environment, the traditional acoustic detection technologies of submarines are gradually limited, and the importance of non-acoustic detection technologies of submarines is increasingly shown. This article respectively introduced the magnetic anomaly detection technology, laser detection technology, wake detection technology, electric field detection technology, and other non-acoustic detection technologies of submarines, described the advantages and limitations of these technologies, and predicted their development trend, so as to provide a reference for the development of detection technologies of submarines.
-
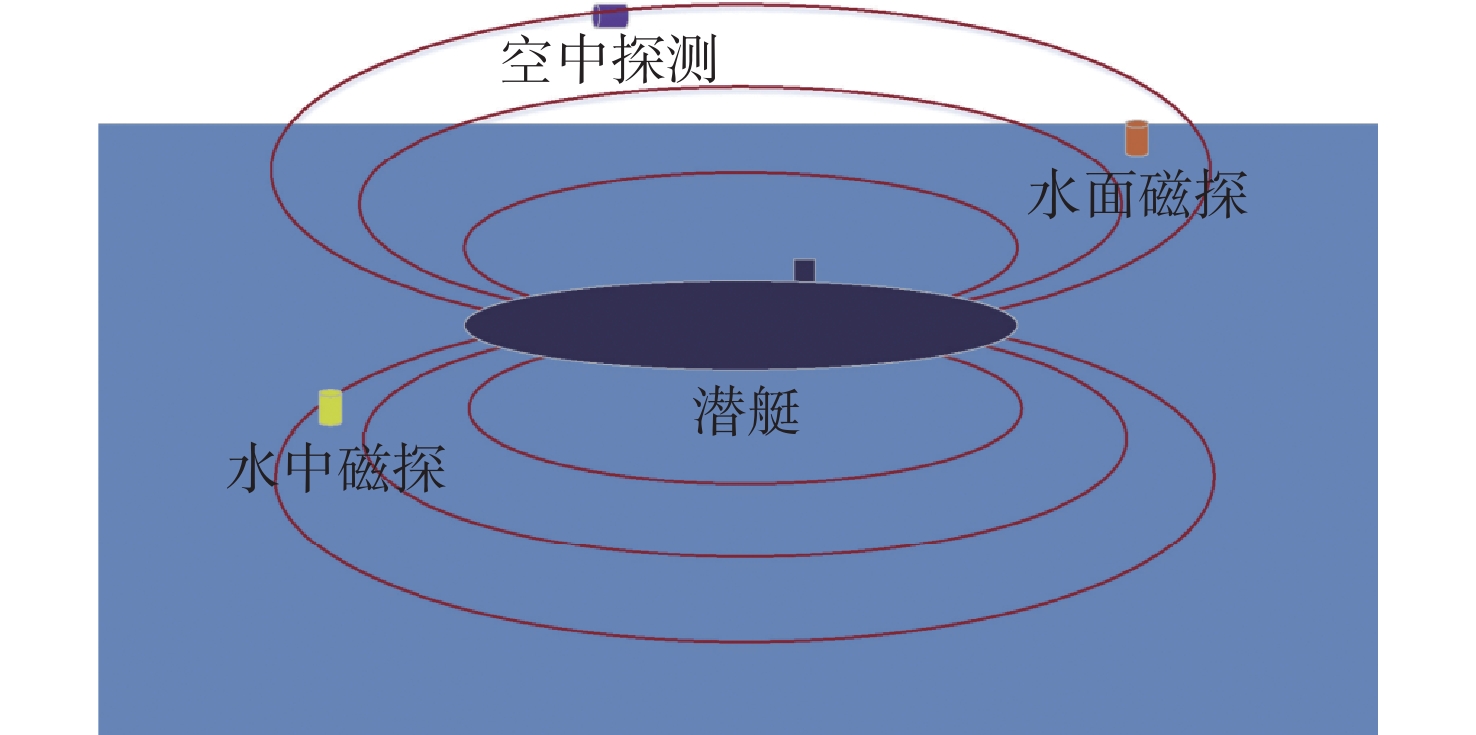
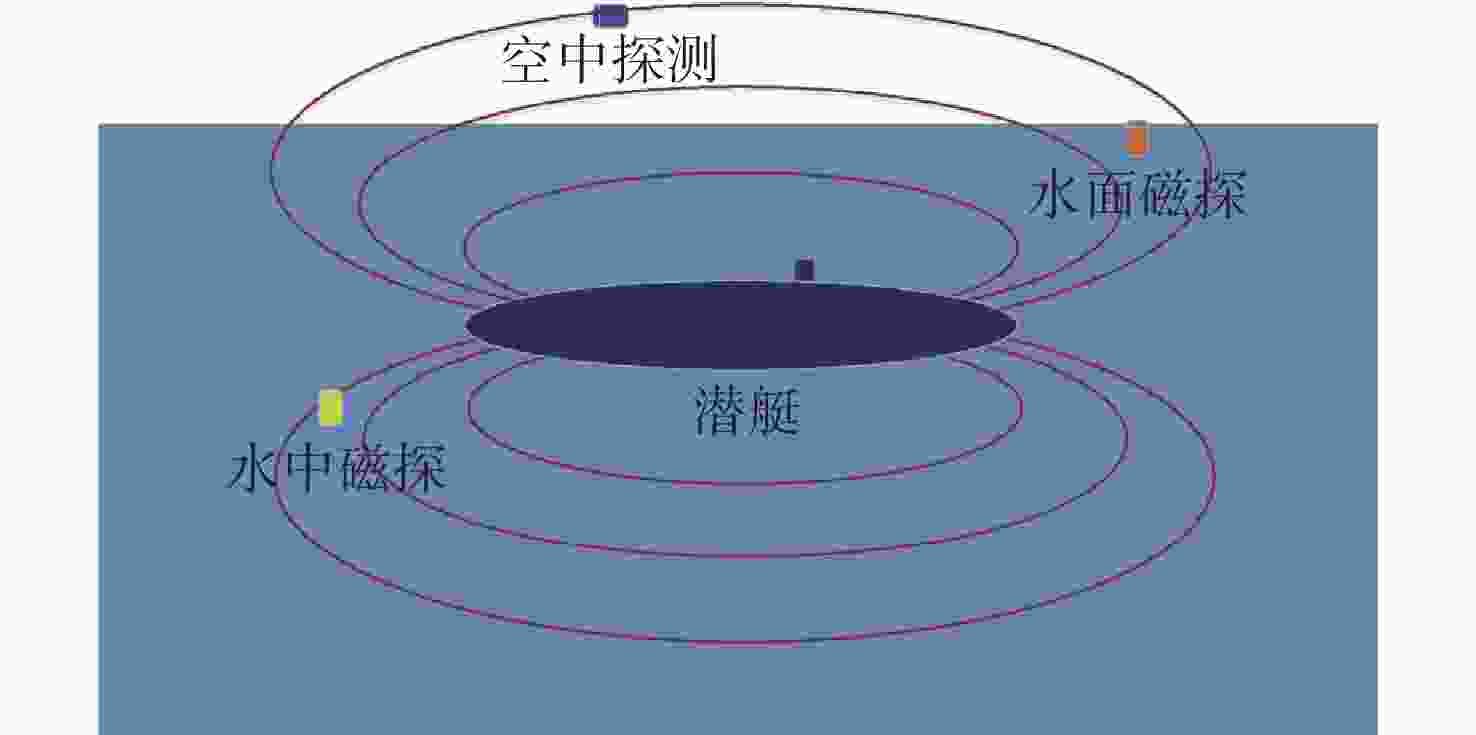
表 1 AN/ASQ-81型磁探仪性能指标
Table 1. Performance index of AN/ASQ-81 megnetometer
探测目标 最大作用距离/m 定位误差/m 深海 浅海 常规潜艇 — 290 ≤200 核潜艇 450 350 ≤300 表 2 典型激光水下探测系统
Table 2. Typical laser underwater detection system
探测系统 国别 飞行高度
/m探测深度
/mSparta水下激光成像系统 美国 — <50 SM2000水下激光成像系统 美国 — 45 “鹰眼”水下激光海洋探测系统 瑞典 — 70 LADSMK II水深测量系统 澳大利亚 500 0~70 表 3 各种探潜技术对比分析
Table 3. Comparative analysis of various submarine detection technologies
探潜技术 优势 劣势 磁异探潜 ① 定位精度较高
② 执行能力强
③ 受水文条件影响较低① 磁场信号较弱
② 磁场衰减迅速激光探潜 ① 探测方向性好
② 定位较准确
③ 透过性和准直度高
④ 成像和测距效果较理想水体对光的衰减较为严重, 经多次散射后, 很难找到激光原始信息 SAR探潜 ① 定位精度高
② 探测范围广
③ 发现目标快
④ 能在恶劣环境和黑夜中工作SAR工作频段是微波频段, 微波很难穿透海水, 因此探测范围受限 电场探潜 ① 极低频电磁波频率低、衰减小
② 受海况和天气条件等影响较小探测范围有限 红外探潜 ① 隐蔽性高
② 日夜均可使用恶劣天气对其影响较大 重力梯度探潜 ① 隐蔽性高
② 对外界环境的敏感度小尚处于理论阶段, 技术突破性难度较大 废气探潜 隐蔽性高 受风力等气象条件影响较大 核辐射探潜 ① 核潜艇不可避免存在核辐射
② 受气象和海况条件影响较小技术尚未成熟 -
[1] 梅风华, 侯旺. 非声探潜技术在航空尾迹探测上的应用[J]. 电光与控制, 2017, 24(7): 62-65.Mei Fenghua, Hou Wang. Application of non-acoustic submarine exploration technology in aviation wake detection[J]. Electro-Optics & Control, 2017, 24(7): 62-65. [2] 宫继祥. 浅海非声探潜[J]. 现代舰船, 1996(11): 29-31.Gong Jixiang. Non-acoustic diving in shallow sea[J]. Modern Ships, 1996(11): 29-31. [3] 成建波, 孙心毅. 航空磁异常探潜技术发展综述[J]. 声学与电子工程, 2018(3): 46-49.Cheng Jianbo, Sun Xinyi. Review on the development of avionically anomalous submarine exploration technology[J]. Acoustics & Electronic Engineering, 2018(3): 46-49. [4] 艾艳辉, 赵志平. 非声探测技术面面观[J]. 水雷战与舰船防护, 2003(3): 43-46. [5] 崔国恒, 于德新. 非声探潜技术现状及其对抗措施[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2007, 32(12): 10-13.Cui Guoheng, Yu Dexin. Current situation of non-acoustic submarine exploration technology and countermeasures[J]. Fire Power & Command and Control, 2007, 32(12): 10-13. [6] 王翠珍, 唐金元. 现代航空搜潜技术[M]. 北京: 海潮出版社, 2003: 51-52. [7] 翁行泰, 曹梅芬, 吴文福, 等. 磁异探潜中潜艇的数学模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 1995(3): 27-32.Weng Xingtai, Cao Meifen, Wu Wenfu, et al. Mathematical model of submarine in magnetic exploration[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 1995(3): 27-32. [8] 孙明太. 航空反潜战术[M]. 北京: 军事科学出版社, 2003: 99-106. [9] 陈正想, 卢俊杰. 弱磁探测技术发展现状[J]. 水雷战与舰船防护, 2011, 19(4): 1-5. [10] Fletche R B. Antonelli L T. Experimental detection and reception performance for uplink underwater acoustic communication using a remote in-air acousto-optic sensor[J]. Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2006, 31(1): 179-187. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2005.861248 [11] 李哲, 邓甲昊, 周卫平. 水下激光探测技术及其进展[J]. 船舶电子工程, 2008, 48(12): 8-11.Li Zhe, Deng Jiahao, Zhou Weiping. Underwater laser detection technology and its progress[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2008, 48(12): 8-11. [12] 方尔正, 桂晨阳, 王欢. 潜艇的非声学探测技术[J]. 国防科技工业, 2020(6): 66-68.Fang Erzheng, Gui Chenyang, Wang Huan. Non-acoustic detection technology of submarine[J]. Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense, 2020(6): 66-68. [13] Stefasnick T. The nonacoustic detection of submarines[J]. Scientific American, 1998, 258(3): 41-47. [14] 张军, 张效慈, 赵峰, 等. 源于水动力学的潜艇尾迹非声探测技术研究之进展[J]. 船舶力学, 2003, 7(2): 121-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2003.02.016Zhang Jun, Zhang Xiaoci, Zhao Feng, et al. Research progress on non-acoustic detection technology of submarine wake derived from hydrodynamics[J]. Ship Mechanics, 2003, 7(2): 121-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2003.02.016 [15] Zhang Z J, Stern F. Free-surface wave-induced separation[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1996, 118(3): 546-554. doi: 10.1115/1.2817793 [16] 彭亮, 王建勋, 邓海华, 等. 水下非声探测与隐身技术综述[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2014, 36(5): 6-10. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2014.05.002Peng Liang, Wang Jianxun, Deng Haihua, et al. Review of underwater non-acoustic detection and stealth technology[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2014, 36(5): 6-10. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2014.05.002 [17] 梁志城. 现代反潜武备[M]. 北京: 海潮出版社, 2003. [18] Madurasinghe D, Tuck E O. The induced electromagnetic fields associated with submerged moving bodies in an unstratified conducting fluid[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2014, 19(6): 193-199. [19] Madurasinghe D. Induced electromagnetic fields associated with large ship wakes[J]. Wave Motion, 2014, 20(2): 283-292. [20] 林春生, 龚沈光. 舰船物理场[M]. 2版. 北京: 兵器工业出版社, 2007. [21] 龚沈光, 卢新成. 舰船电场特性初步分析[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2008, 36(6): 54-57.Gong Shenguang, Lu Xincheng. Preliminary analysis of electric field characteristics of ships[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2008, 36(6): 54-57. [22] Roxburgh I S. Thermal infrared detection of submarines springs associated with the Plymouth Limestone[J]. Hydrological sciences journal, 1985, 30(2): 185-196. doi: 10.1080/02626668509490983 [23] Wren G G, May D. Detection of submerged vessels using remote sensing techniques[J]. Australian Defense Force, 1997, 127: 8-15. [24] 孙岚, 李厚朴, 边少峰, 等. 基于重力梯度的潜艇探测方法研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2010, 30(2): 24-27.Sun Lan, Li Houpu, Bian Shaofeng, et al. Research on submarine detection method based on gravity gradient[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2010, 30(2): 24-27. [25] 张志强, 郑晗, 崔银峰. 航空重力垂直梯度探测潜艇方法研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2019, 39(4): 6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2019.04.002Zhang Zhiqiang, Zheng Han, Cui Yinfeng. Research on submarine detection method of aviation gravity vertical gradient[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2019, 39(4): 6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2019.04.002 [26] 吴琼, 滕云田, 张兵, 等. 世界重力梯度仪的研究现状[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(5): 761-767.Wu Qiong, Teng Yuntian, Zhang Bing, et al. Research status of gravity gradiometer in the world[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(5): 761-767. [27] Oger G, Debye P. A method for the determination of the mass of electrolytic ions[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1993, 1(1): 13-16. [28] Lei C, Sun X C, Zhou Y. Noise analysis and improvement of a micro-electro-mechanical-systems fluxgate sensor[J]. Measurement, 2018, 122: 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.03.007 -




 下载:
下载: