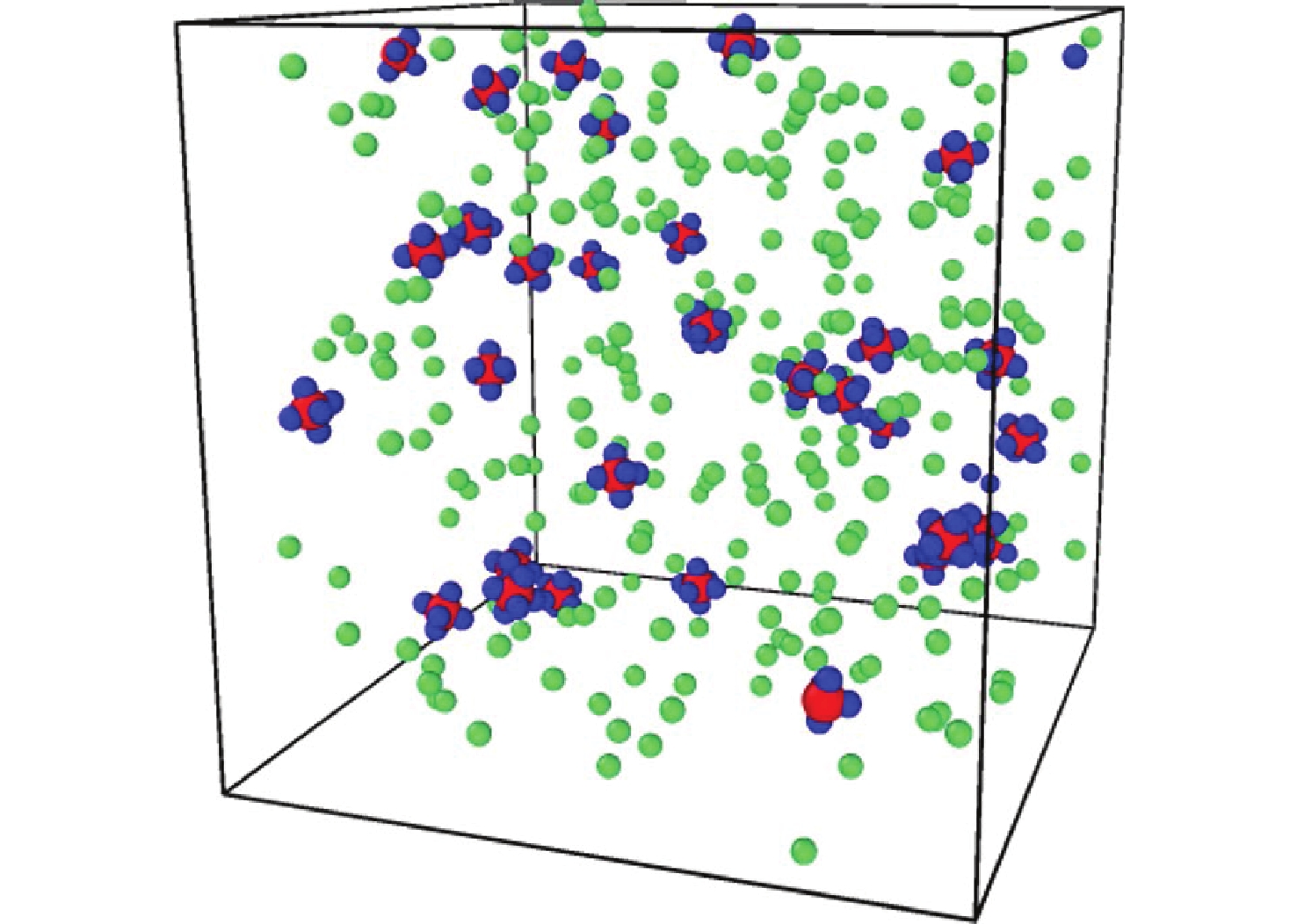
Reaction Path and Mechanisms of Li/SF6 Combustion
-
摘要: 揭示Li/SF6燃烧反应机理是构建燃烧动力学模型、高效组织燃烧过程的关键基础, 但是现有实验测试以及宏观模拟方法难以揭示Li/SF6燃烧的分步反应机理。文中结合ReaxFF反应分子模拟和第一性原理计算方法研究了Li和SF6的微观反应过程, 分析了反应物和产物组分的动态演化特性, 获得了主要反应路径及其反应热。研究发现, 反应的起始过程为SF6分子S-F键的断裂, LiF是反应初始时刻的主要产物; 随着反应的进行, 多余的Li形成Li2并与S成键形成Li2S; 反应后期, 2个LiF分子结合反应形成Li2F2。基于反应物浓度变化获得了Li和SF6的总反应速率, 结果表明, 总反应速率与反应物浓度、反应物比例呈正相关关系, 这是因为反应物浓度或比例的增大均会导致反应物分子之间碰撞概率的增加; 初始温度对总反应速率的影响则相对较小。结合第一性原理得到的反应物焓值, 计算各个分步反应的放热量, 进而得到Li/SF6的反应热为−2216.7 kJ/mol, 与理论值及实验值均接近。研究结果为复杂燃烧反应的分步反应机理揭示和反应热计算提供了有效途径。
-
关键词:
- Li/SF6燃烧反应 /
- 反应路径 /
- 分子动力学 /
- 第一性原理 /
- 反应热
Abstract: Revealing the combustion reaction mechanism of Li/SF6 fuel is the key basis for constructing the combustion kinetics model and efficiently organizing the combustion process. However, it is difficult to reveal the stepwise reaction mechanism of Li/SF6 combustion by existing experimental tests and macroscopic simulation methods. This paper studied the microscopic reaction processes of Li and SF6 by combining the ReaxFF molecular reaction simulation and first-principles calculation method. The dynamic evolution characteristics of reactants and product components were analyzed, and the main reaction paths and reaction heat were obtained. It is found that the breakage of the S-F bond in SF6 molecules is the initial stage of the reaction, and LiF is the main product of the initial reaction. As the reaction progresses, the excessive Li forms Li2 and bonds with S to form Li2S. At the later stage of the reaction, two LiF molecules combine with each other to produce Li2F2. Based on the variation of reactant concentration, the total reaction rates of Li and SF6 are obtained. The results show that the total reaction rate is positively correlated with the reactant concentration and reactant proportion because the rise of reactant concentration or proportion leads to a larger collision probability between reactant molecules. The impact of initial temperature on the total reaction rate is relatively small. According to the enthalpy value of the reactants obtained from the first-principles, the heat release of each stepwise reaction is calculated. The reaction heat for Li/SF6 combustion is −2 216.7 kJ/mol, which is close to the theoretical and experimental values. The research results provide an effective way to reveal the stepwise reaction mechanism and calculate the reaction heat of complex combustion reactions.-
Key words:
- Li/SF6 combustion reaction /
- reaction path /
- molecular dynamics /
- first-principles /
- reaction heat
-
表 1 Li/SF6反应仿真工况
Table 1. Simulation conditions of Li/SF6 reaction
控制变量 变量值 Li/SF6分子数 64/8 128/16 256/32 Li/SF6比例
(SF6分子数为32)Li∶SF6=1∶1 Li∶SF6=2∶1 Li∶SF6=8∶1 Li∶SF6=16∶1 反应初始温度/K 500 600 700 800 900 表 2 Li/SF6反应过程中反应物/产物焓值计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of reactant/product enthalpy value during Li/SF6 reaction
反应物
/产物Etotal
/(kcal/mol)Htotal/(kcal/mol) H=Etotal+Htotal
/(kcal/mol)T=500 K SF6 −625904.86 22.10 −625882.90 LiF −67435.93 4.96 −67435.93 2Li −9400.09 4.54 −9395.07 Li2S −259359.05 7.48 −259352.77 2LiF −134872.48 9.89 −134863.07 Li2F2 −134931.46 11.00 −134920.80 -
[1] Bergthorson J M. Recyclable metal fuels for clean and compact zero-carbon power[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2018, 68: 169-196. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2018.05.001 [2] 张炜, 张为华, 周星, 等. 镁基水反应金属燃料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013. [3] 赵卫兵, 史小锋, 伊寅, 等. 水反应金属燃料在超高速鱼雷推进系统中的应用[J]. 火炸药学报, 2006, 29(5): 53-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2006.05.015Zhao Weibing, Shi Xiaofeng, Yi Yin, et al. Application of hydroreactive metal fuel in super-cavitation torpedo propulsion system[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2006, 29(5): 53-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2006.05.015 [4] 黄庆, 卜建杰, 郑邯勇. Li/SF6热源在鱼雷和 UUV 推进系统中的应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2006, 28(2): 67-71.Huang Qing, Bu Jianjie, Zheng Hanyong. The application of Li/SF6 heat source in the torpedo and the UUV propulsion systems[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2006, 28(2): 67-71. [5] 马为峰, 路骏, 万荣华, 等. 非对称加热条件下锅炉反应器蒸汽生成过程参数影响研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2021, 29(3): 326-332.Ma Weifeng, Lu Jun, Wan Ronghua, et al. Study on parameter effect of the boiler reactor steam generation process under asymmetric heating[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2021, 29(3): 326-332. [6] 白杰, 党建军, 曹蕾蕾. 基于Li/SF6能源的新型UUV动力系统热力性能分析[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(2): 212-216.Bai Jie, Dang Jianjun, Cao Leilei. Thermodynamic performance analysis of a new type of UUV power system based on Li/SF6 Energy[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(2): 212-216. [7] Harper A D. Thermochemical power systems for underwater applications[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Unmanned Untethered Submersible Technology. Durham, NH, USA: IEEE, 1989: 136-152. [8] Hsu K Y, Chen L D. An experimental study of Li-SF6 wick combustion and morphology analysis of combustion products[C]//27th Joint Propulsion Conference. Sacramento,CA,USA: AIAA, 1991: 2447. [9] Lyu H Y, Chen L D, Hsu K Y. Prediction of LI-SF6 wick combustion[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 1992, 8(6): 1131-1137. doi: 10.2514/3.11453 [10] 朱强. 硫化锂热力学性质的估算[J]. 舰船防化, 1999(C00): 81-85. [11] 朱强. Li/SF6锅炉反应器喷嘴材料的研究[J]. 舰船防化, 1995(4): 21-23. [12] 张文群, 张振山. 非理想多相共存体系的平衡计算[J]. 火炸药学报, 2003, 26(3): 39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2003.03.011Zhang Wenqun, Zhang Zhenshan. Equilibrium computation of multiphase non-ideal system[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2003, 26(3): 39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2003.03.011 [13] 张文群, 张振山. Li/SF6气液浸没燃烧反应的相平衡计算[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2005, 13(2): 17-20.Zhang Wenqun, Zhang Zhenshan. Phase equilibrium calculation of lithium-sulfur hexafluoride (Li/SF6) gas-liquid submerged combustion[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2005, 13(2): 17-20. [14] 张文群, 张振山. 应用 Gibbs 自由能最小法研究 Li/SF6气液浸没燃烧反应[J]. 兵工学报, 2005, 26(6): 812-815. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2005.06.022Zhang Wenqun, Zhang Zhenshan. A study on Li/SF6 gas-liquid fuel combustion with the minimum of Gibbs energy[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2005, 26(6): 812-815. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2005.06.022 [15] Dahikar S K, Joshi J B, Shah M S, et al. Experimental and computational fluid dynamic study of reacting gas jet in liquid: Flow pattern and heat transfer[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(2): 827-849. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2009.09.035 [16] Parnell L A, Edmunds D G, Rogerson D J. Combustion instabilities of submerged oxidiser jets in liquid metal fuel[C]//Proceedings of the Second ONR Propulsion Meeting on Energy Materials Combustion, Combustion Underwater Propulsion. Pennsylvania, USA: Elsevier, 1989: 188-195. [17] Hsu K Y, Chen L D. An experimental investigation of Li and SF6 wick combustion[J]. Combustion and Flame, 1995, 102(1-2): 73-86. doi: 10.1016/0010-2180(94)00238-N [18] 郑邯勇, 卜建杰. 六氟化硫在熔融锂中的浸没喷射反应过程[J]. 化工学报, 1996, 47(6): 656-662.Zheng Hanyong, Bu Jianjie. The submerged jet reaction process of sulfur hexafluoride into molten lithium[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 1996, 47(6): 656-662. [19] 李维维, 马为峰, 韩直亚, 等. 锂/六氟化硫热源启动技术研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2021, 29(6): 674-679. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2021.06.005Li Weiwei, Ma Weifeng, Han Zhiya, et al. Start-up technology of lithium/sulfur hexafluoride heat source[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2021, 29(6): 674-679. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2021.06.005 [20] Chan S H, Zhao Y G, Janke P J, et al. Combustion of turbulent gaseous fluorine jets submerged in molten lithium fuel[C]//AIAA/ASME Thermophysics and Heat Transfer Conference. Milwaukee, USA: Elsevier, 1990: 23-32. [21] Chan S H, Abou-Ellailt M M M. Multifluid model of turbulence for Li-SF6 submerged combustion[J]. AIAA Journal, 1993, 31(8): 1526-1529. doi: 10.2514/3.49086 [22] Dahikar S K, Gulawani S S, Joshi J B, et al. Effect of nozzle diameter and its orientation on the flow pattern and plume dimensions in gas-liquid jet reactors[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(24): 7471-7483. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2007.08.035 [23] Chen L, Damaso R C. Wick-type liquid-metal combustion[R]. Iowa, US: The University of Iowa, 1992. [24] Gulawani S S, Dahikar S K, Joshi J B, et al. CFD simulation of flow pattern and plume dimensions in submerged condensation and reactive gas jets into a liquid bath[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2008, 63(9): 2420-2435. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2008.01.027 [25] Russo Jr M F, Li R, Mench M, et al. Molecular dynamic simulation of aluminum-water reactions using the ReaxFF reactive force field[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(10): 5828-5835. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.02.035 [26] Senftle T P, Hong S, Islam M M, et al. The ReaxFF reactive force-field: development, applications and future directions[J]. NPG Computational Materials, 2016, 2(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1038/s41524-016-0001-z [27] Islam M M, Bryantsev V S, Van Duin A C T. ReaxFF reactive force field simulations on the influence of teflon on electrolyte decomposition during Li/SWCNT anode discharge in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161(8): E3009. doi: 10.1149/2.005408jes [28] Delley B. Time dependent density functional theory with DMol3[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2010, 22(38): 384208. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/22/38/384208 [29] 朱传征, 许海涵. 物理化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000. -





 下载:
下载: