3D Flow Field Characteristics and Hydrodynamic Optimization of Supercavitating Torpedoes Based on THINC/QQ Scheme
-
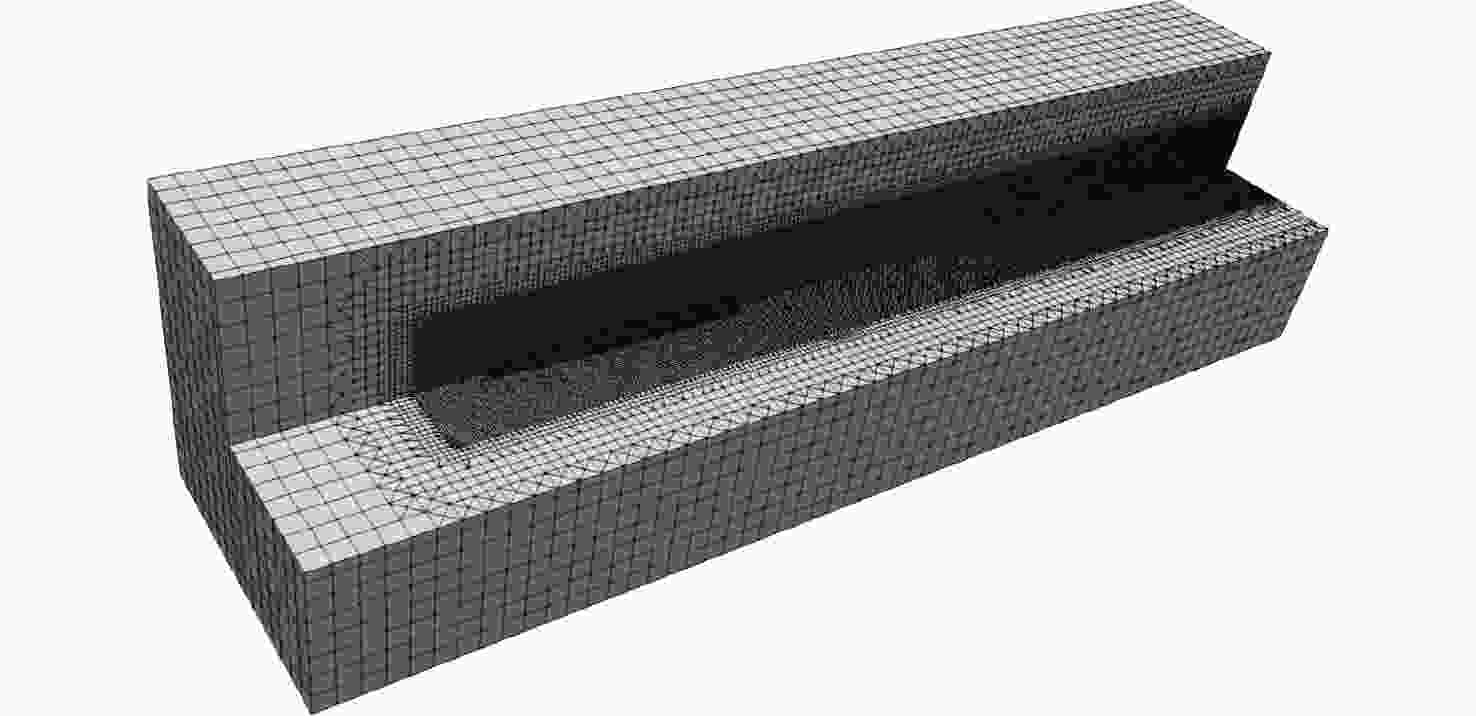
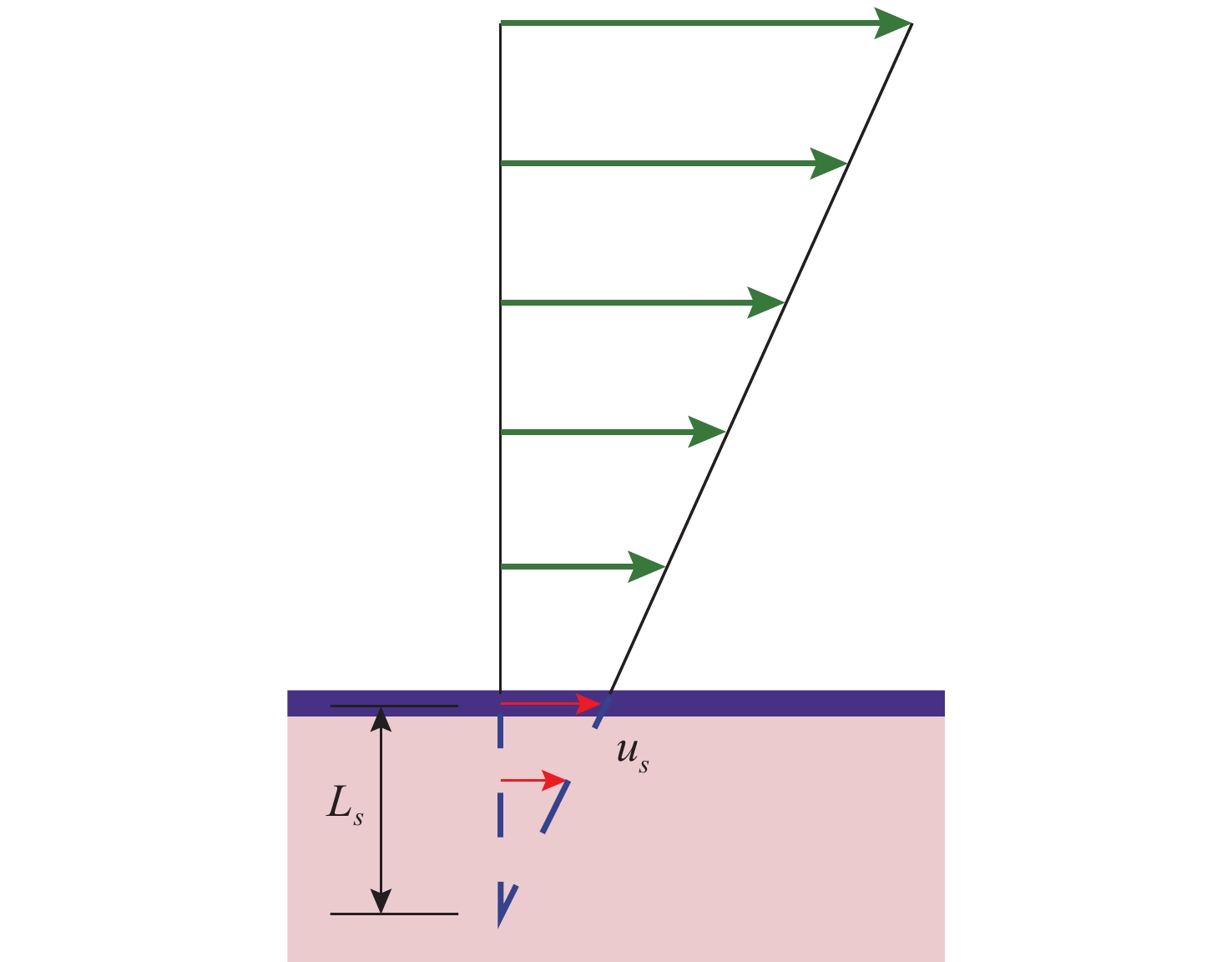
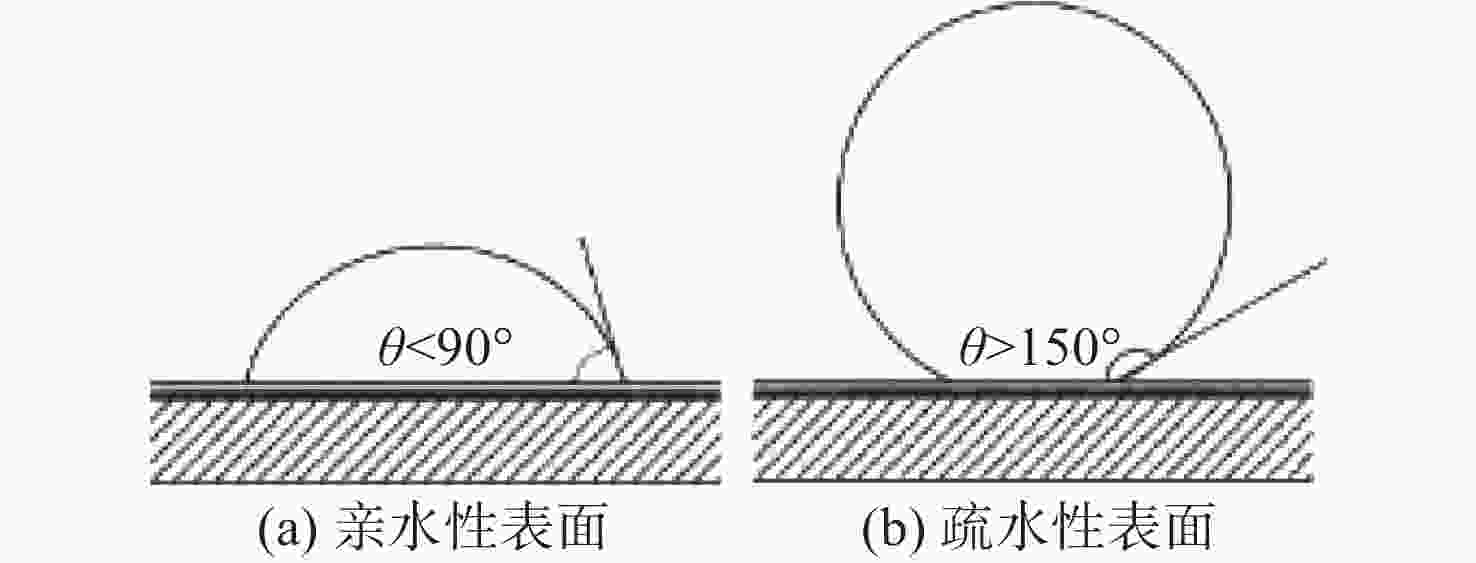
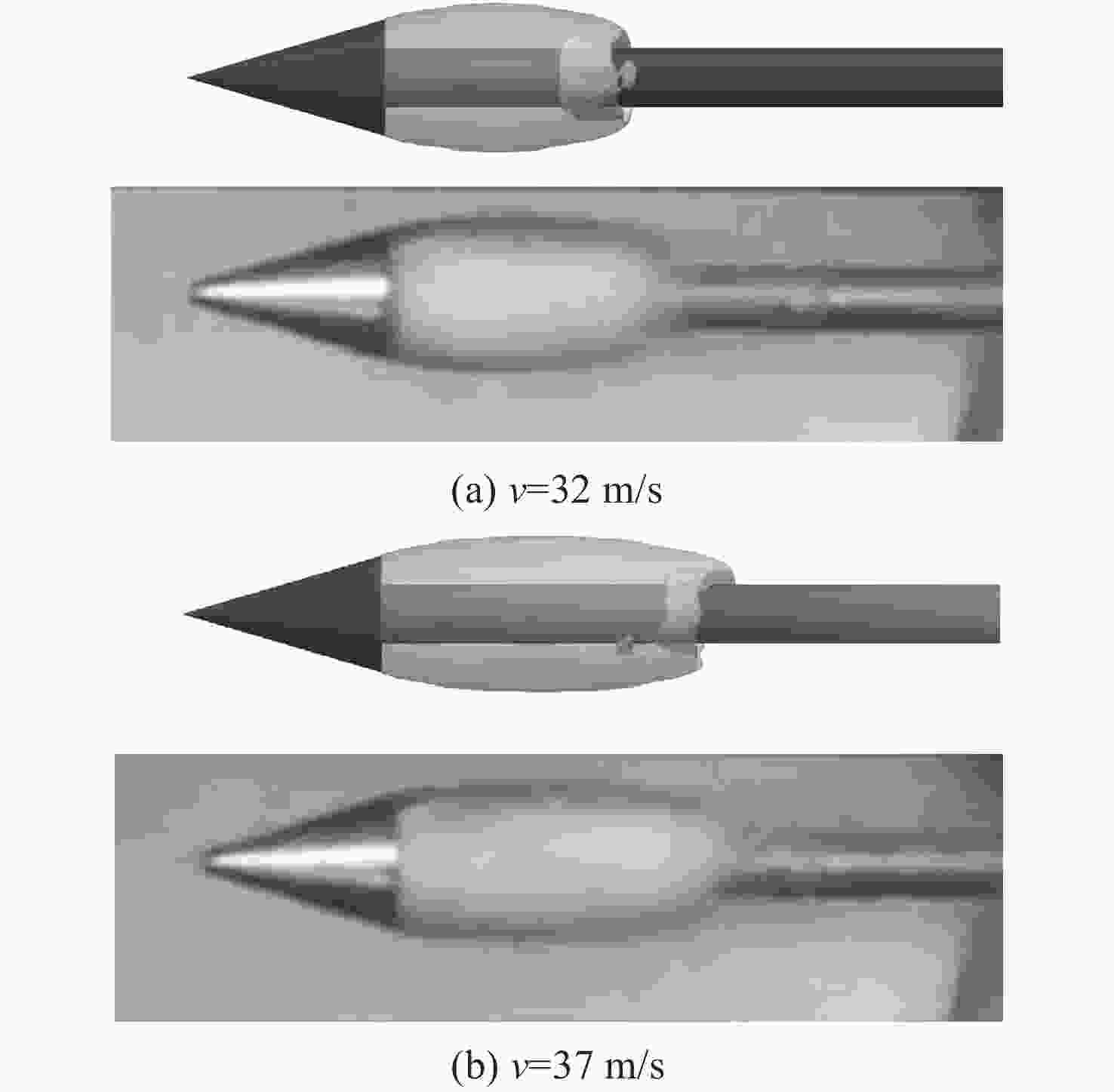
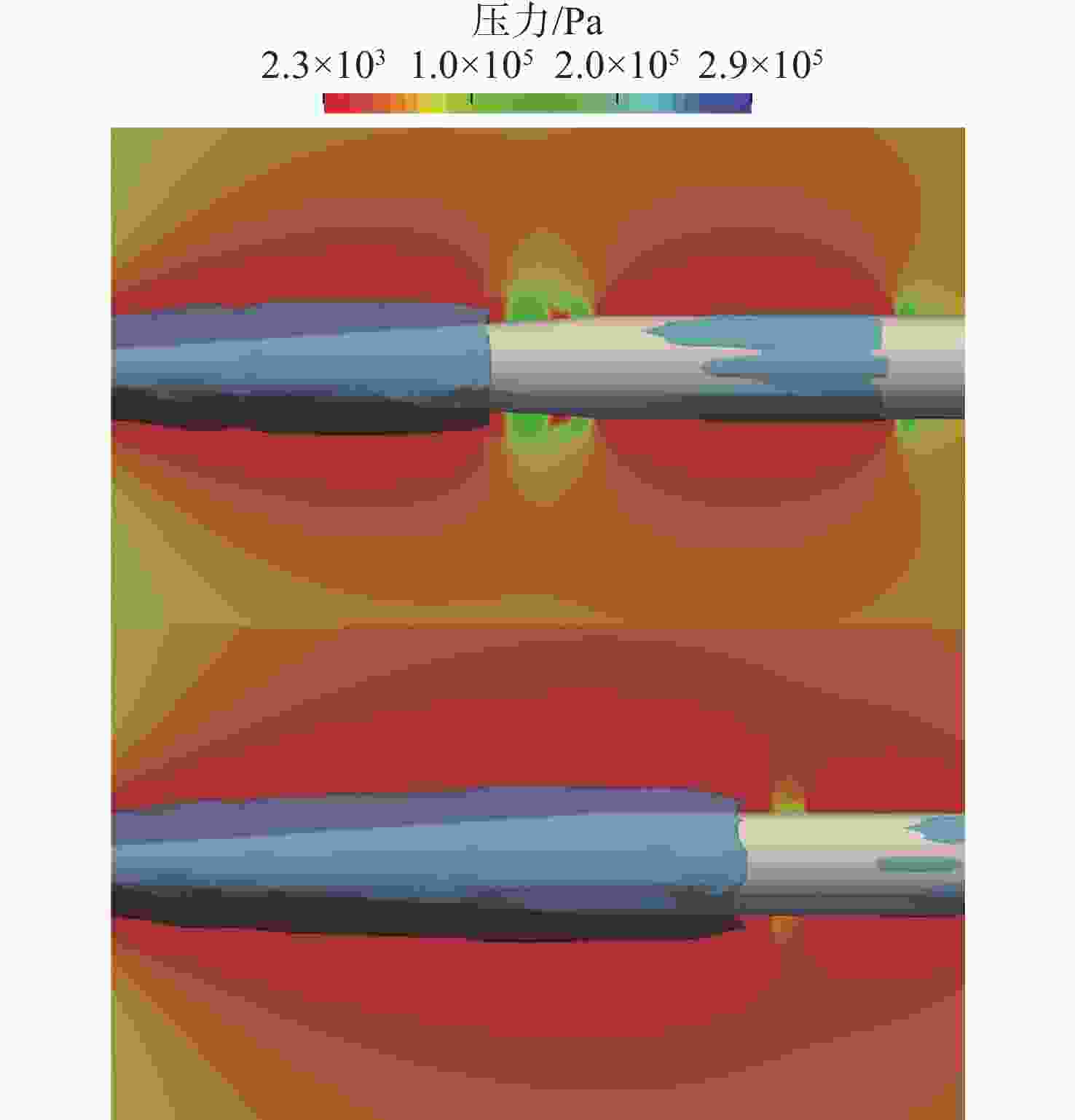
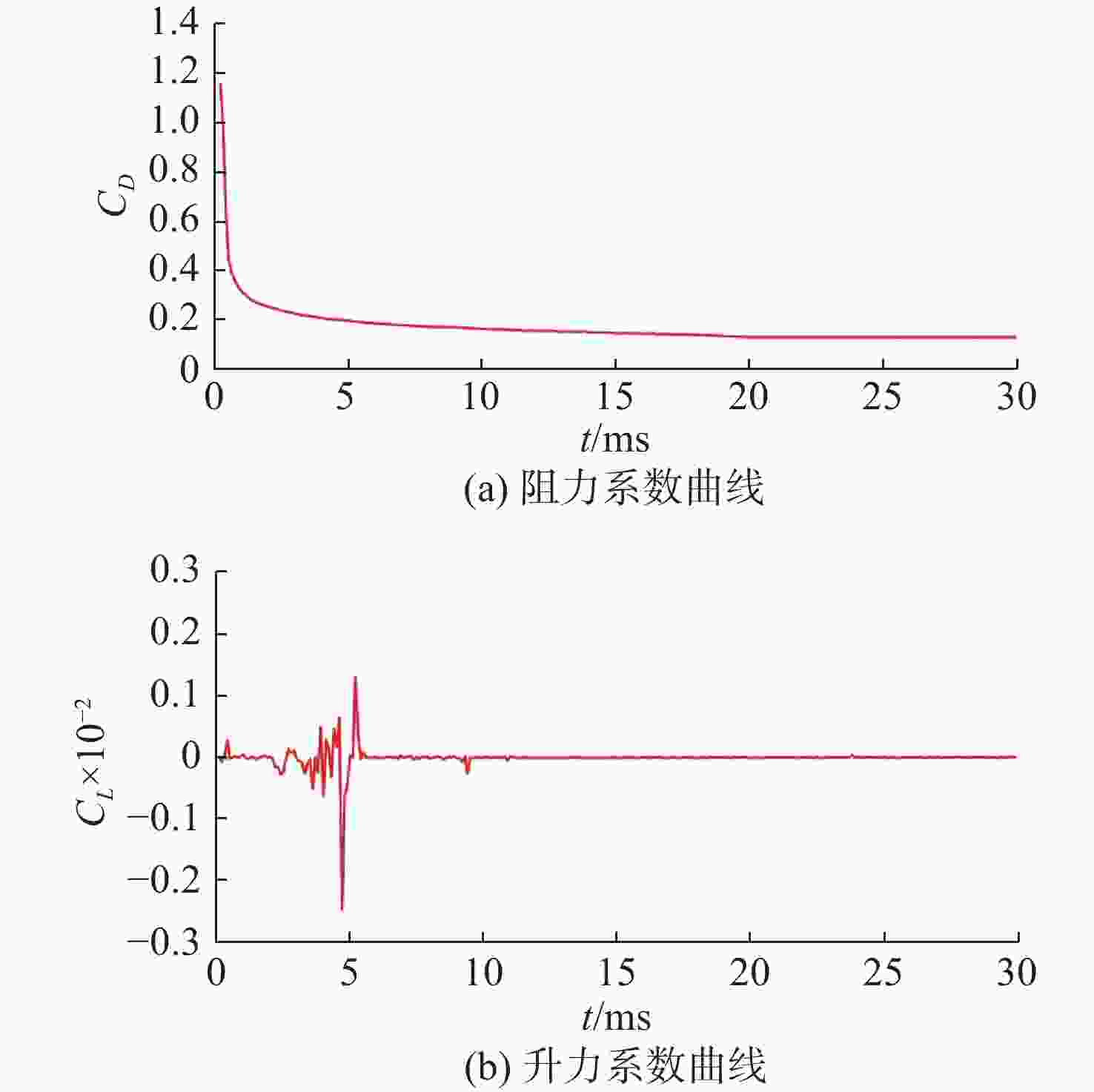
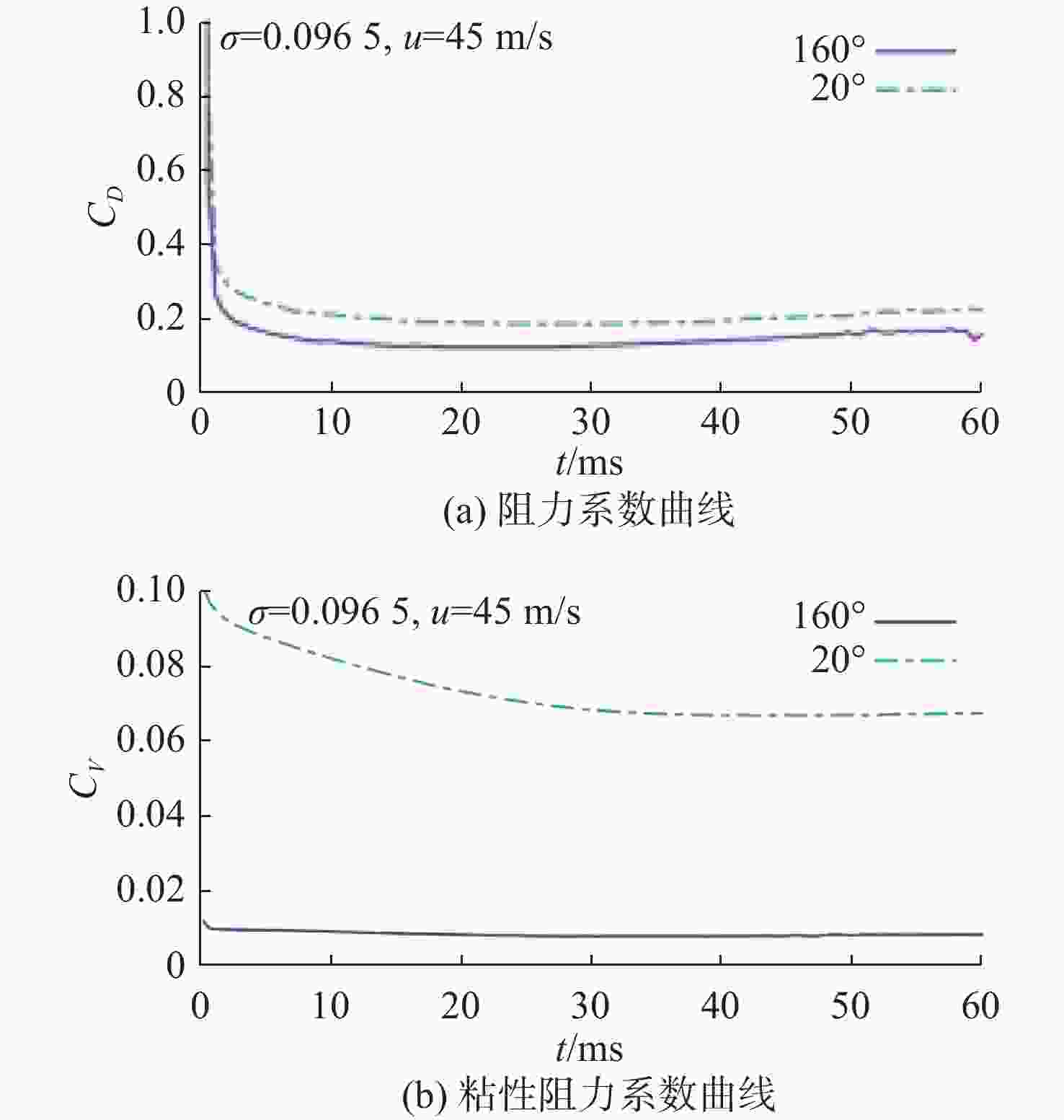
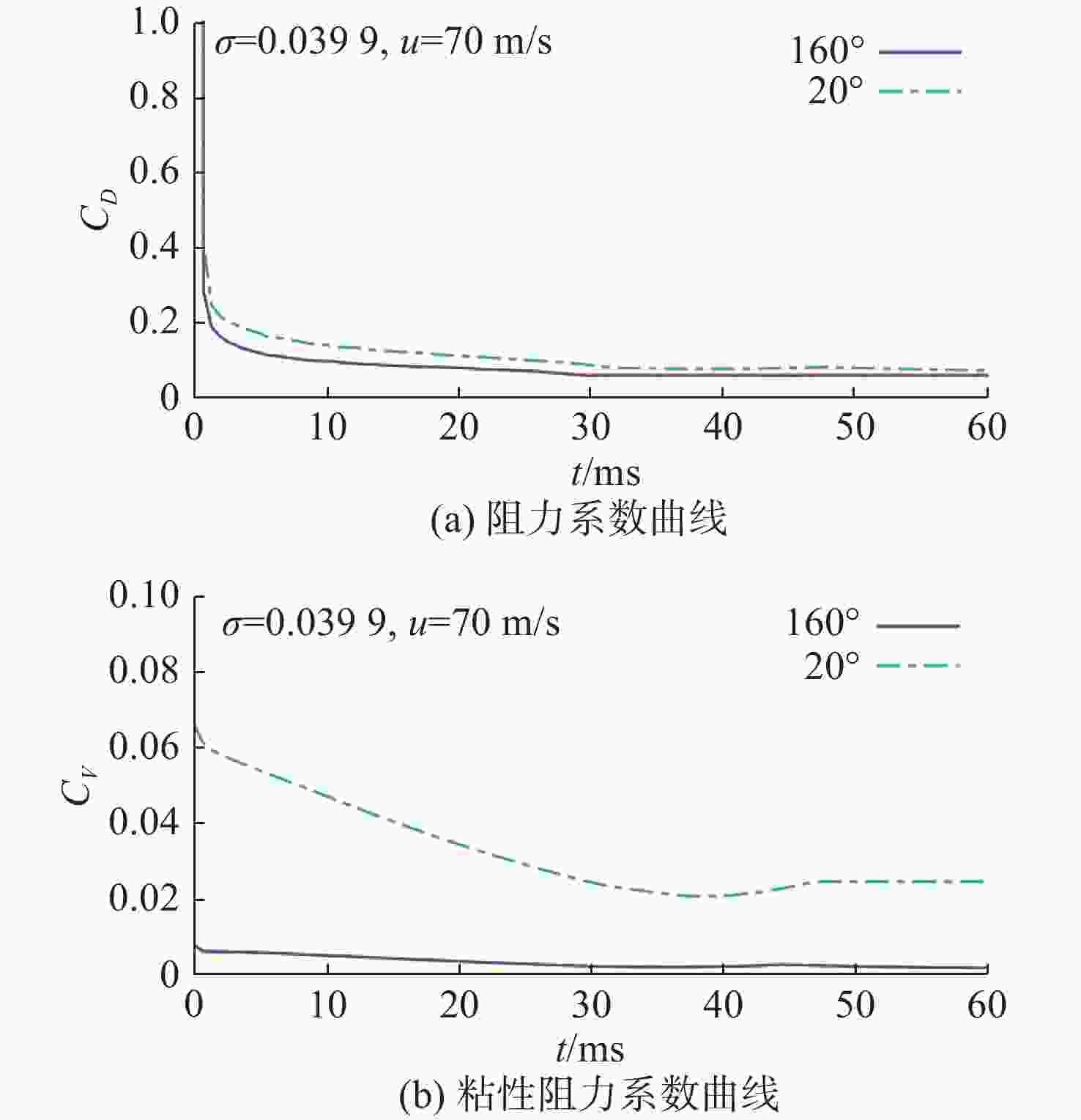
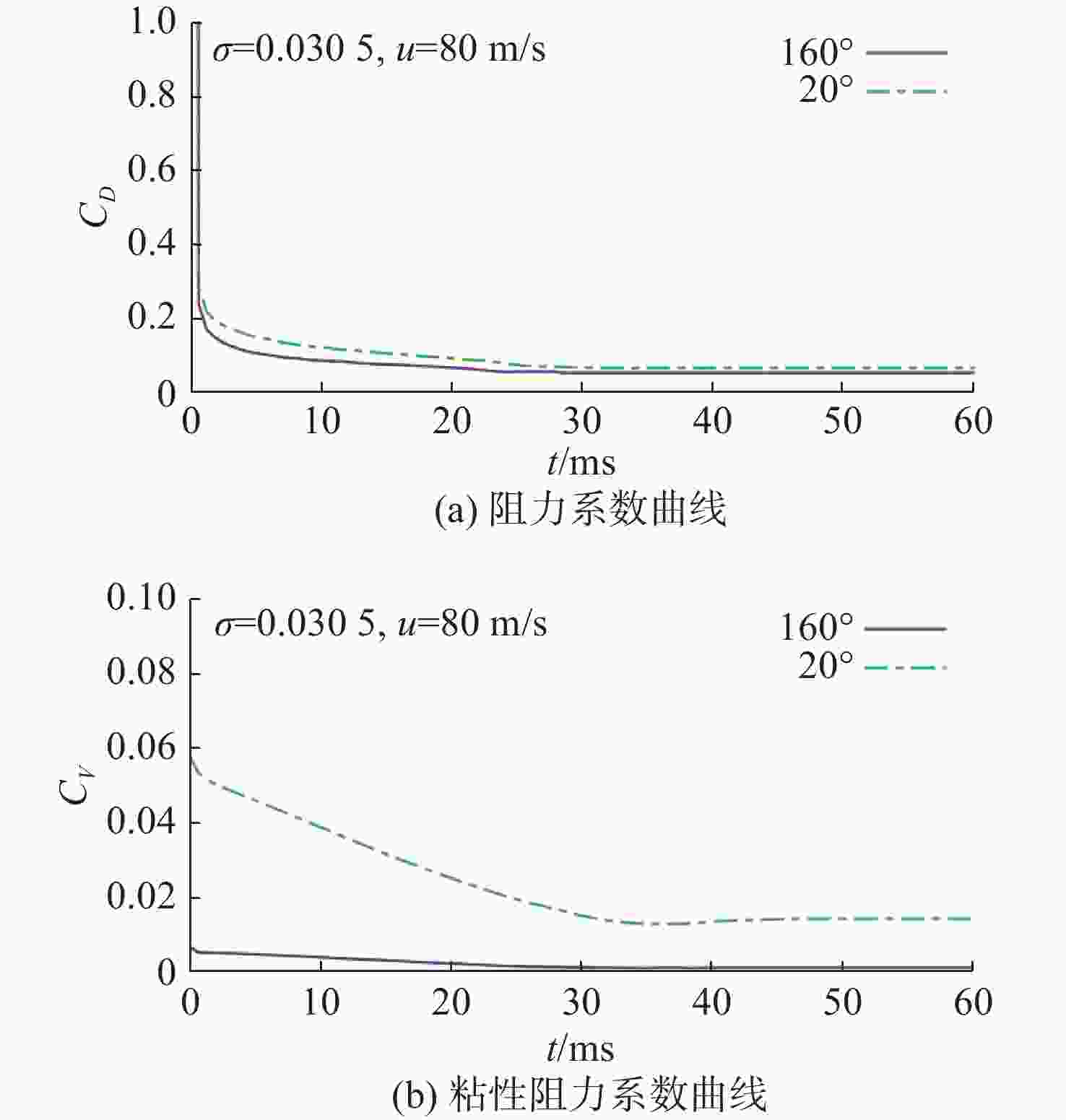
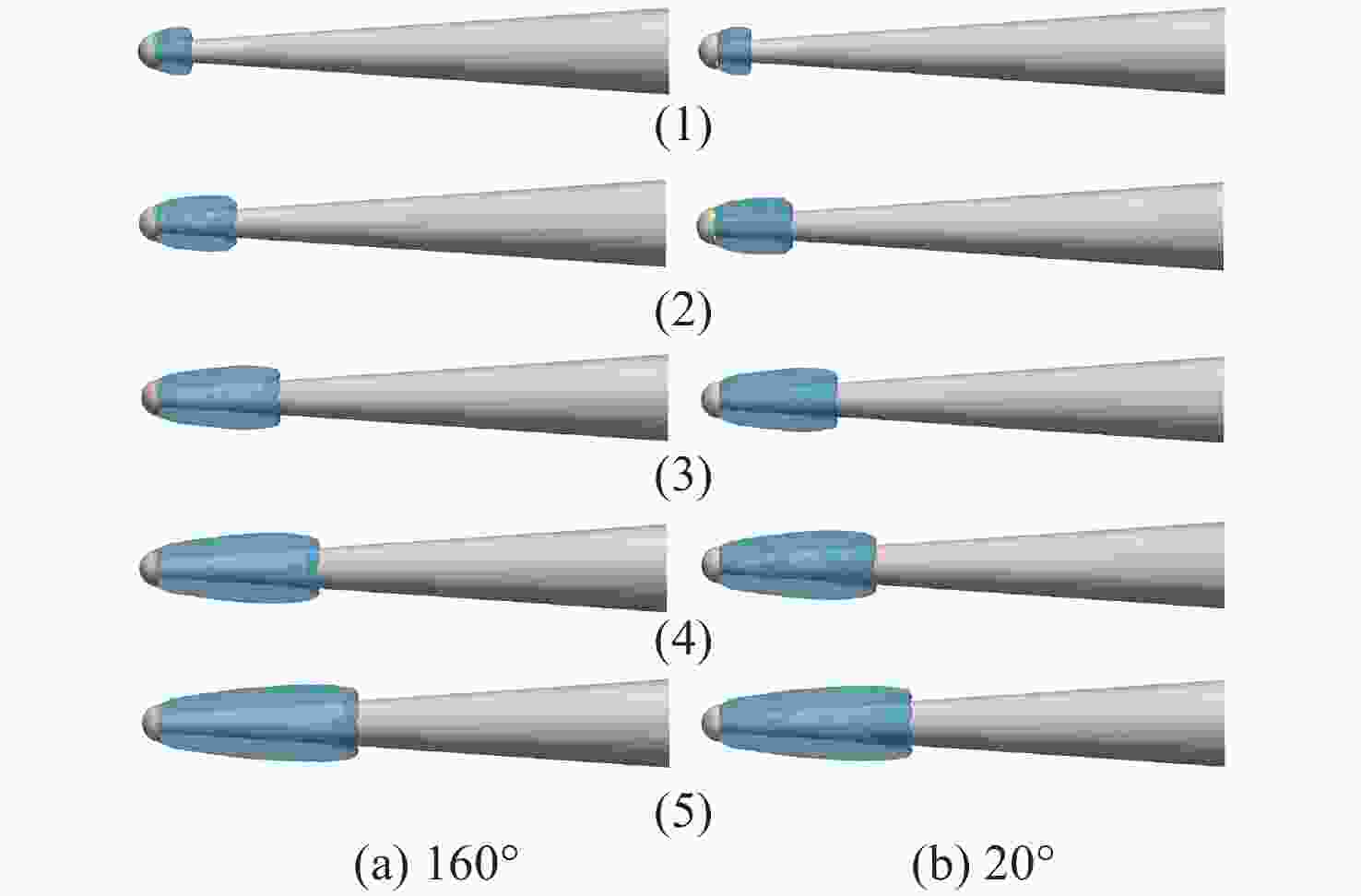
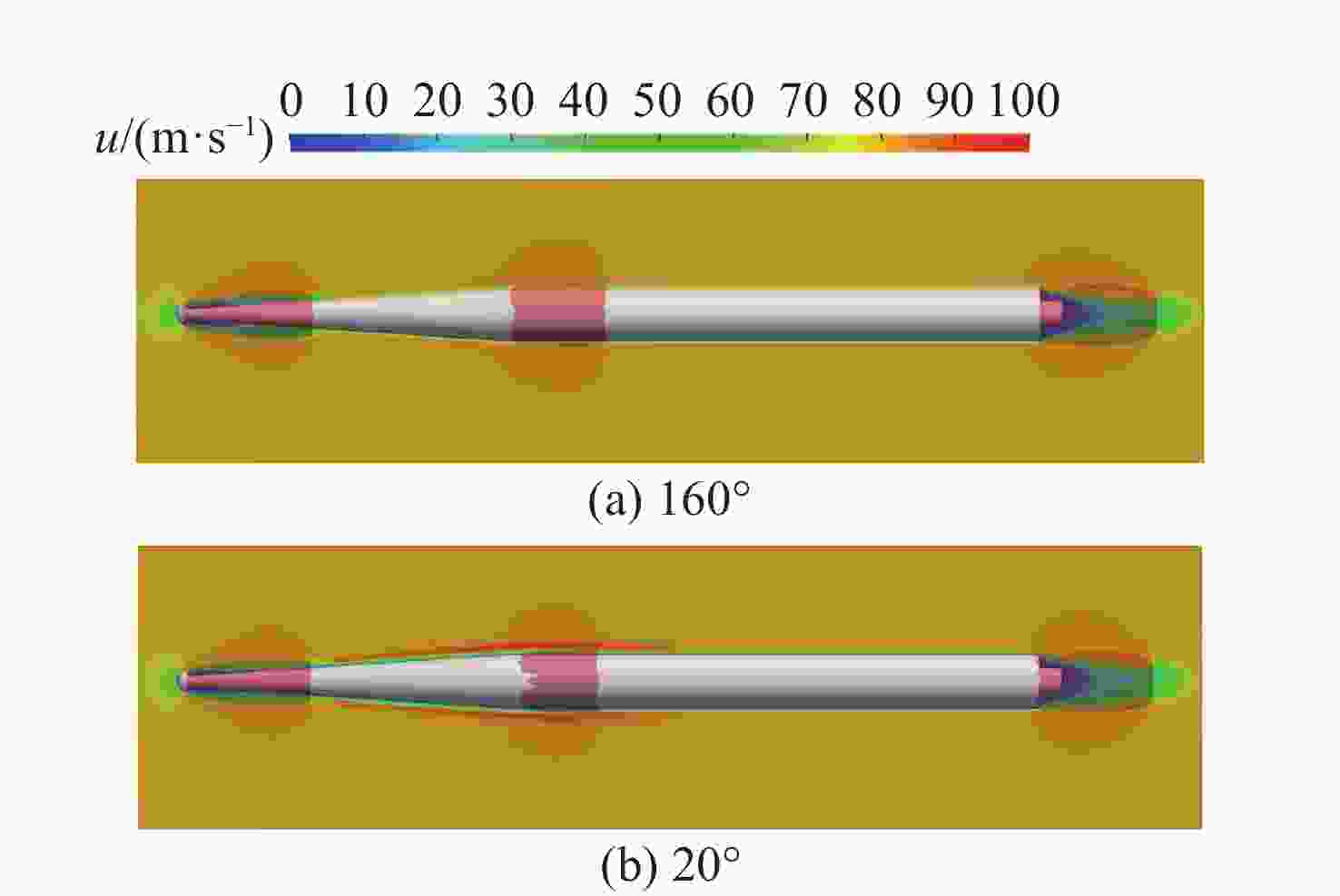
摘要: 为了研究超空泡鱼雷的超空泡形态演化及水动力特性, 采用开源软件OPENFOAM对超空泡鱼雷自然空泡的复杂流动过程进行了三维数值仿真研究。首先, 基于THINC/QQ格式、剪切应力传输k-ω湍流模型以及Schnerr-Sauer空化模型在非结构网格上建立了不可压缩流体体积函数多相流模型, 并通过与水洞实验案例对比验证了该求解器的准确性。在此基础上, 该研究对无尾翼鱼雷模型开展了不同速度、不同空化器形状以及不同表面浸润性条件下的超空泡流动数值仿真, 给出了典型工况下超空泡鱼雷的三维流场演化过程以及水动力变化规律, 对比了多种空化器形状和尺寸参数的超空泡流场和水动力特性。结果表明: 具有一定锥度或者本身阻力系数较小的空化器可有效降低航行阻力, 但因损失空泡体积可能会降低航行稳定性。文中还新颖地研究了鱼雷表面材料亲疏水性及其布置位置对超空泡水动力性能的影响, 可为超空泡减阻领域的相关研究提供参考。Abstract: The OPENFOAM platform was used to perform three-dimensional numerical simulations of the complex flow process of supercavitating torpedoes to investigate the morphological evolution of cavitation and hydrodynamic characteristics of supercavitating torpedoes. A numerical model of the volume of incompressible fluid was developed by integrating the THINC/QQ scheme, shear stress transport (SST) k-ω turbulence model and Schnerr-Sauer cavitation model, and the accuracy of the solver was comparatively verified by the results of the water tunnel experiments. Furthermore, the supercavitating behaviors were numerically investigated for a tailless torpedo considering crucial parameters including velocity, cavitator shape and surface wettability, and the three-dimensional flow field evolution process and hydrodynamic features of the supercavitating torpedo under typical operating conditions were obtained. In addition, the supercavitating flow field and hydrodynamic features of various cavitators with different shapes and sizes were compared. Results show that a cavitator with a certain taper or a low drag coefficient can effectively decrease the navigating drag. However, the reduced volume of the cavity may affect the stability of navigation. The effect of the hydrophobic material on the torpedo surface and its distribution on the hydrodynamic performance of the supercavitating torpedo was investigated as well. The results can provide some guidance for studies on drag reduction for supercavitating torpedoes.
-
Key words:
- supercavitating torpedo /
- cavitator /
- drag reduction
-
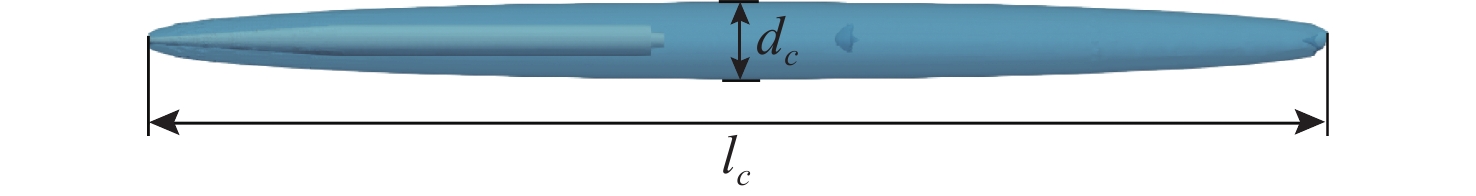
表 1 超空泡尺度网格收敛性测试
Table 1. Mesh convergence test on the supercavity scale
网格编号 网格数 特征长度(${{{l_c}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{l_c}} D}} \right. } D} $) 特征直径(${ { {d_c} } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { { {d_c} } D} } \right. } D}$) 网格1 0.85×106 71.126 6.323 网格2 1.14×106 70.364 6.086 网格3 1.74×106 69.238 5.891 网格4 2.51×106 69.725 5.903 表 2 超空泡尺度数值结果验证
Table 2. Validation of numerical results of supercavity scale
Reichardt
公式Logvinovich
公式文中
方法相对误差
R/%相对误差
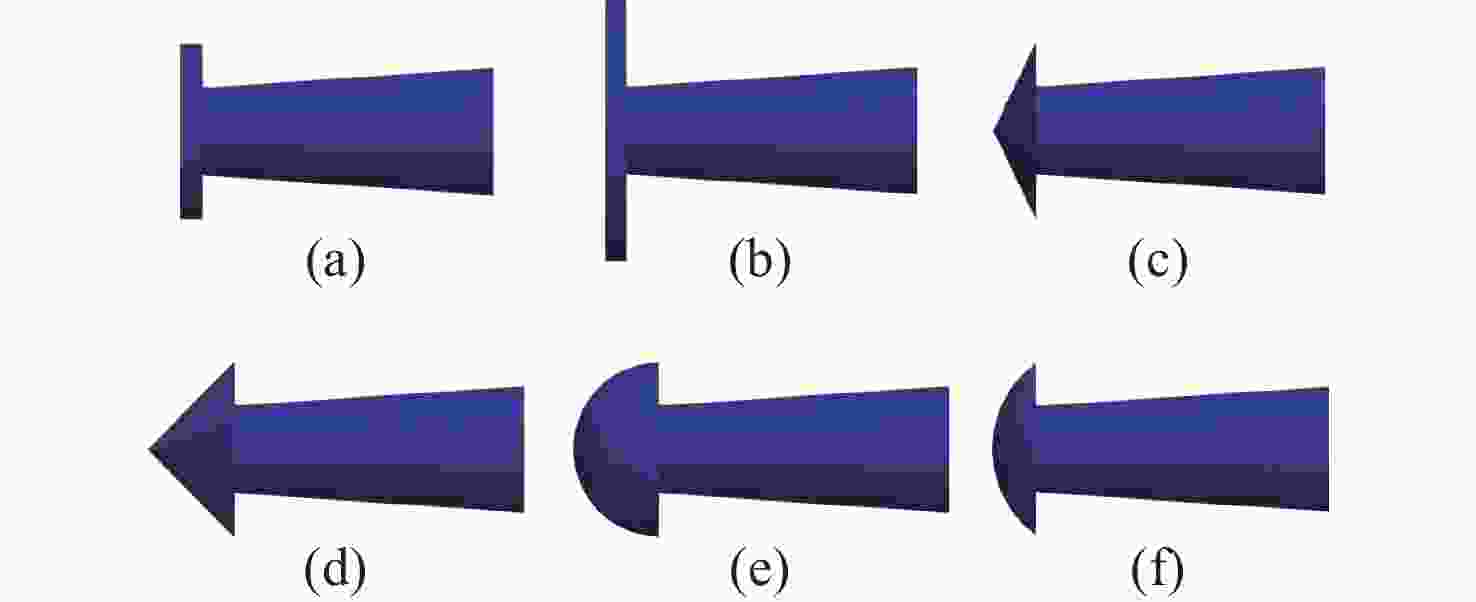
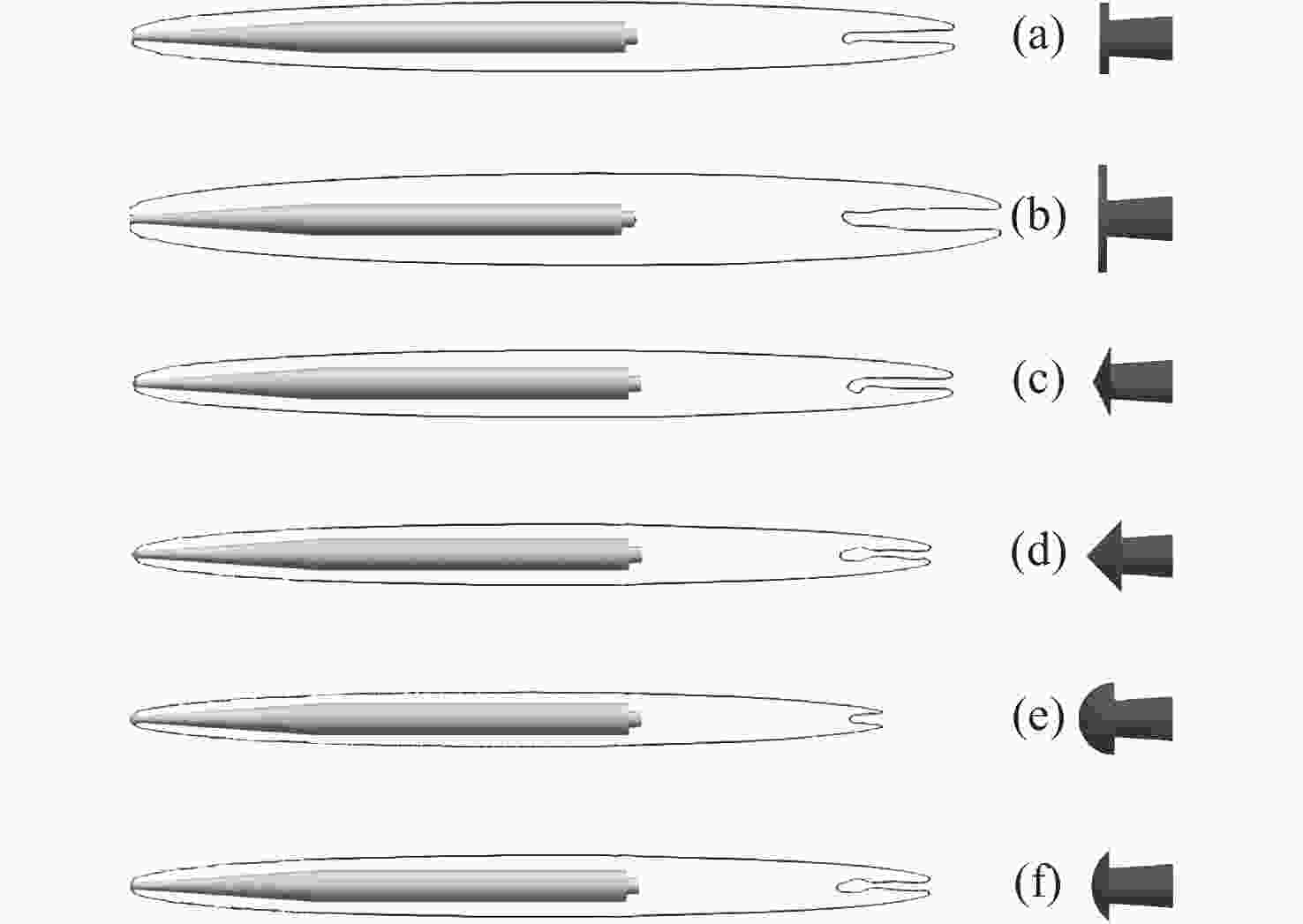
L/%特征长度 67.016 67.142 69.238 3.32 3.17 特征直径 5.744 5.660 5.891 2.56 4.08 表 3 不同空化器超空泡阶段阻力系数
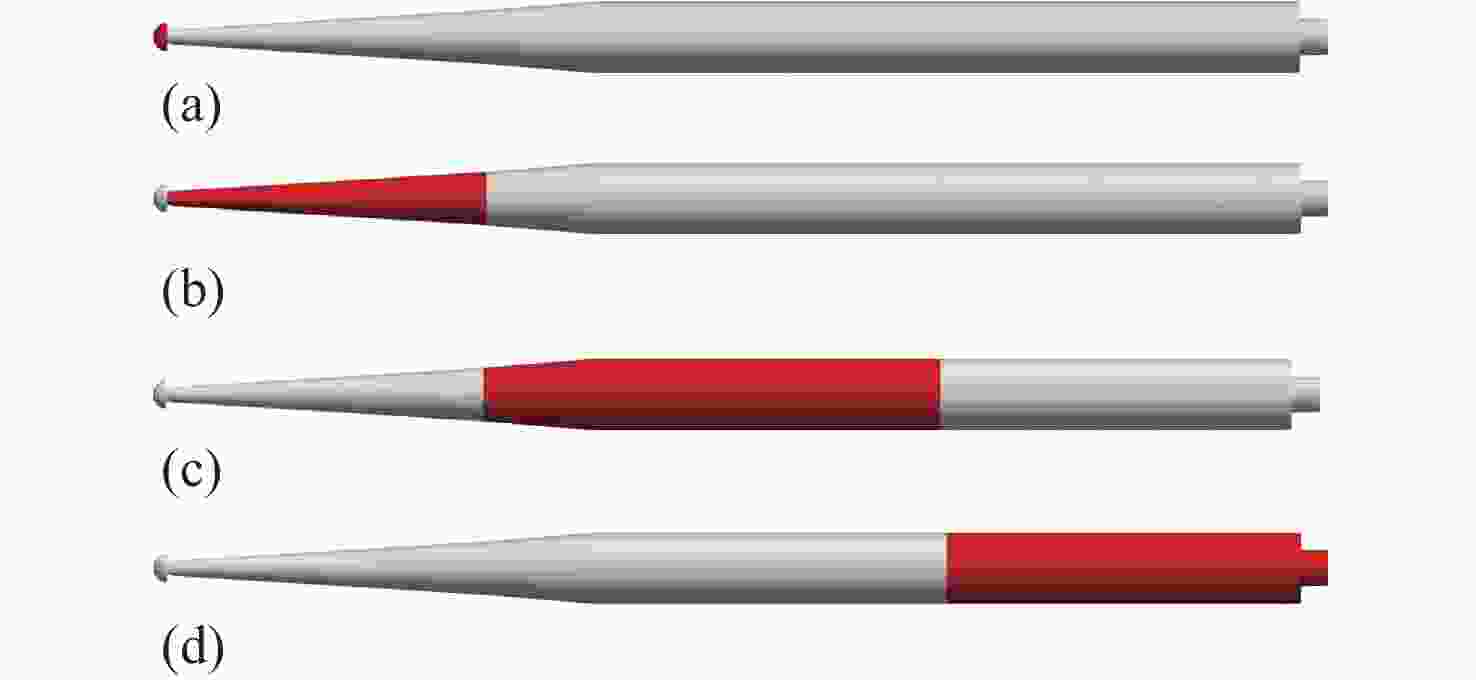
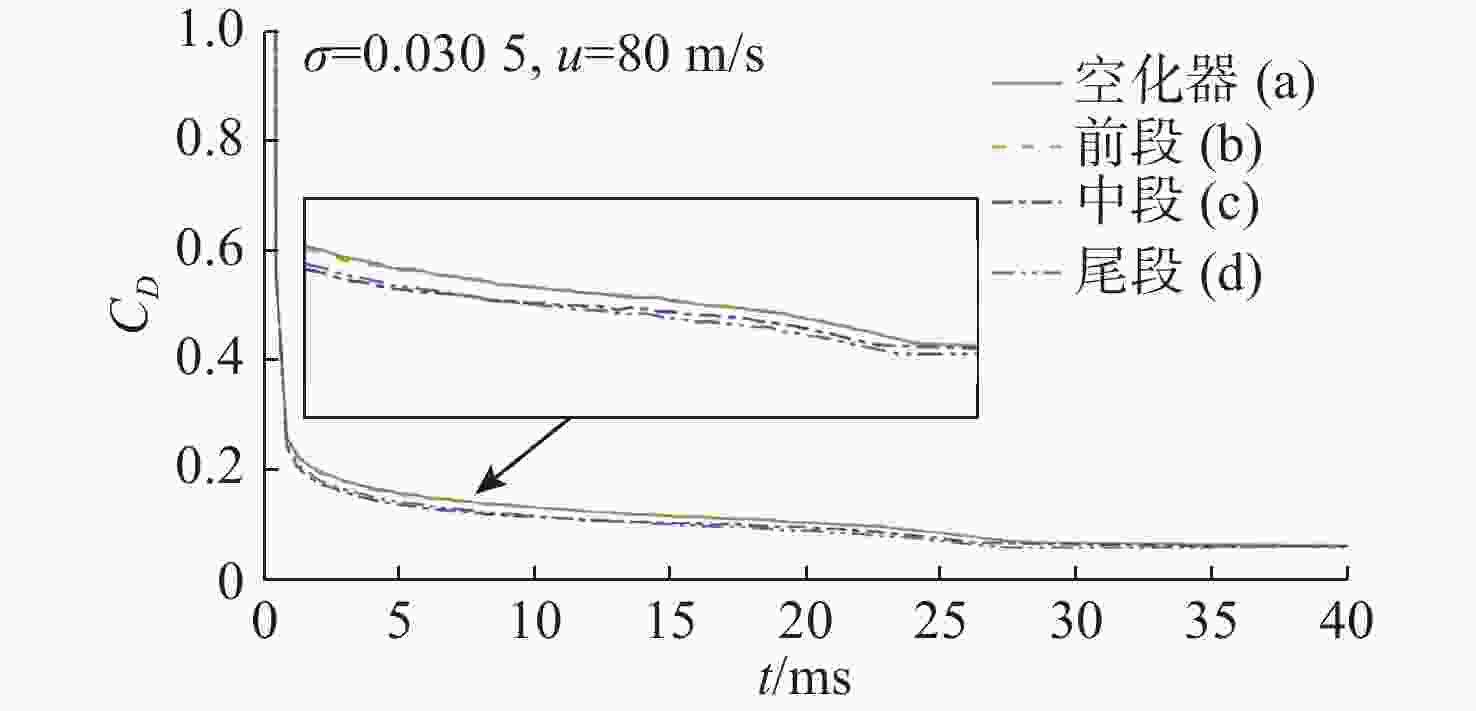
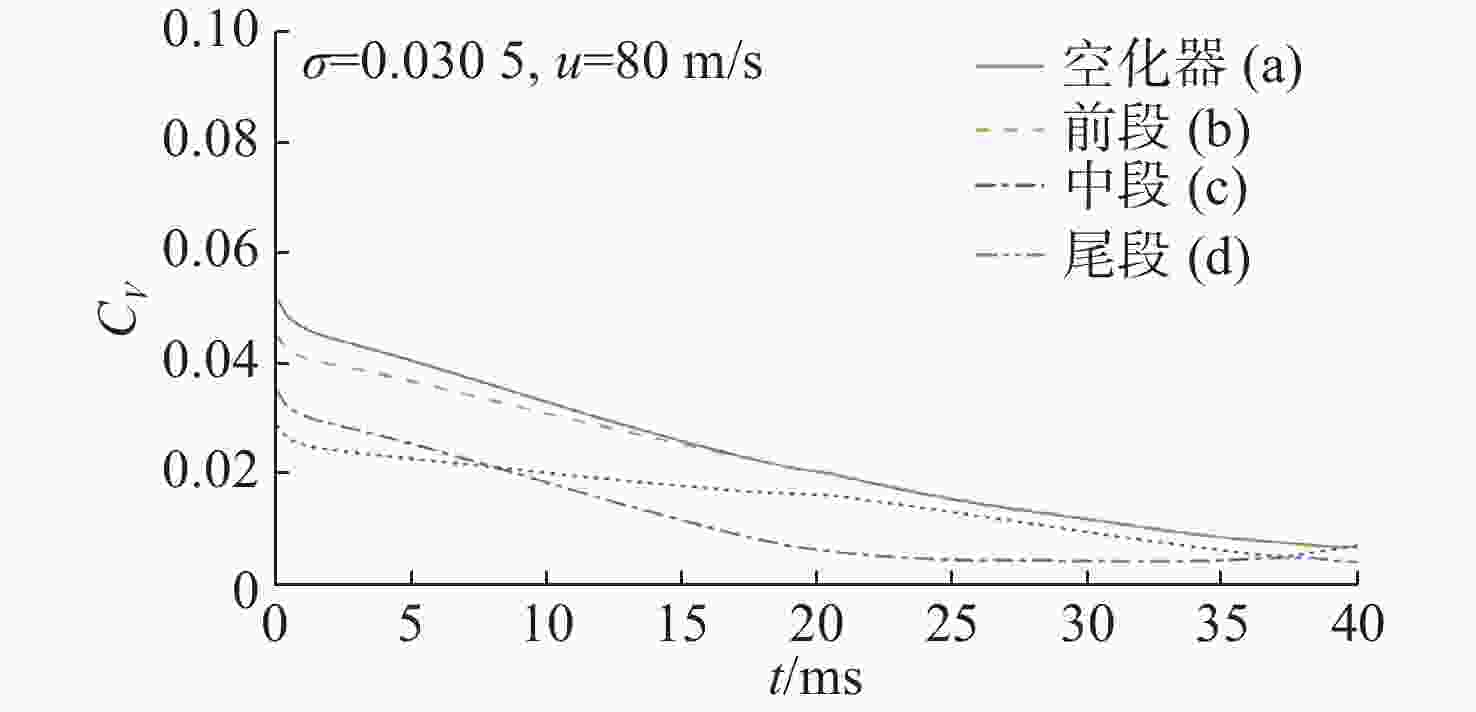
Table 3. Drag coefficients for different cavitators at the supercavity stage
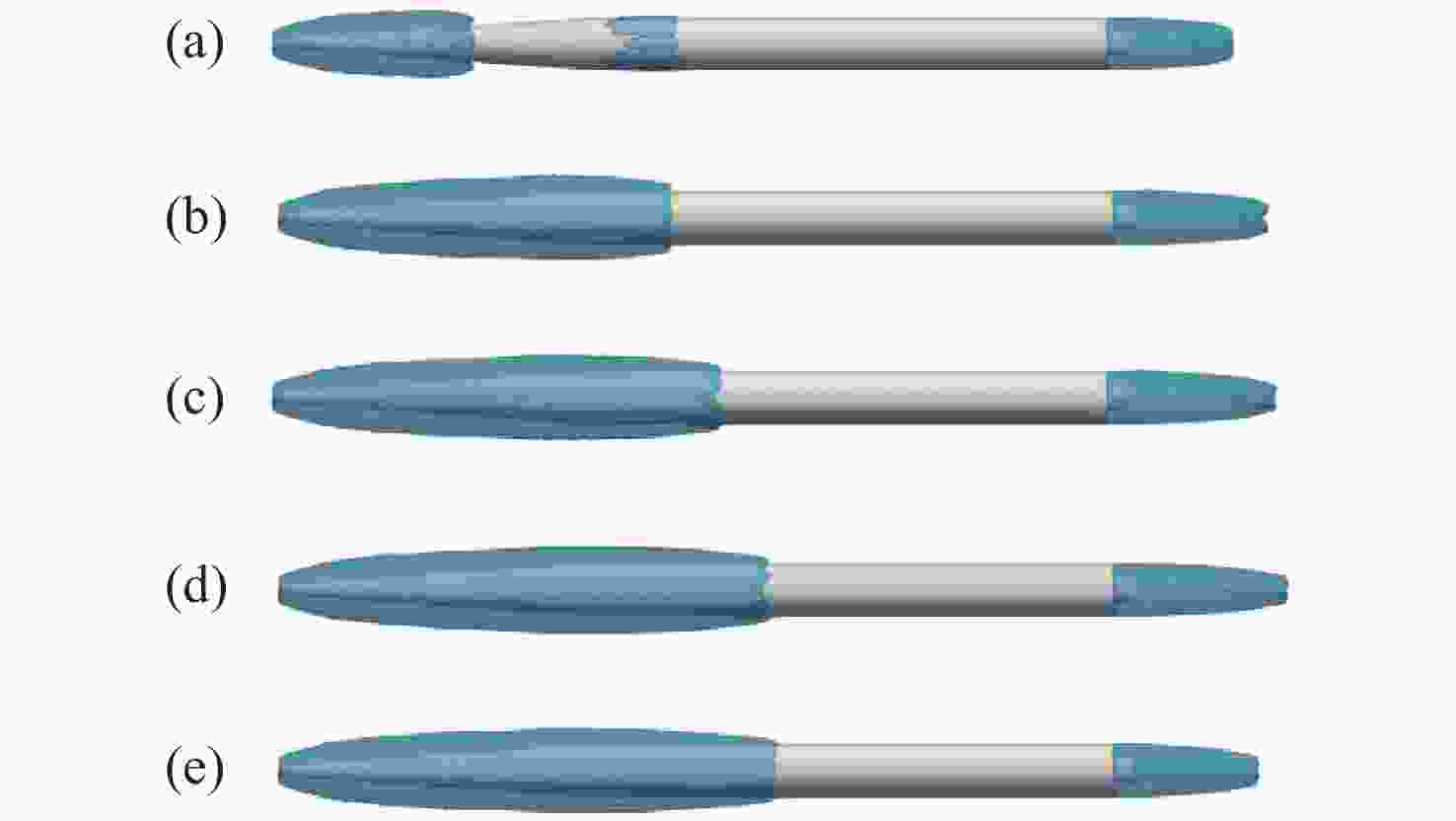
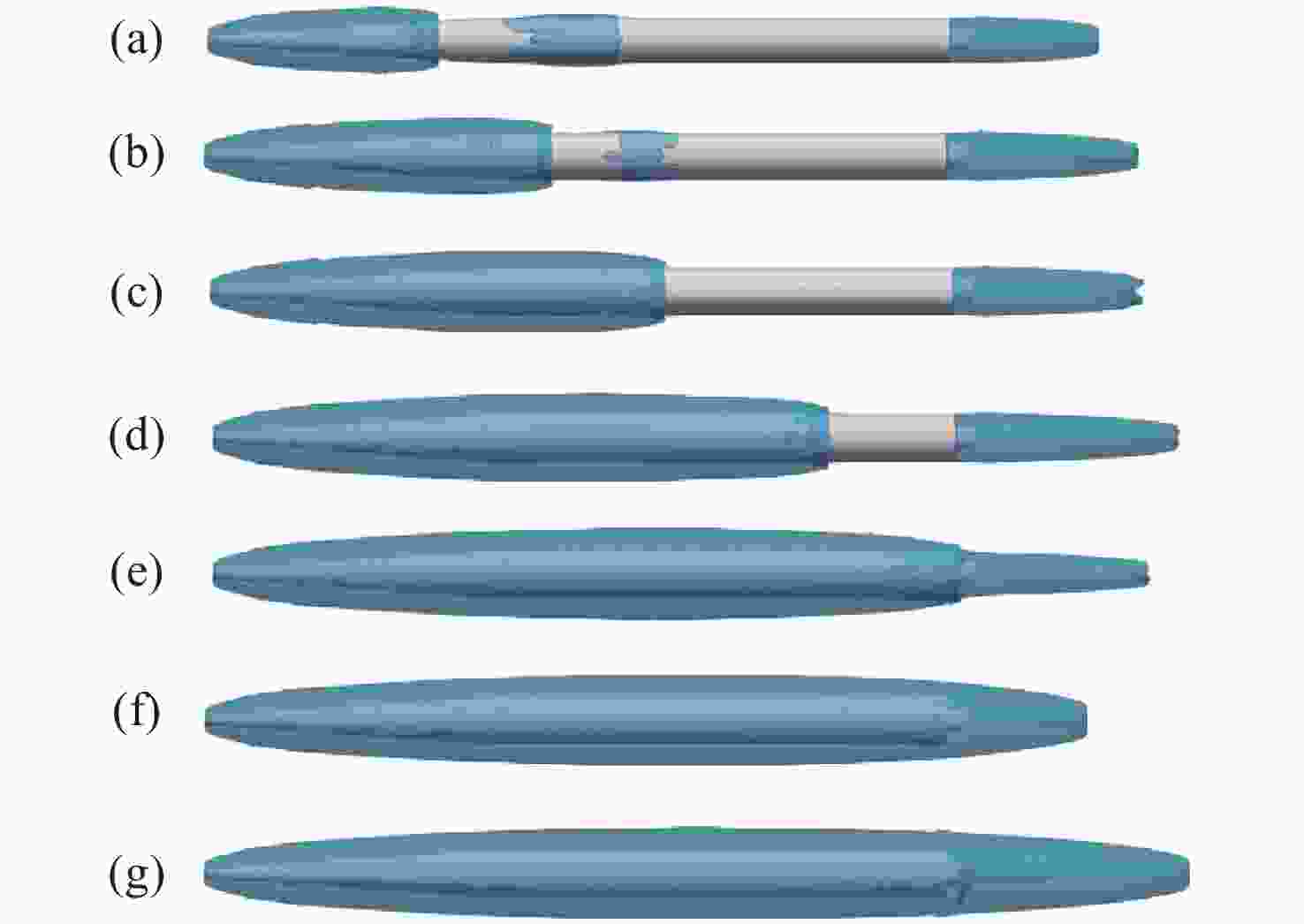
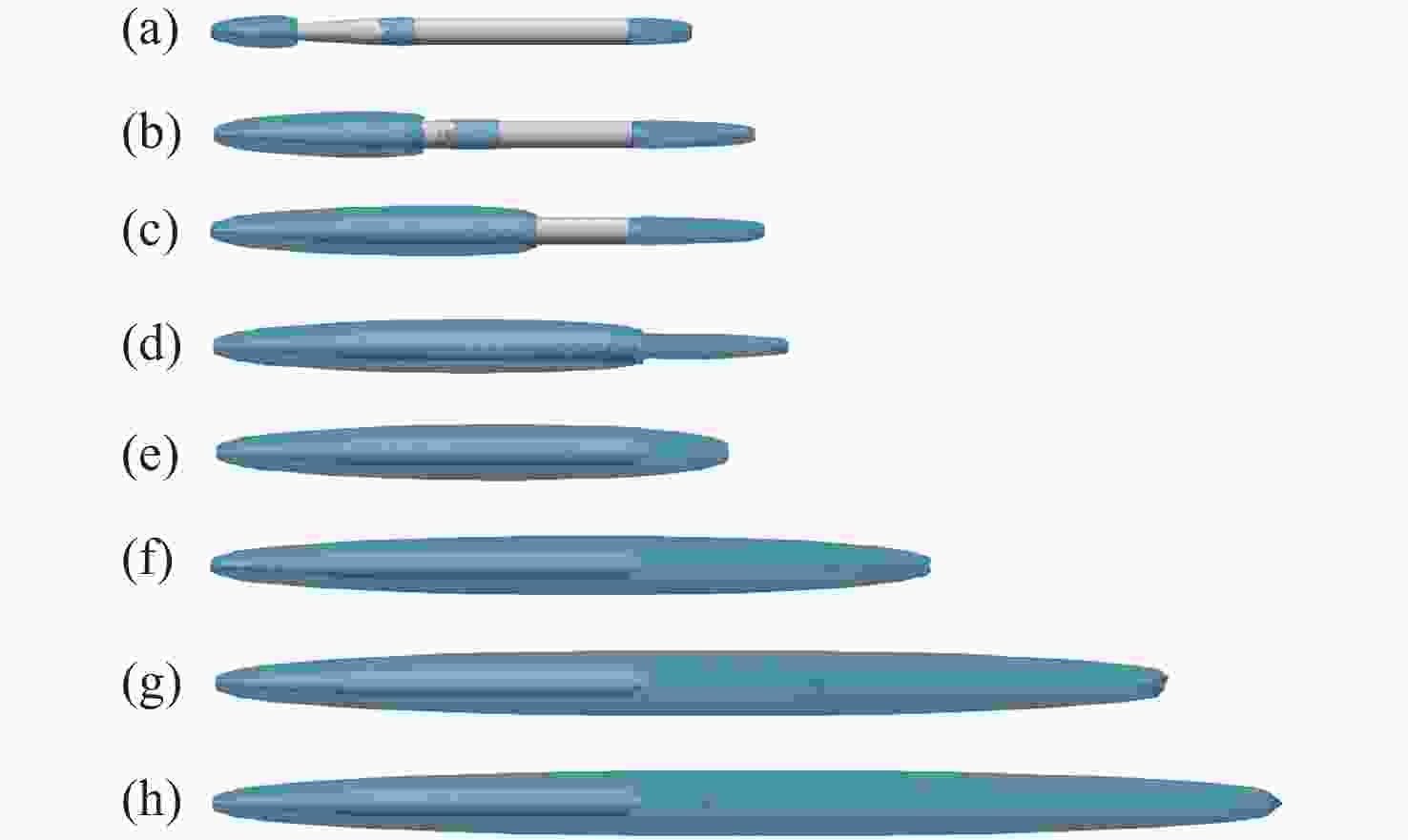
空化器头型 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) ${C_D}$ 0.127 0.296 0.098 0.075 0.056 0.080 -
[1] Kuklinski R, Castano J, Henoch C. Experimental Study of Ventilated Cavities on Dynamic Test Model[C]//CAV2001. Pasadena, CA: California Institute of Technology, 2001. [2] Ahn B K, Lee T K, Kim H T, et al. Experimental Investigation of Supercavitating Flows[J]. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 2012, 4(2): 123-131. doi: 10.2478/IJNAOE-2013-0083 [3] Saranjam B. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of an Unsteady Supercavitating Moving Body[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2013, 59: 9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2012.12.021 [4] 贾力平, 于开平, 张嘉钟, 等. 空化器参数对超空泡形成和发展的影响[J]. 力学学报, 2007, 23(2): 210-216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2007.02.010Jia Li-ping, Yu Kai-ping, Zhang Jia-zhong, et al. Influence of Cavitator Parameters on Formation and Development of Supercavity[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2007, 23(2): 210-216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2007.02.010 [5] 王瑞, 党建军, 姚忠. 不同外形空化器绕回转体超空化特性试验研究[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(1): 20-24.Wang Rui, Dang Jian-jun, Yao Zhong. Experimental Study on the Supercavitation Characteristics of Cavitators with Different Profiles around the Rotating Body[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(1): 20-24. [6] 齐江辉, 郑亚雄. 空化器形状对超空泡流场影响的数值模拟[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2018, 39(9): 85-88. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.09.018Qi Jiang-hui, Zheng Ya-xiong. Numerical Simulation Study on Supercavitation Flow-Field with Different Cavitator Shapes[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2018, 39(9): 85-88. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.09.018 [7] Kim M J, Kim S H, Lee K C, et al. Cavitator Design for Straight Running Supercavitating Torpedoes[J]. Applied Science. 2021, 11(14): 6247. [8] 李雨田. 超空泡航行器流体动力CFD计算[J]. 鱼雷技术, 2015, 23(4): 262-268.Li Yu-tian. Calculation of Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Supercavity Vehicle with CFD Method[J]. Torpedo Technology, 2015, 23(4): 262-268. [9] 赵潇雨, 周维. 自然超空泡形态特性的数值模拟[J]. 四川兵工学报, 2010, 31(12): 49-52.Zhao Xiao-yu, Zhou Wei. Numerical Simulation of the Morphological Properties of Natural Super Vacuoles[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2010, 31(12): 49-52. [10] 黄超, 翁翕, 刘谋斌. 超疏水小球低速入水空泡研究[J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(1): 36-45. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-310Huang Chao, Weng Xi, Liu Mou-bin. Study on Low-speed Water Entry of Super-hydrophobic Small Spheres[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2019, 51(1): 36-45. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-310 [11] Xie B, Xiao F. Toward Efficient and Accurate Interface Capturing on Arbitrary Hybrid Unstructured Grids: The THINC Method with Quadratic Surface Representation and Gaussian Quadrature[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 349: 415-440. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2017.08.028 [12] Menter F R, Kuntz M, Langtry R. Ten Years of Industrial Experience with the SST Turbulence Model[J]. Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer, 2003, 4(1): 625-632. [13] Schnerr G H, Sauer J. Physical and Numerical Modeling of Unsteady Cavitation Dynamics[C]//4th International Conference on Multiphase Flow. New Orleans: ICMF, 2001. [14] Serebryakov V V. Some Models of Prediction of Supercavitation Flows Based on Slender Body Approximation[C]//CAV2001. Pasadena, CA: California Institute of Technology, 2001. [15] 张宇文, 袁绪龙, 邓飞. 超空泡航行体流体动力学[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014. [16] Zhang R, Di Q, Wang X, et al. Numerical Study of the Relationship between Apparent Slip Length and Contact Angle by Lattice Boltzmann Method[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. B, 2012, 24(4): 535-540. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(11)60275-8 [17] Javadpour M, Farahat S, Ajam H, et al. An Experimental and Numerical Study of Supercavitating Flows Tric Cavitators[J]. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2016, 54(3): 795-810. [18] Rerchardt H. The Laws of Cavitation Bubbles at Axially Symmetrical Bodies in a Flow[R]. Spring Quarry, Great Britain: Ministry of Aircraft Production, 1946: 322-326. [19] Logvinovich G V. Hydrodynamics of Flow with Free Boundaries[M]. Kiev: Naukova Duma, 1969. [20] Self M W, Ripken J F. Steady-state Cavity Studies in a Free-jet Water Tunnel[R/OL]. (1955-07-01)[2021-12-03]. http://www.doc88.com/p-9733182144216.html. -




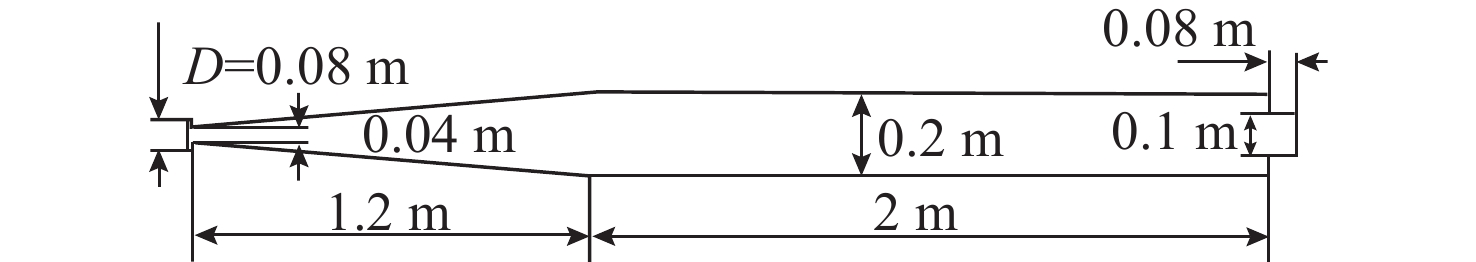
 下载:
下载: