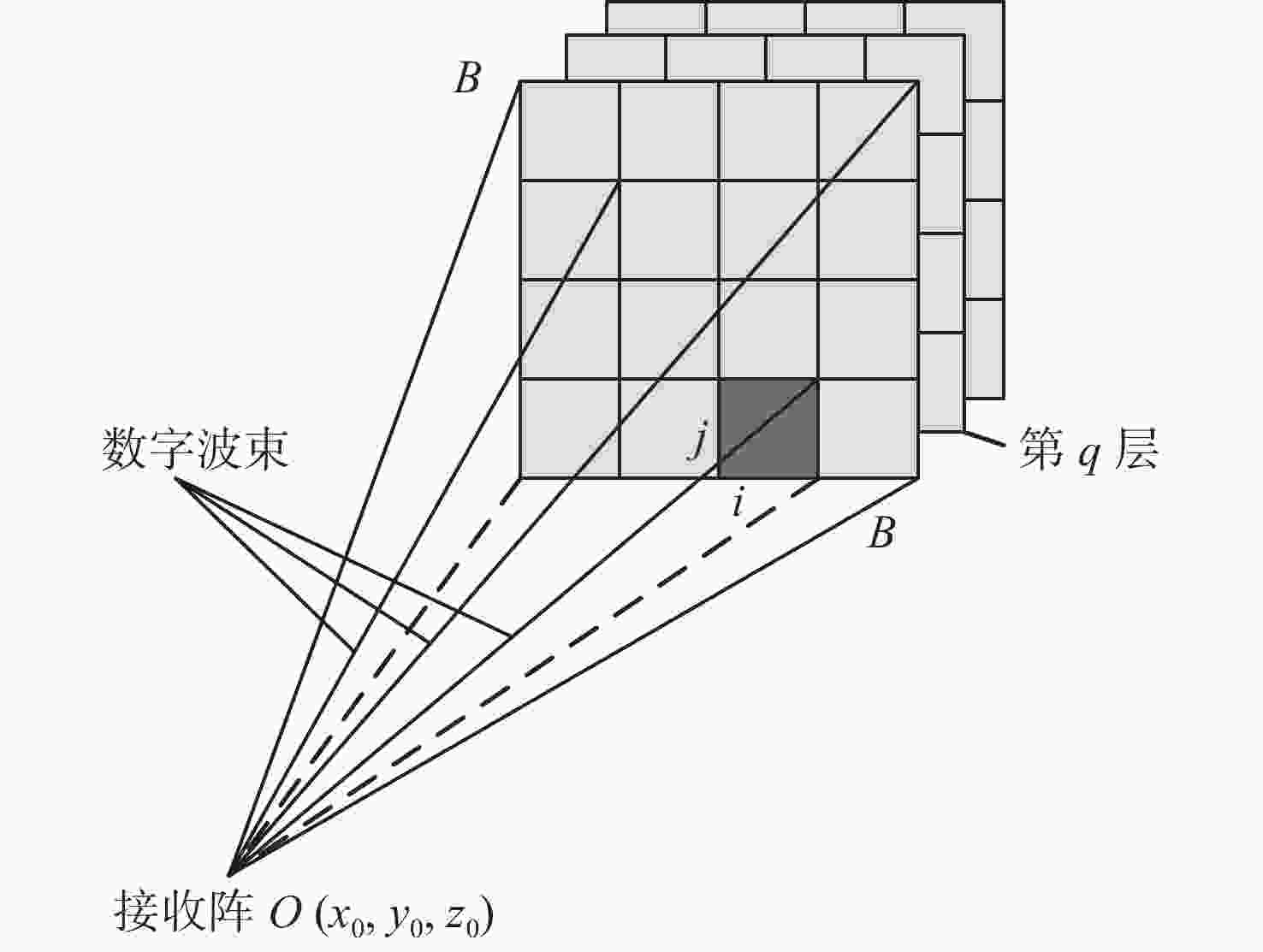
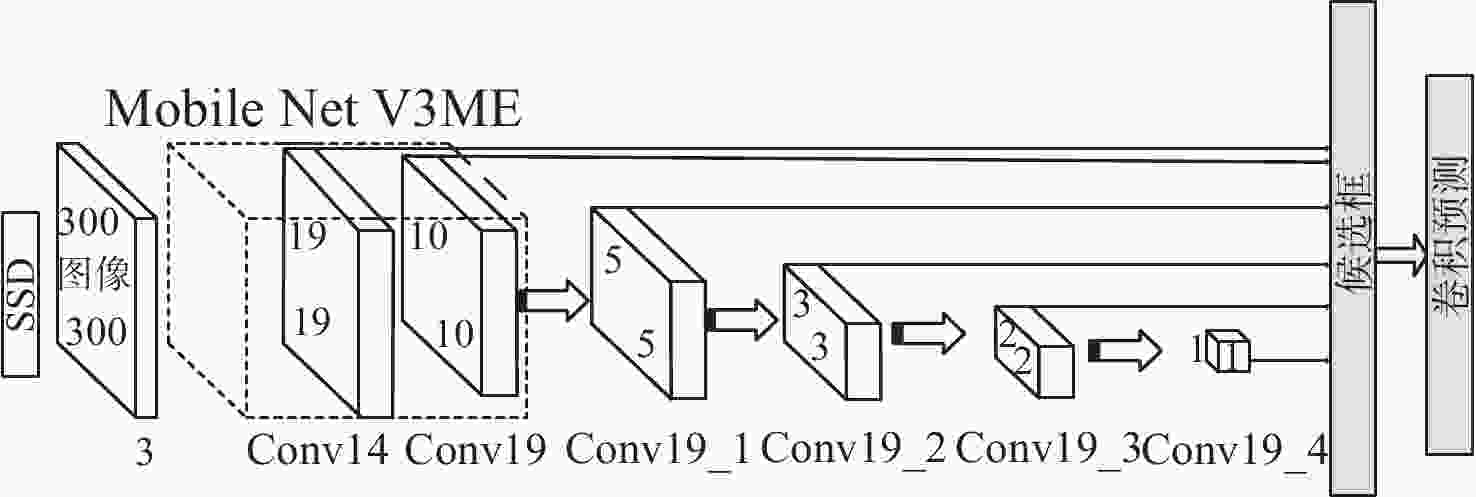
A Method of Erect Rail Barricade Recognition Based on Forward-Looking 3D Sonar
-
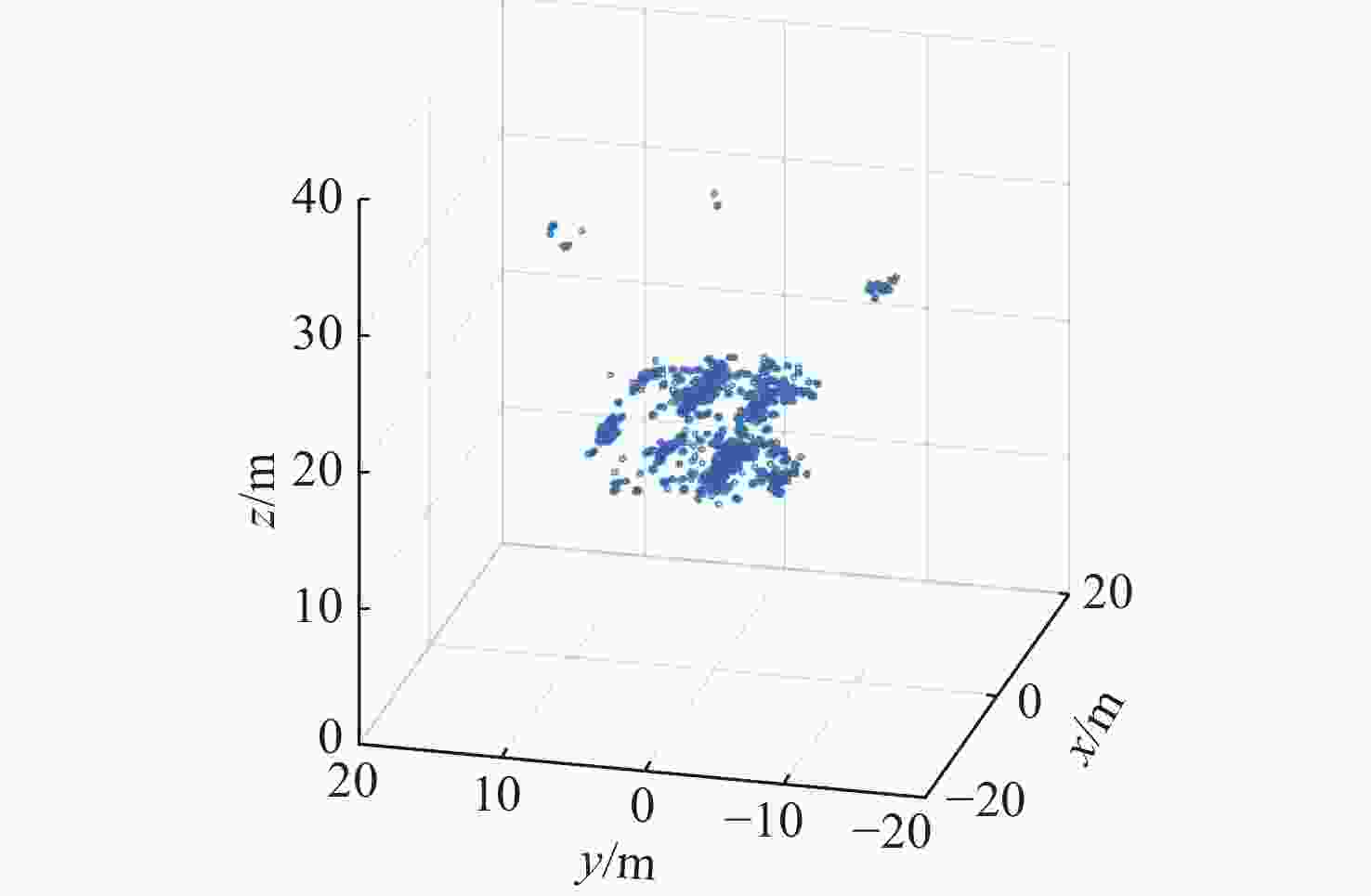
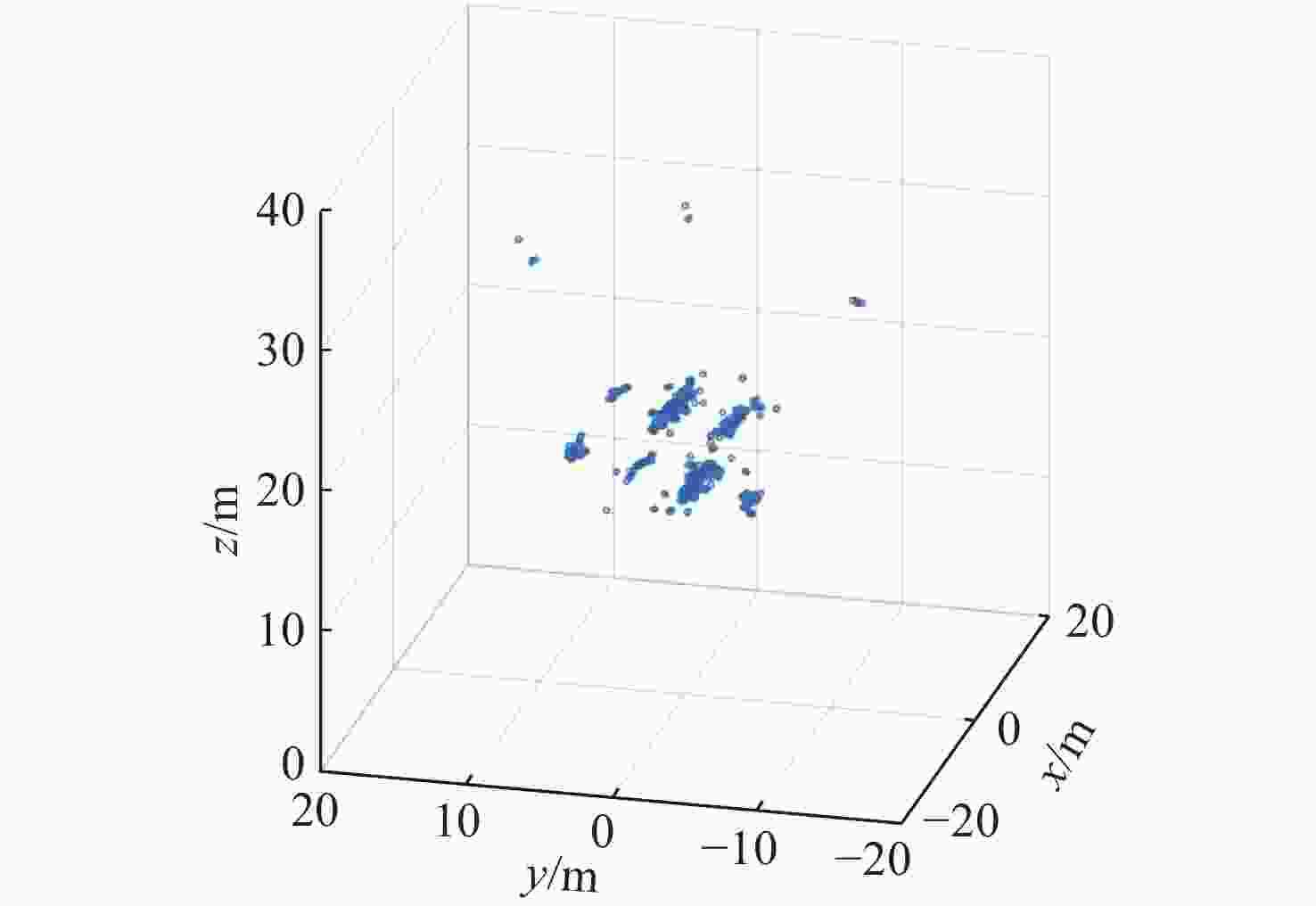
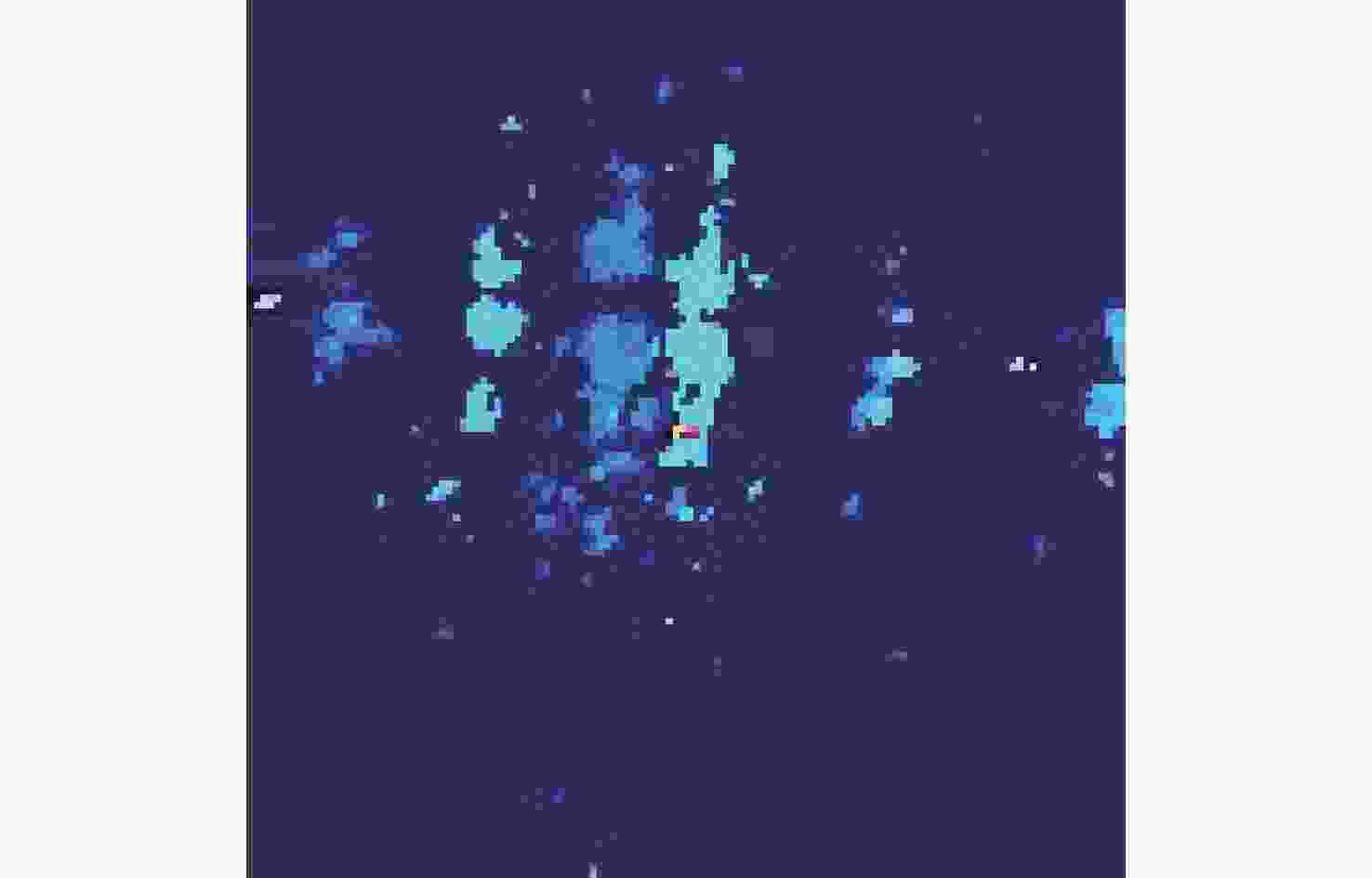
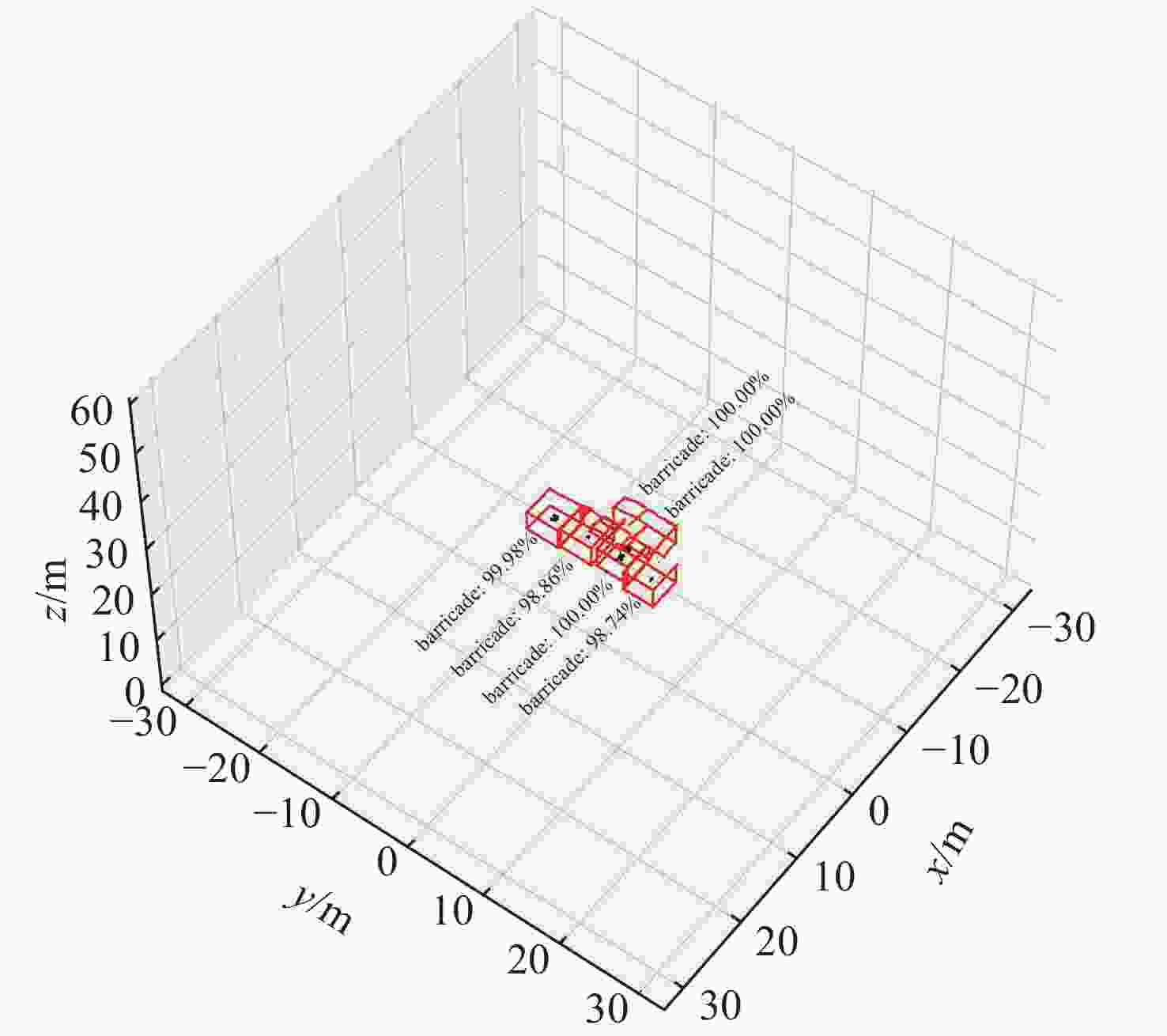
摘要: 针对轨条砦目标探测和识别困难的问题, 文中利用前视三维成像声呐提高轨条砦目标探测效果, 并设计一种基于单步检测(SSD)的三维点云目标识别方法(PCSSD)。该方法首先对原始波束域数据进行阈值滤波和直通滤波处理; 接着, 对滤波后的三维点云数据进行前向投影, 并得到深度灰度图和深度伪彩图; 而后, 利用SSD目标检测模型对深度伪彩图进行检测识别; 随后, 从深度灰度图检测目标特征中计算目标的深度范围; 最后, 结合二维目标检测结果和深度范围对三维点云中的轨条砦目标进行标注。与此同时, 提出了一个基于多尺度注意力机制的特征提取模块, 并利用该模块设计了改进的目标检测模型SSD-MV3ME。在三维点云轨条砦目标检测数据集GTZ上, SSD-MV3ME在检测时间基本相等的条件下, 检测精度比轻量化目标检测模型SSD-MV3提升1.05%, 模型参数减少2 482 KB。实验结果表明, 基于SSD-MV3ME的PCSSD更适合轨条砦目标识别任务。Abstract: To alleviate the difficulty in detecting and recognizing erect rail barricades, a forward-looking three-dimensional(3D) imaging sonar is used to improve the effectiveness of erect rail barricade recognition, and a single shot detector(SSD)-based 3D point cloud(PCSSD) target recognition method is proposed. First, the original beam domain data are processed using a threshold filter and pass-through filter. Next, forward projection of the filtered 3D point cloud data is performed, and the grayscale depth image and pseudo color depth image are obtained. The SSD was then used to recognize the targets from the pseudo color depth image. Subsequently, the depth range of the selected targets is calculated based on the characteristics of the targets recognized from the grayscale depth image. Finally, erect rail barricades in the form of 3D point clouds were detected by combining the two-dimensional detection results and the corresponding depth range. A feature extraction block based on the multi-scale attention mechanism was proposed, and a novel target detector SSD-MV3ME was used for the design. On the 3D point cloud erect rail barricades dataset GTZ, under the condition of the same detection time, the detection accuracy of SSD-MV3ME was higher than that of the lightweight target detection model SSD-MV3 by 1.05%, and the model parameters had less than 2 482 kB. The results show that the PCSSD based on SSD-MV3ME is more suitable for erect rail barricade recognition tasks.
-
表 1 轨条砦目标检测数据集
Table 1. Dataset of erect rail barricades for target detection
训练 验证 测试 图像数量 444 140 88 目标数量 1 128 346 203 表 2 目标检测模型性能比较
Table 2. Performance comparsion of target detection models
模型 注意力 mAP/% 参数大小/kB 时间/ms SSD-MV3 SE 87.08 10 825 12.96 SSD-MV3E ECA 87.58 8 335 11.96 SSD-MV3ME MECA 88.13 8 343 13.28 表 3 MECA不同数量多尺度卷积核对SSD-MV3ME性能的影响
Table 3. Effect of different accounts of MECA multiscale convolutions kernel on the performance of SSD-MV3ME
数量 注意力机制 mAP/% 参数大小/kB 时间/ms 1 MECA 87.58 8 335 11.96 2 MECA 87.60 8 339 12.79 3 MECA 88.13 8 343 13.28 4 MECA 88.26 8 347 13.94 -
[1] 鲍小恒, 堵永国, 白书欣. 一种新型轨条砦灵巧破障炸弹的设计[J]. 工兵装备研究, 2006, 25(1): 5-8.Bao Xiao-heng, Du Yong-guo, Bai Shu-xin. Design on a New Smart Breaching Bomb for Rail Obstacles[J]. Engineer Equipment Research, 2006, 25(1): 5-8. [2] 杨子庆, 张婉. 外军登陆作战上陆阶段工程保障装备的现状与特点[J]. 工兵装备研究, 2006, 25(1): 56-59.Yang Zi-qing, Zhang Wan. Status Quo and Characteristics of Foreign Engineer Support Equipment during Assault Landing Operation[J]. Engineer Equipment Research, 2006, 25(1): 56-59. [3] 张少光, 孙严峰, 蒋洪涛. 台军抗登陆地雷障碍物的发展与研究[J]. 工兵装备研究, 2007, 26(4): 57-60.Zhang Shao-guang, Sun Yan-feng, Jiang Hong-tao. Development and Research on Anti-landing Mine Obstacles of Taiwan Army[J]. Engineer Equipment Research, 2007, 26(4): 57-60. [4] 冷画屏, 周世华, 肖利辉. 两栖登陆部队指挥信息系统建设研究[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2015, 37(1): 11-14.Leng Hua-ping, Zhou Shi-hua, Xiao Li-hui. Research on Construction of Amphibious Landing Force Command Information System[J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2015, 37(1): 11-14. [5] 程亚楠, 刘晓东, 张东升. 基元扰动对三维前视声纳测向性能的影响分析[J]. 网络新媒体技术, 2020, 9(5): 15-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-347X.2020.05.003Cheng Ya-nan, Liu Xiao-dong, Zhang Dong-sheng, et al. Influence of Sensor Uncertainty on the Direction Estimation of 3D Forward-looking Sonar[J]. Journal of Network New Media, 2020, 9(5): 15-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-347X.2020.05.003 [6] Yann L C, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep Learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [7] Kwok R. Deep Learning Powers a Motion-Tracking Revolution[J]. Nature, 2019, 574(7776): 137-138. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-02942-5 [8] Zhou Y, Tuzel O. Voxelnet: End-to-end Learning for Point Cloud Based 3d Object Detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018: 4490-4499. [9] Yan Y, Mao Y, Li B. Second: Sparsely Embedded Convolutional Detection[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3337. doi: 10.3390/s18103337 [10] Lang A H, Vora S, Caesar H, et al. Pointpillars: Fast Encoders for Object Detection from Point Clouds[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019: 12697-12705. [11] Yang Z, Sun Y, Liu S, et al. 3DSSD: Point-based 3d Single Stage Object Detector[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020: 11040-11048. [12] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-time Object Detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016: 779-788. [13] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [14] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: Single Shot Multibox Detector[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [15] Haward A G, Zhu M L, Chen B, et al. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications[J/OL]. ArXiv Preprint (2017-04-17)[2022-09-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861. [16] Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, et al. Mobilenetv2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018: 4510-4520. [17] Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation Networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018: 7132-7141. [18] Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G, et al. Searching for Mobilenetv3[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019: 1314-1324. [19] Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. -





 下载:
下载: